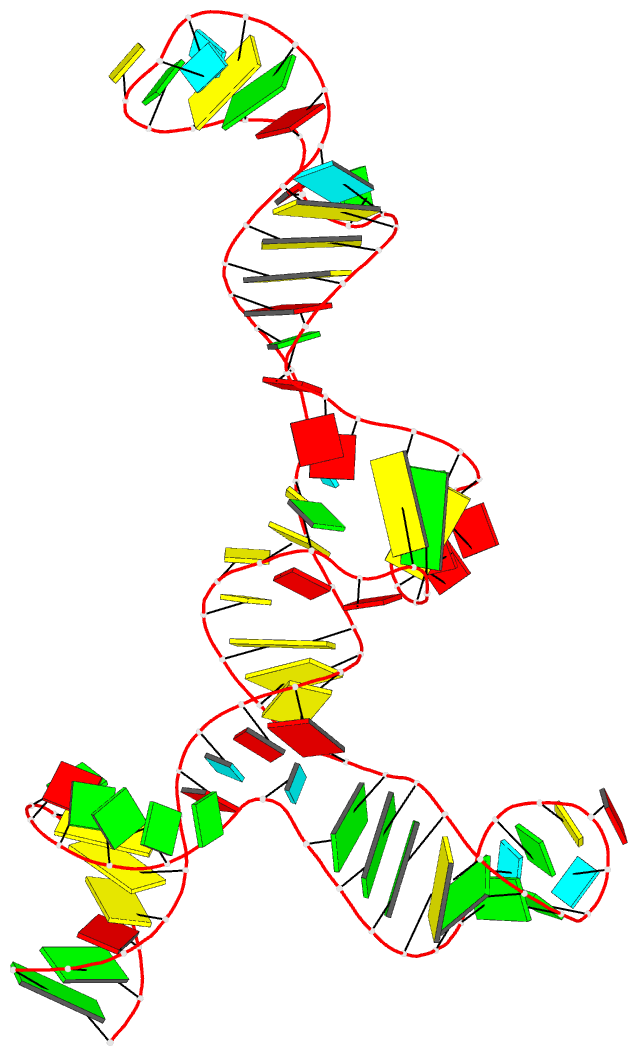
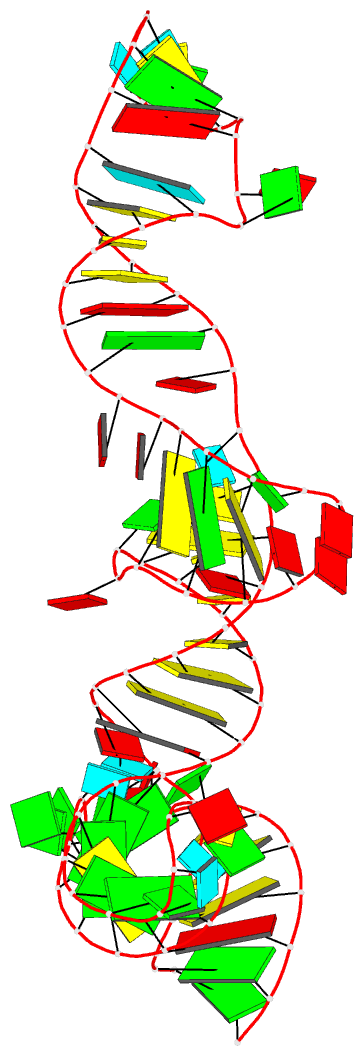
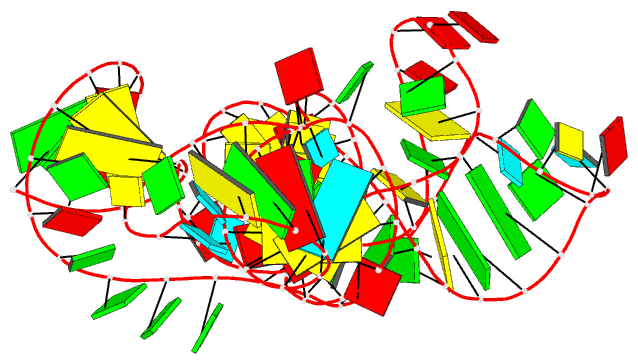
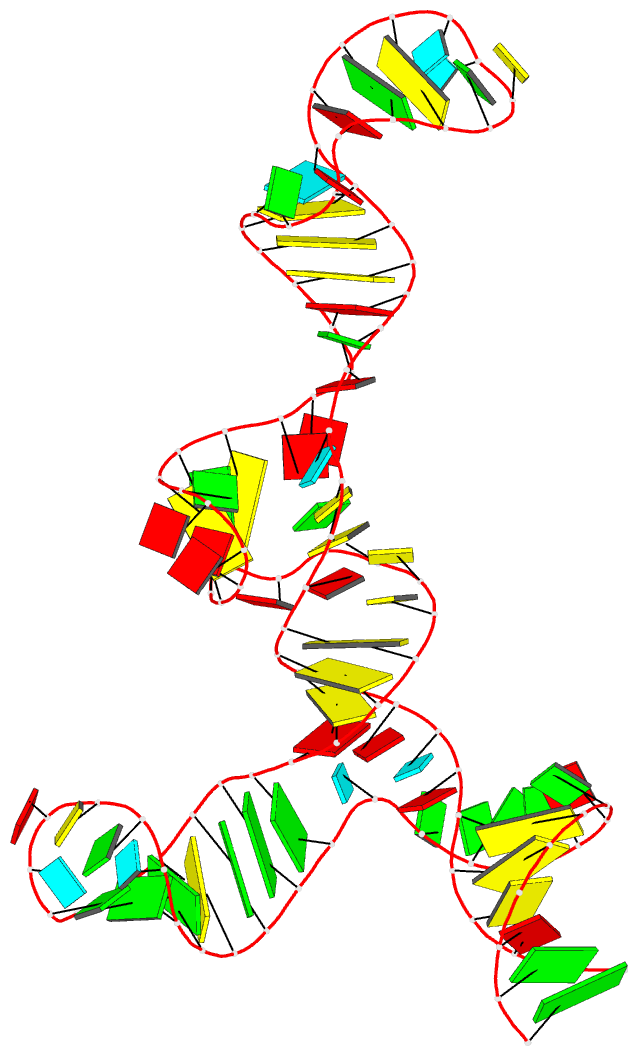
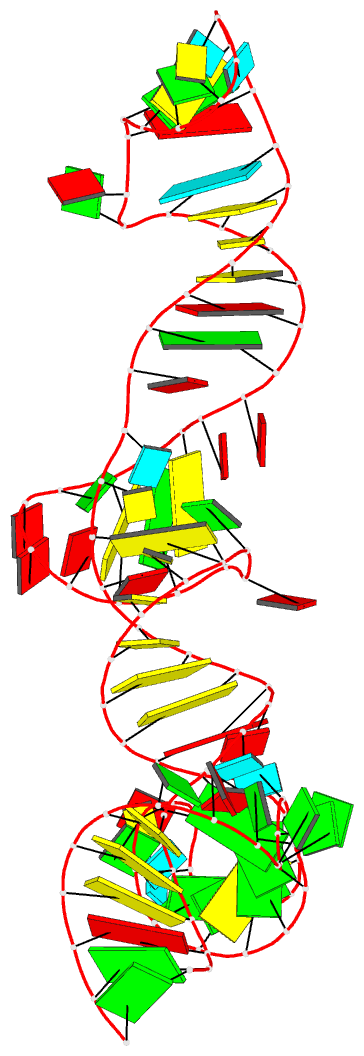
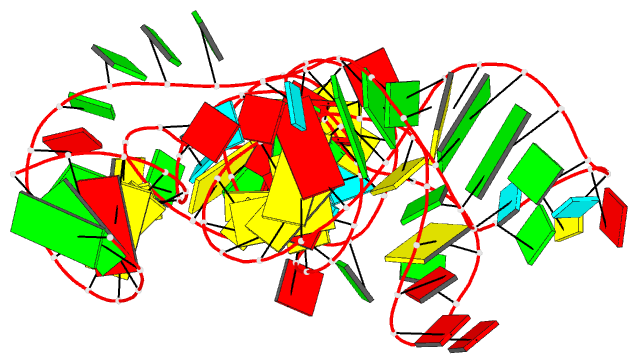
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7shx; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- RNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- A functional snp regulates e-cadherin expression by dynamically remodeling the 3d structure of a promoter-associated non-coding RNA transcript, NMR, minimized average structure
- Reference
- Sharma S, Pisignano G, Merulla J, Catapano CV, Varani G (2022): "A functional SNP regulates E-cadherin expression by dynamically remodeling the 3D structure of a promoter-associated non-coding RNA transcript." Nucleic Acids Res., 50, 11331-11343. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac875.
- Abstract
- Transcription of E-cadherin, a tumor suppressor that plays critical roles in cell adhesion and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, is regulated by a promoter-associated non-coding RNA (paRNA). The sense-oriented paRNA (S-paRNA) includes a functional C/A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP rs16260). The A-allele leads to decreased transcriptional activity and increased prostate cancer risk. The polymorphic site is known to affect binding of a microRNA-guided Argonaute 1 (AGO1) complex and recruitment of chromatin-modifying enzymes to silence the promoter. Yet the SNP is distant from the microRNA-AGO1 binding domain in both primary sequence and secondary structure, raising the question of how regulation occurs. Here we report the 3D NMR structure of the 104-nucleotide domain of the S-paRNA that encompasses the SNP and the microRNA-binding site. We show that the A to C change alters the locally dynamic and metastable structure of the S-paRNA, revealing how the single nucleotide mutation regulates the E-cadherin promoter through its effect on the non-coding RNA structure.