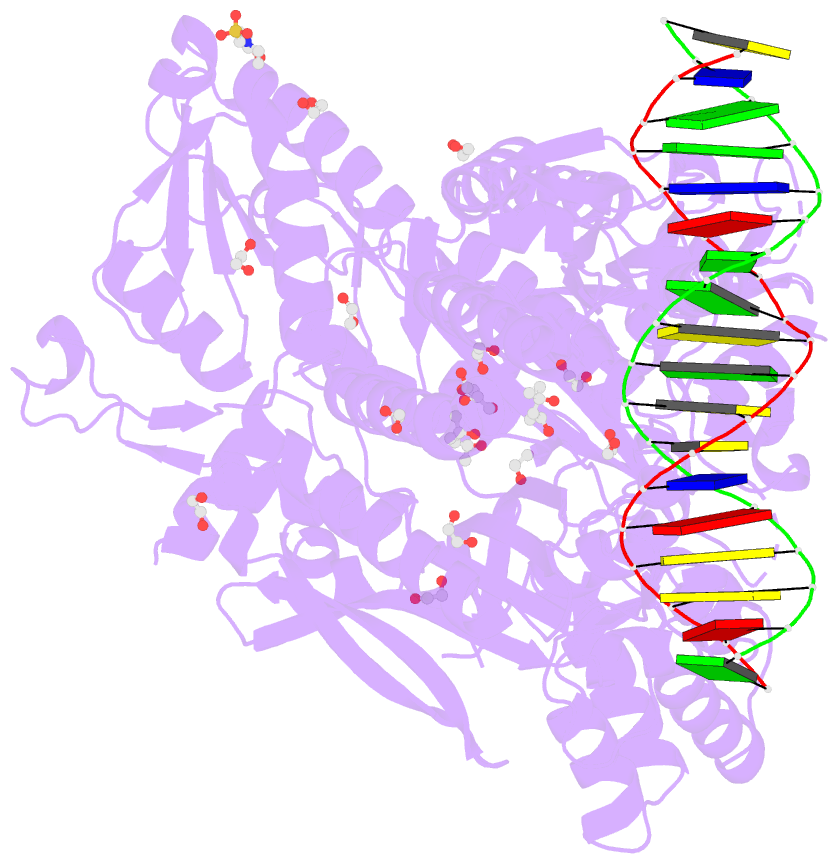
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
8f69;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.2 Å)
- Summary
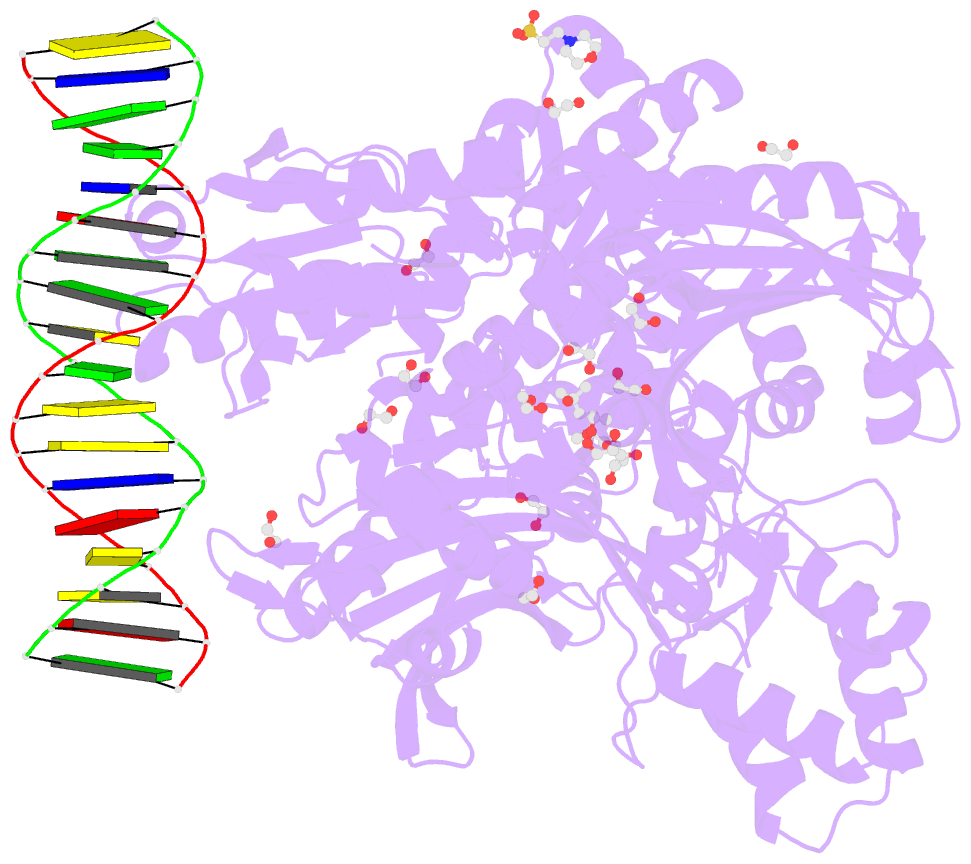
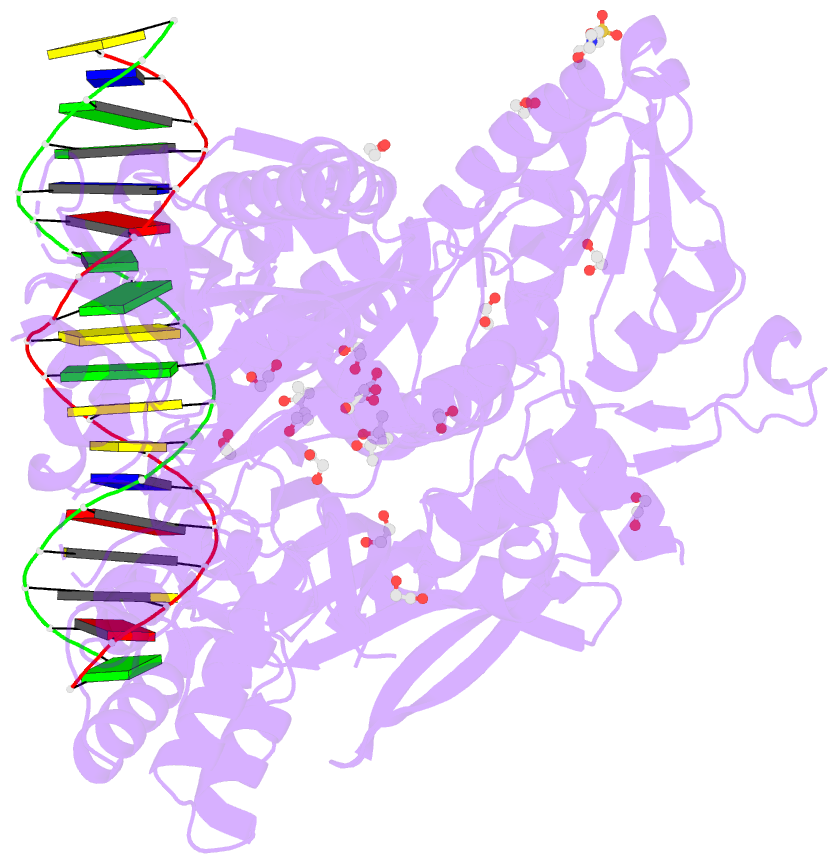
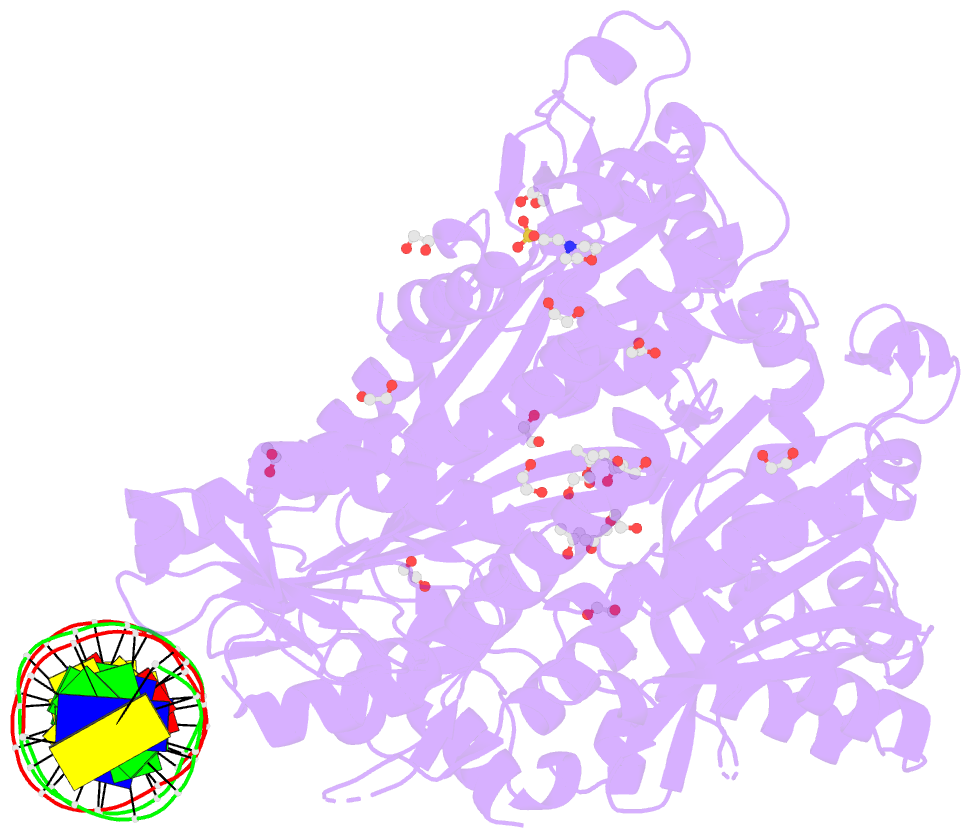
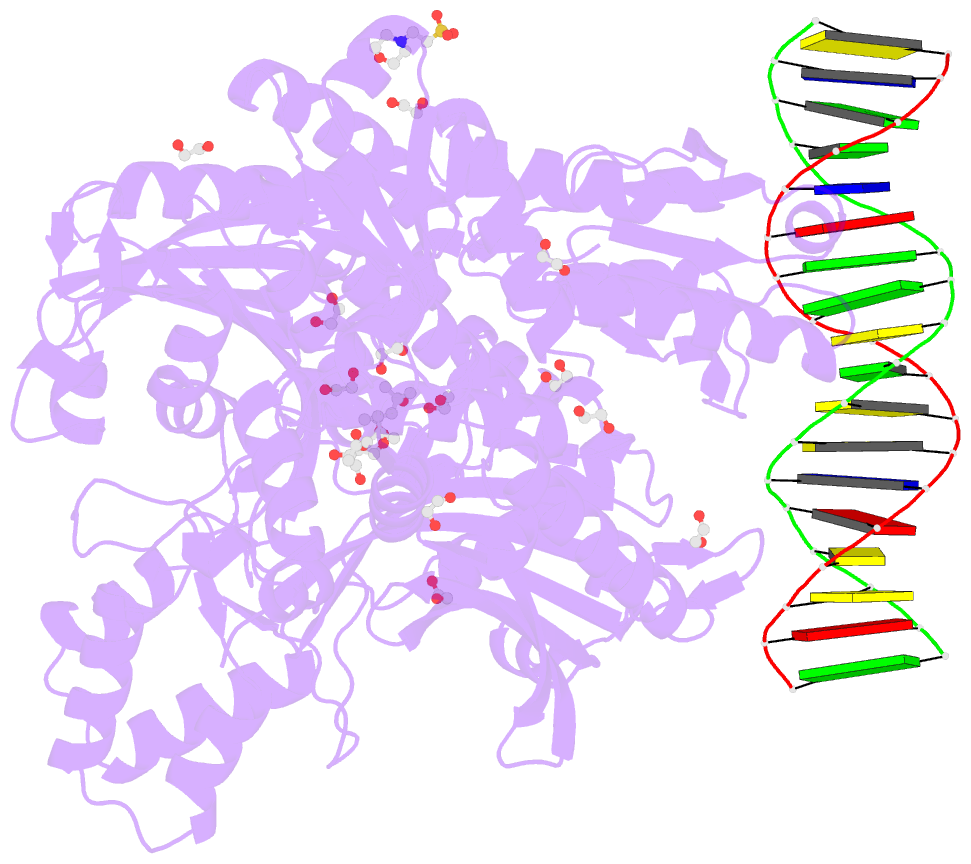
- Crystal structure of murine polg2 dimer bound to
DNA
- Reference
-
Wojtaszek JL, Hoff KE, Longley MJ, Kaur P, Andres SN,
Wang H, Williams RS, Copeland WC (2023): "Structure-specific
roles for PolG2-DNA complexes in maintenance and
replication of mitochondrial DNA." Nucleic Acids
Res., 51, 9716-9732. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad679.
- Abstract
- The homodimeric PolG2 accessory subunit of the
mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma (Pol γ) enhances DNA
binding and processive DNA synthesis by the PolG catalytic
subunit. PolG2 also directly binds DNA, although the
underlying molecular basis and functional significance are
unknown. Here, data from Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) and
X-ray structures of PolG2-DNA complexes define dimeric and
hexameric PolG2 DNA binding modes. Targeted disruption of
PolG2 DNA-binding interfaces impairs processive DNA
synthesis without diminishing Pol γ subunit affinities. In
addition, a structure-specific DNA-binding role for PolG2
oligomers is supported by X-ray structures and AFM showing
that oligomeric PolG2 localizes to DNA crossings and
targets forked DNA structures resembling the mitochondrial
D-loop. Overall, data indicate that PolG2 DNA binding has
both PolG-dependent and -independent functions in
mitochondrial DNA replication and maintenance, which
provide new insight into molecular defects associated with
PolG2 disruption in mitochondrial disease.