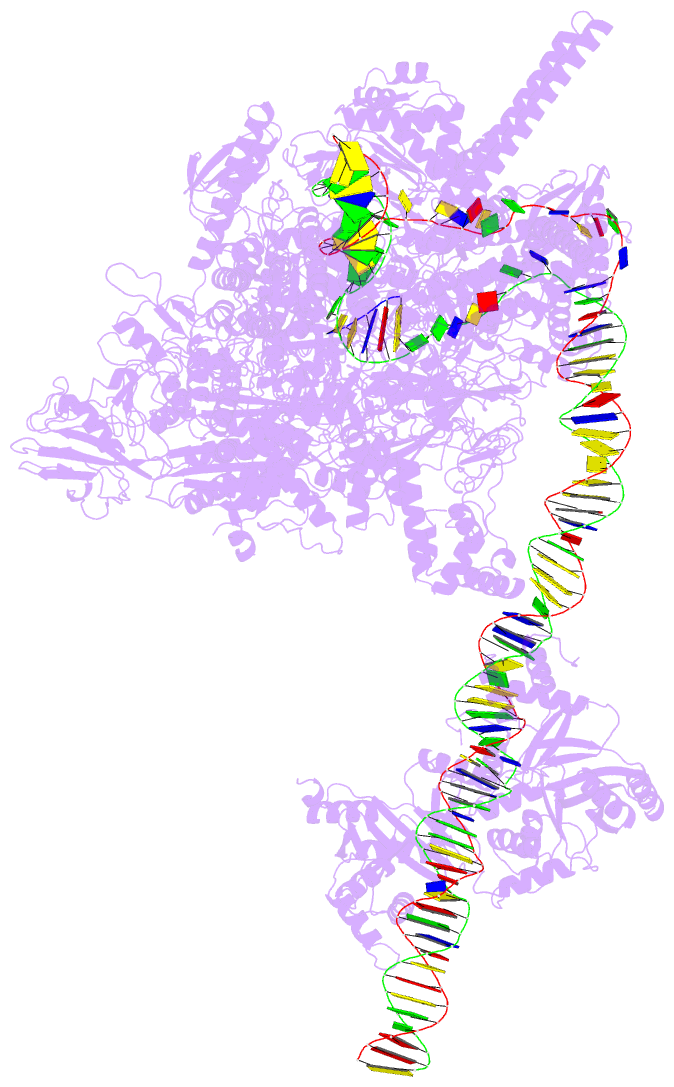
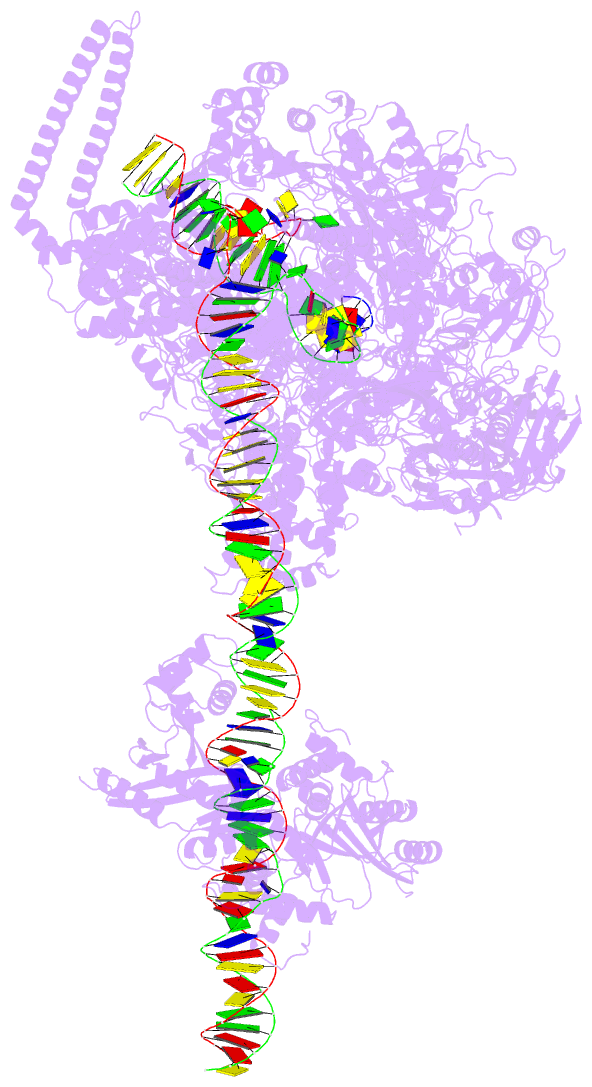
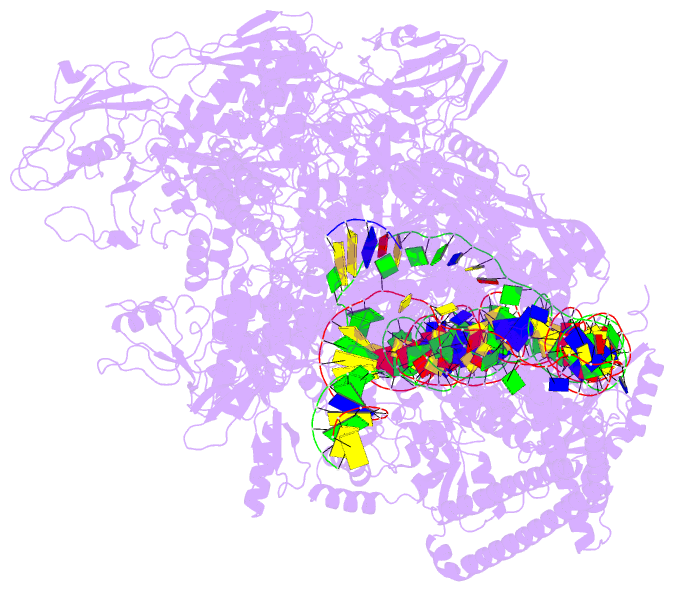
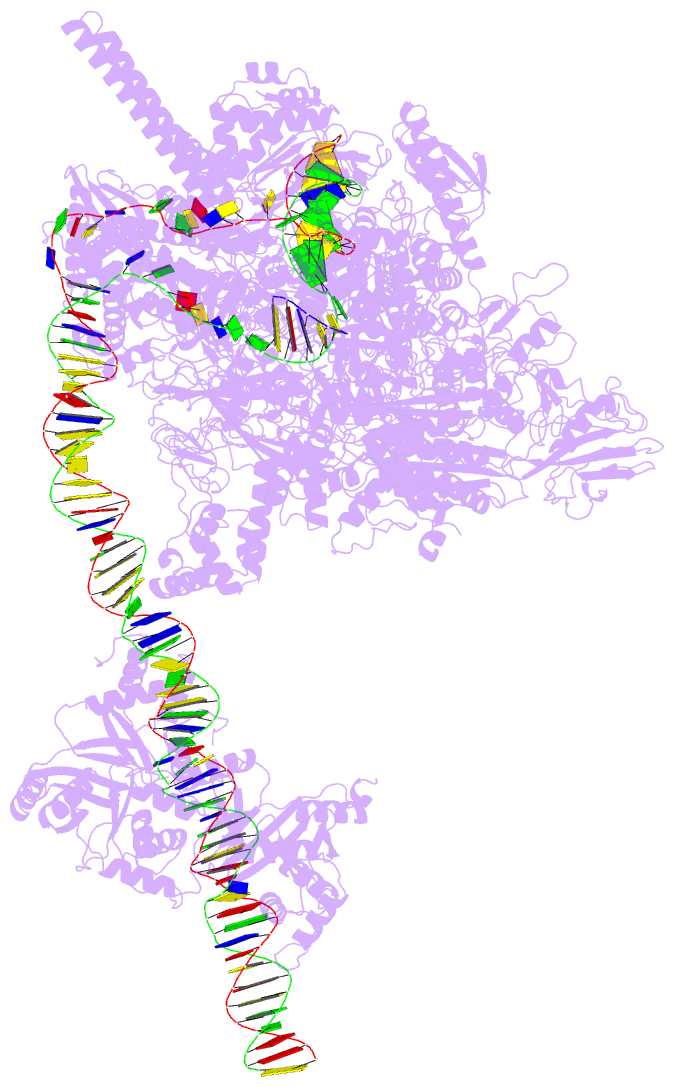
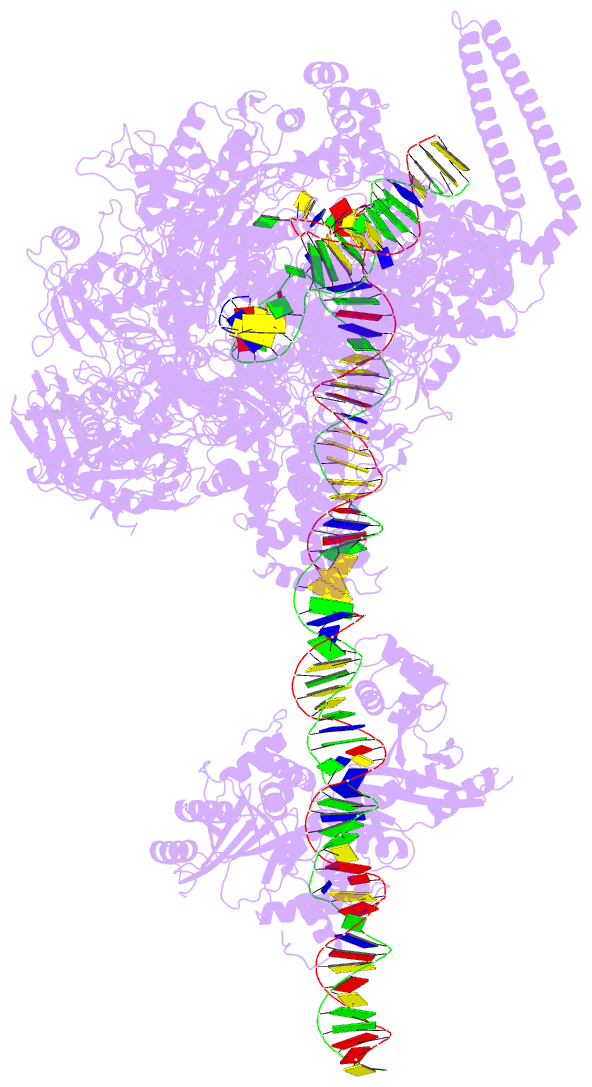
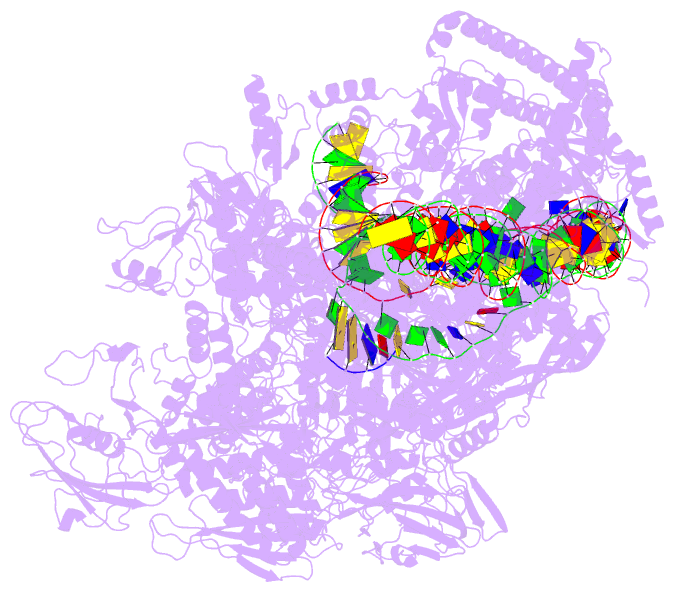
DSSR-PyMOL cartoon-block schematics: PDB entry 7x74
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7x74; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.7 Å)
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of streptomyces coelicolor transcription initial complex with two zur dimers
- Reference
- Yang X, Wang Y, Liu G, Deng Z, Lin S, Zheng J (2022): "Structural basis of Streptomyces transcription activation by zinc uptake regulator." Nucleic Acids Res., 50, 8363-8376. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac627.
- Abstract