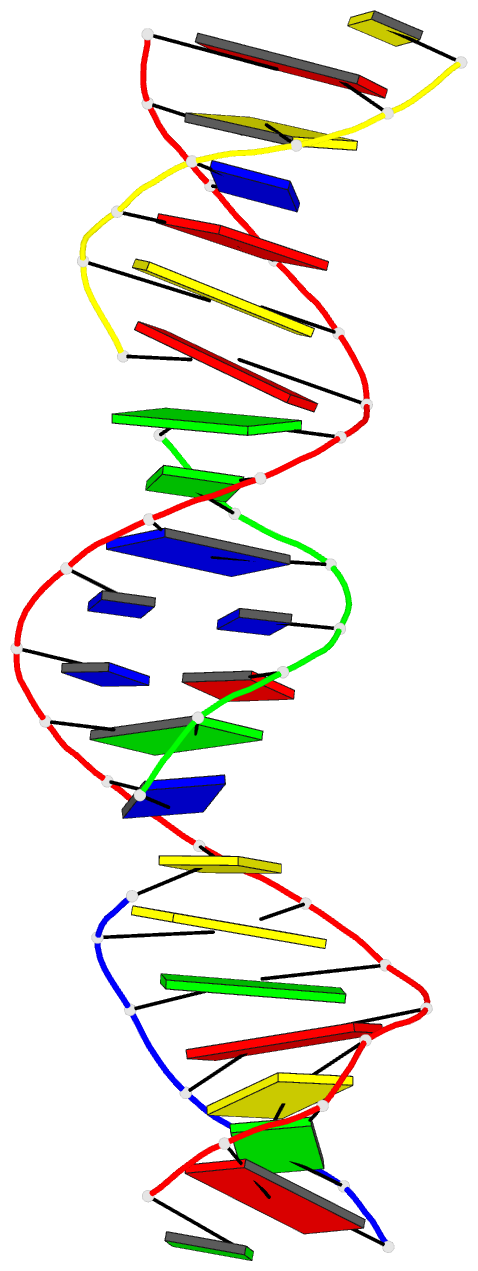
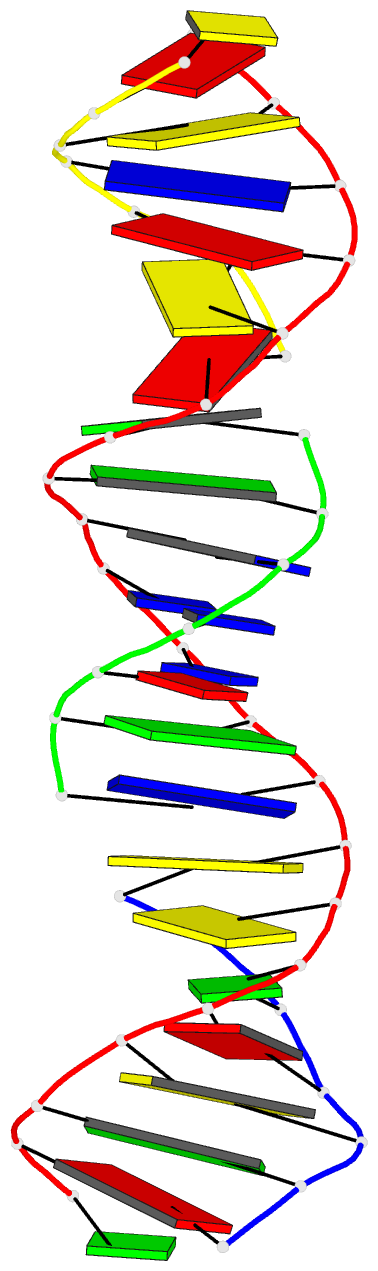
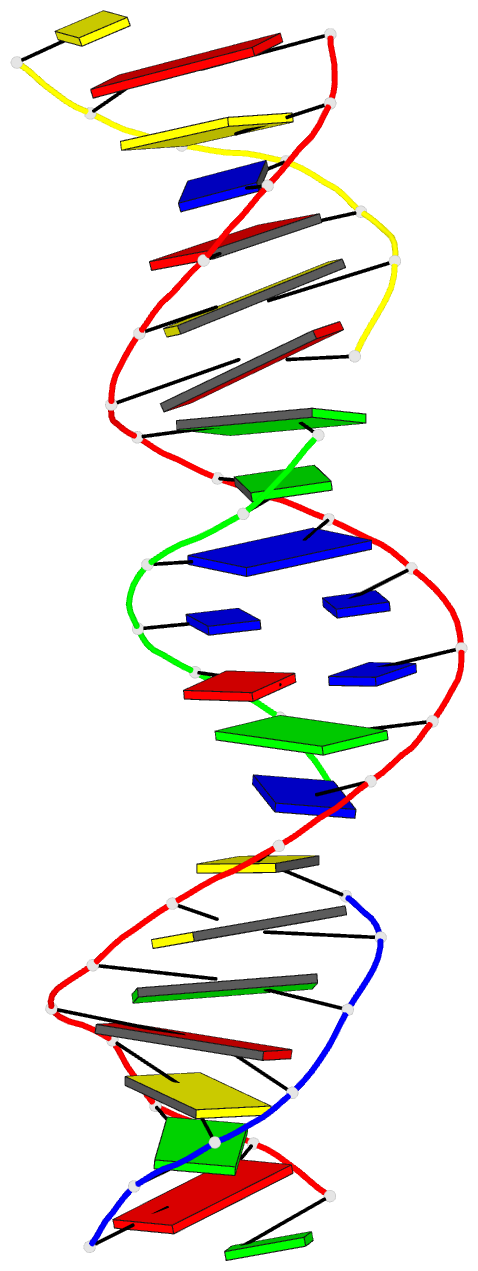
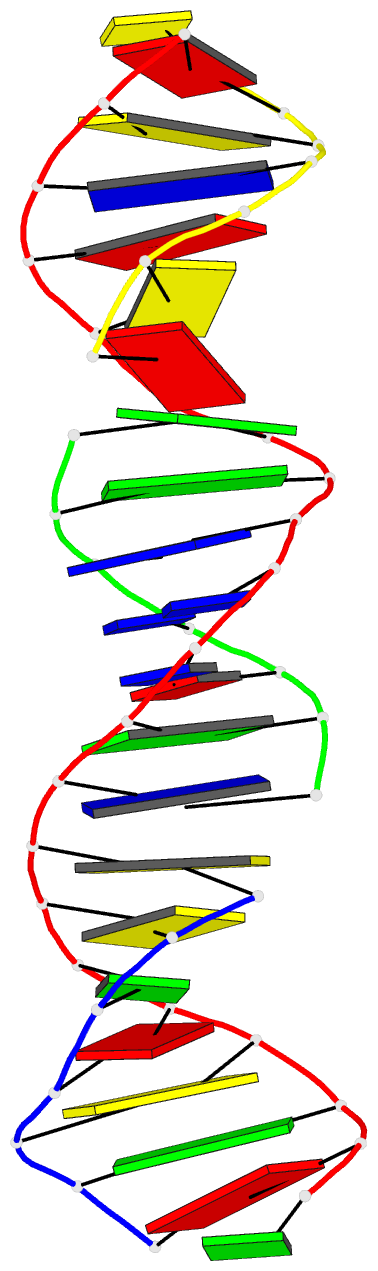
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7sm3; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.74 Å)
- Summary
- [t:hg2+-ag+:t--ph 10] metal-mediated DNA base pair in tensegrity triangle in ag+ and hg2+ solution
- Reference
- Lu B, Ohayon YP, Woloszyn K, Yang CF, Yoder JB, Rothschild LJ, Wind SJ, Hendrickson WA, Mao C, Seeman NC, Canary JW, Sha R, Vecchioni S (2023): "Heterobimetallic Base Pair Programming in Designer 3D DNA Crystals." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 145, 17945-17953. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c05478.
- Abstract
- Metal-mediated DNA (mmDNA) presents a pathway toward engineering bioinorganic and electronic behavior into DNA devices. Many chemical and biophysical forces drive the programmable chelation of metals between pyrimidine base pairs. Here, we developed a crystallographic method using the three-dimensional (3D) DNA tensegrity triangle motif to capture single- and multi-metal binding modes across granular changes to environmental pH using anomalous scattering. Leveraging this programmable crystal, we determined 28 biomolecular structures to capture mmDNA reactions. We found that silver(I) binds with increasing occupancy in T-T and U-U pairs at elevated pH levels, and we exploited this to capture silver(I) and mercury(II) within the same base pair and to isolate the titration points for homo- and heterometal base pair modes. We additionally determined the structure of a C-C pair with both silver(I) and mercury(II). Finally, we extend our paradigm to capture cadmium(II) in T-T pairs together with mercury(II) at high pH. The precision self-assembly of heterobimetallic DNA chemistry at the sub-nanometer scale will enable atomistic design frameworks for more elaborate mmDNA-based nanodevices and nanotechnologies.