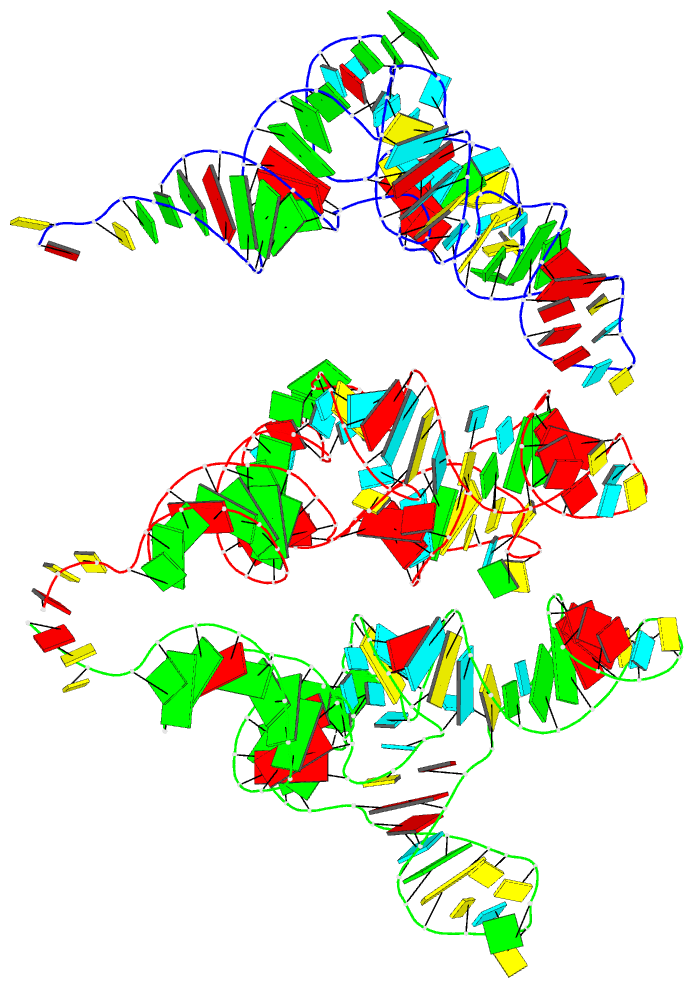
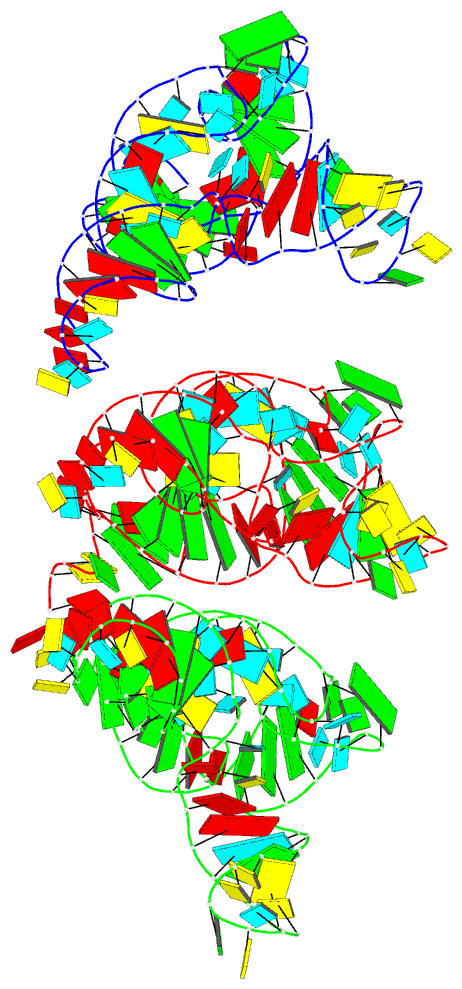
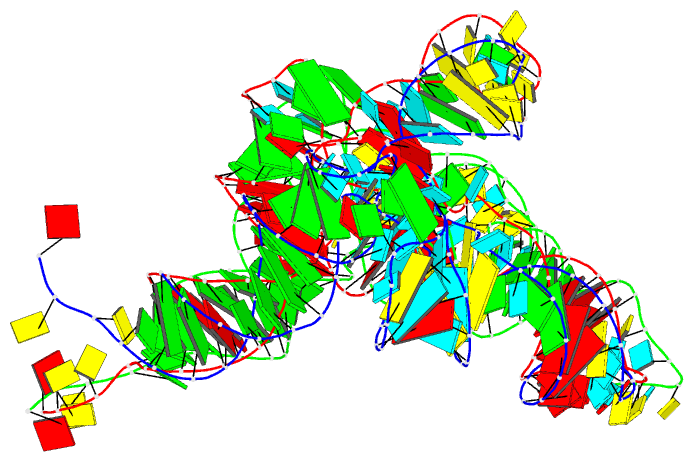
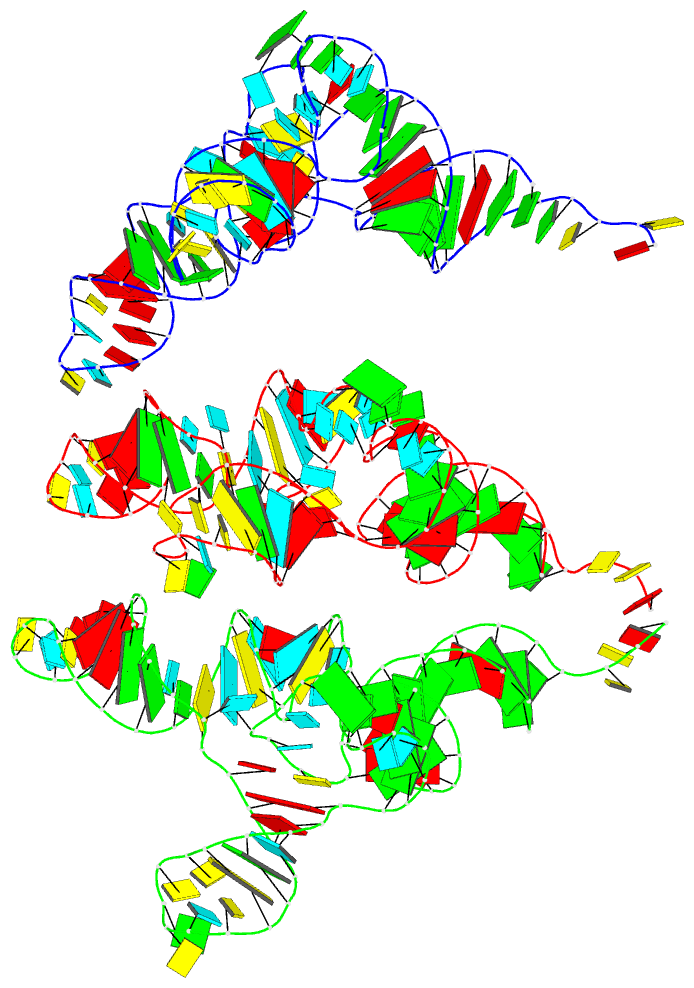
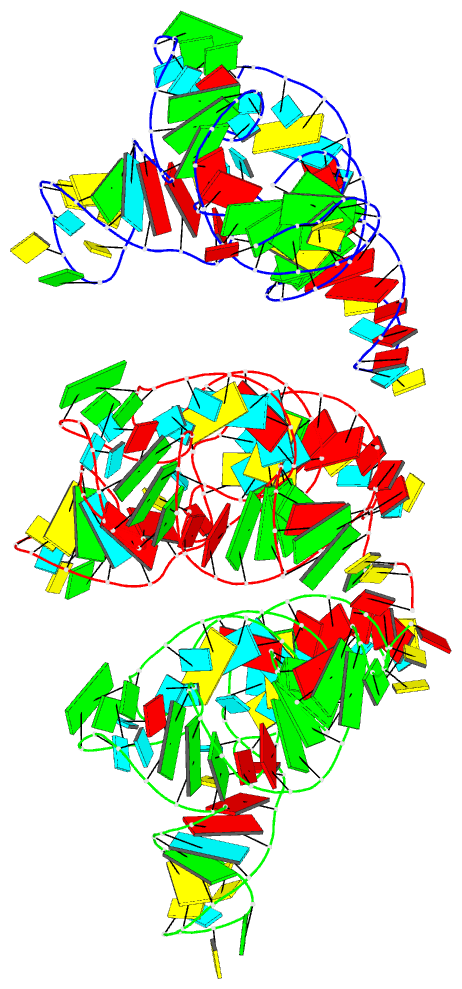
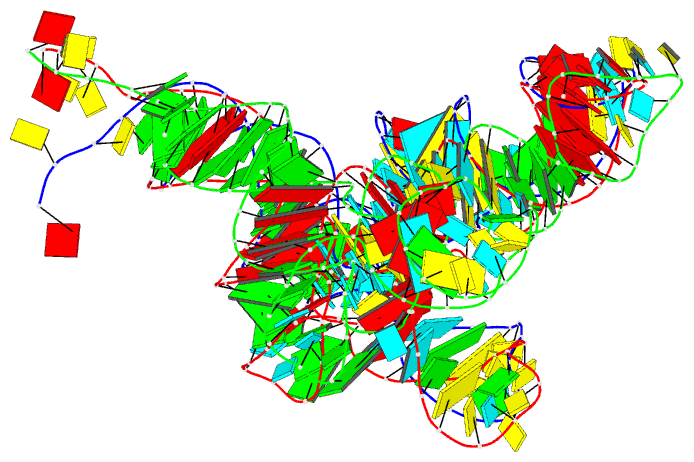
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7ur5; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.6 Å)
- Summary
- Allo-trnautu1 in the a, p, and e sites of the e. coli ribosome
- Reference
- Prabhakar A, Krahn N, Zhang J, Vargas-Rodriguez O, Krupkin M, Fu Z, Acosta-Reyes FJ, Ge X, Choi J, Crnkovic A, Ehrenberg M, Puglisi EV, Soll D, Puglisi J (2022): "Uncovering translation roadblocks during the development of a synthetic tRNA." Nucleic Acids Res., 50, 10201-10211. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac576.
- Abstract
- Continued expansion of the genetic code has required the use of synthetic tRNAs for decoding. Some of these synthetic tRNAs have unique structural features that are not observed in canonical tRNAs. Here, the authors applied single-molecule, biochemical and structural methods to determine whether these distinct features were deleterious for efficient protein translation on the ribosome. With a focus on selenocysteine insertion, the authors explored an allo-tRNA with a 9/3 acceptor domain. They observed a translational roadblock that occurred in A to P site tRNA translocation. This block was mediated by a tertiary interaction across the tRNA core, directing the variable arm position into an unfavorable conformation. A single-nucleotide mutation disrupted this interaction, providing flexibility in the variable arm and promoting efficient protein production.