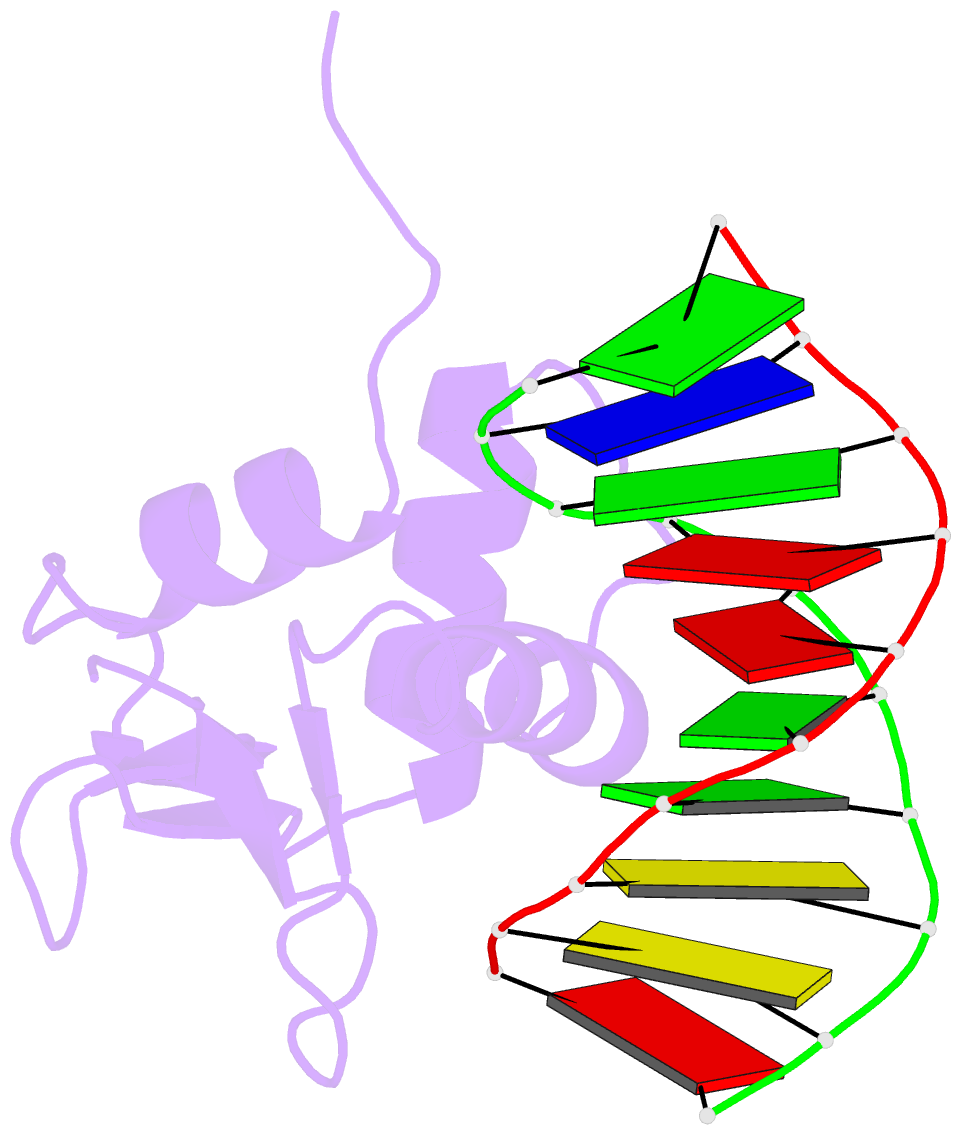
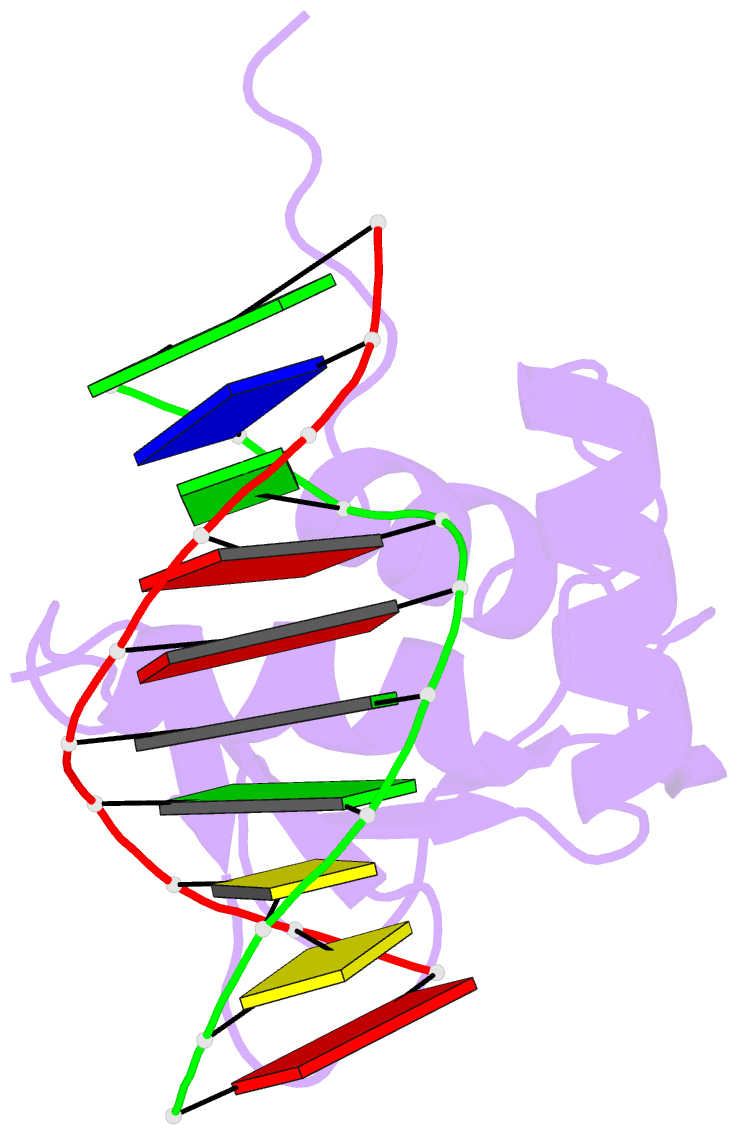
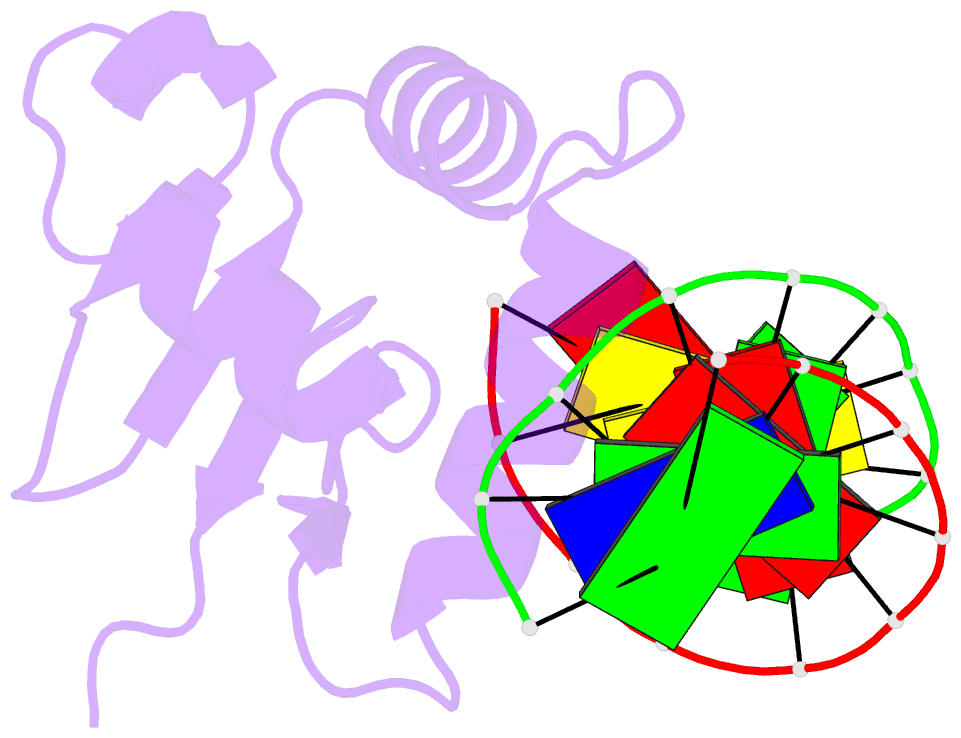
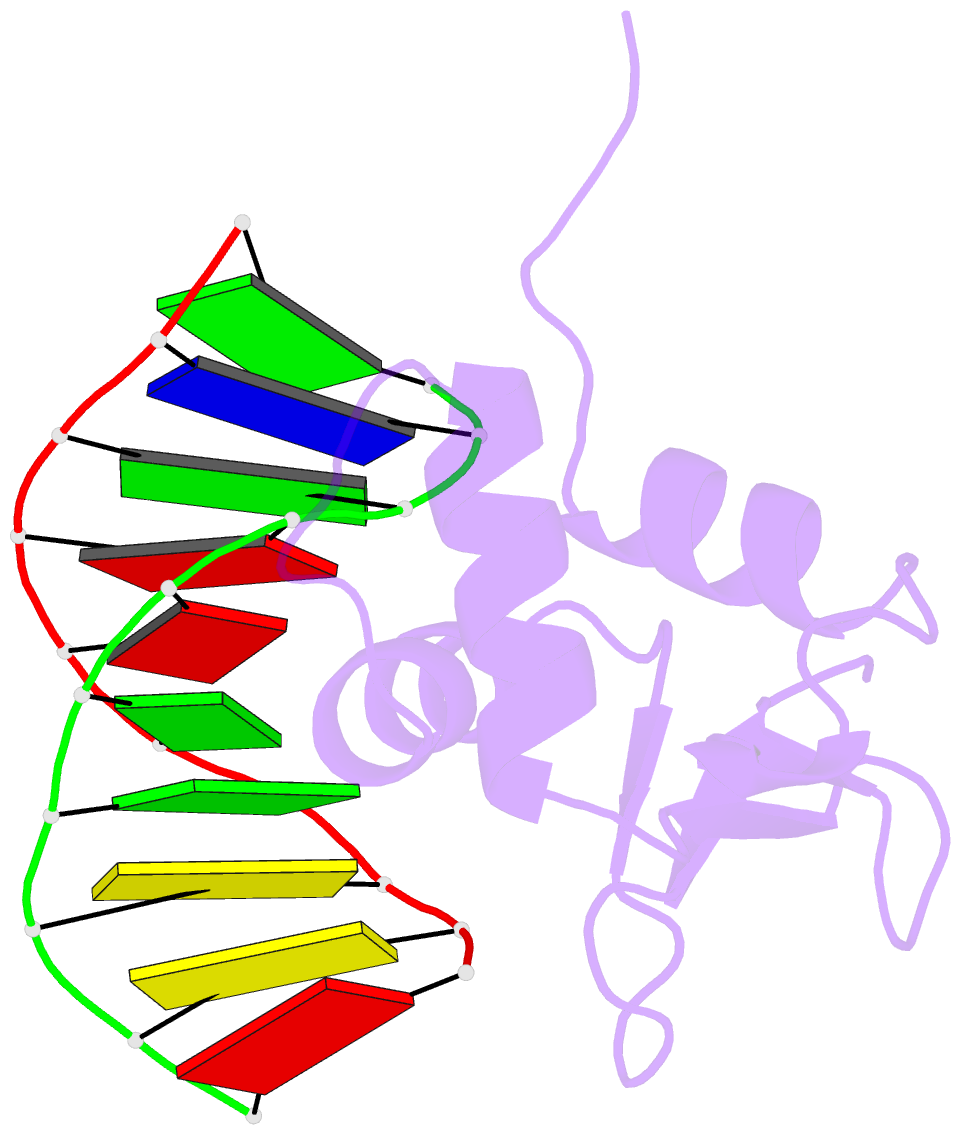
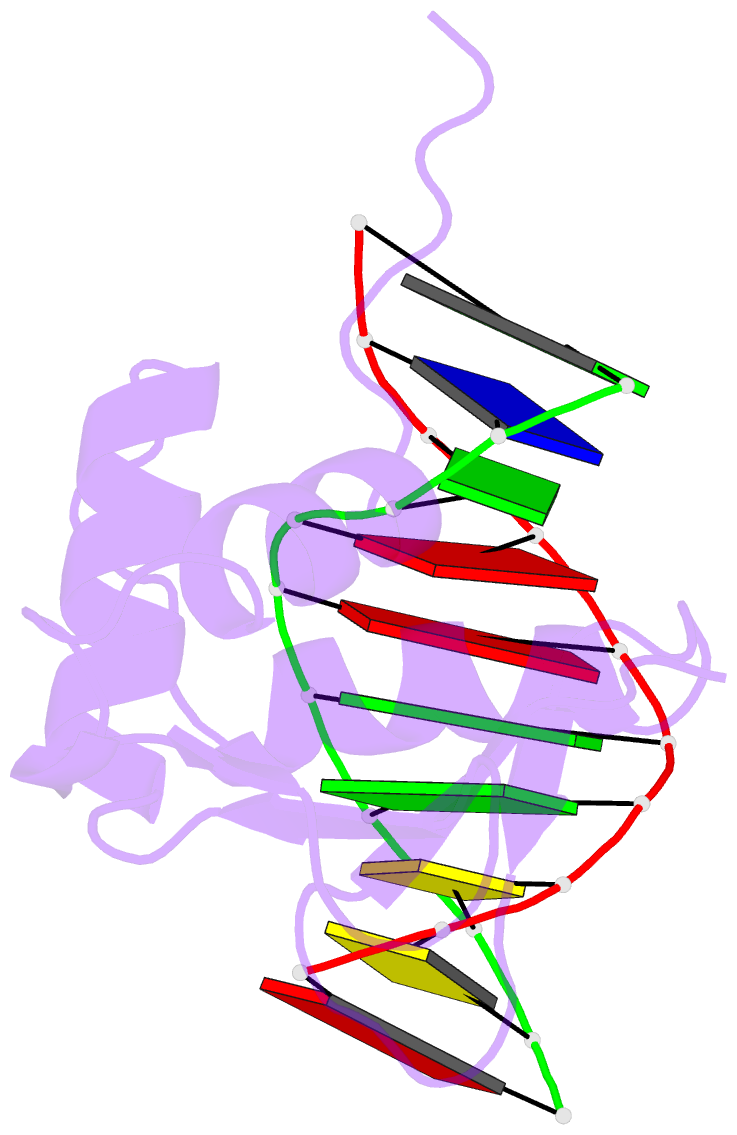
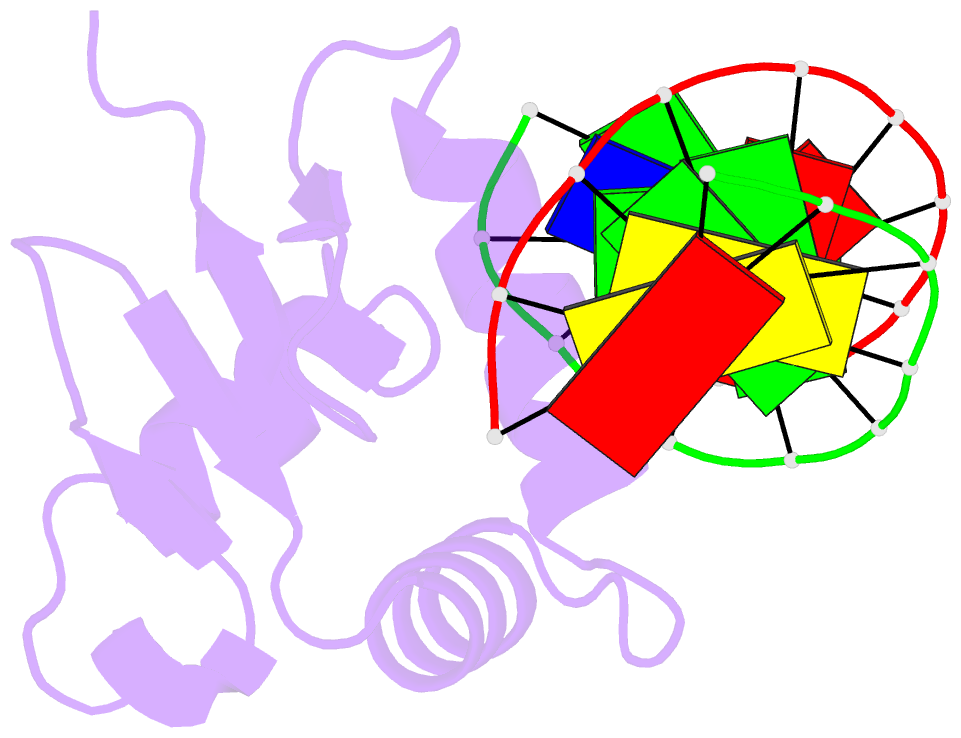
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7jsa; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.85 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of the DNA binding domain of human transcription factor erf in the reduced form, in complex with double-stranded DNA accggaagtg
- Reference
- Hou C, McCown C, Ivanov DN, Tsodikov OV (2020): "Structural Insight into the DNA Binding Function of Transcription Factor ERF." Biochemistry. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00774.
- Abstract
- ETS family transcription factors control development of different cell types in humans, whereas deregulation of these proteins leads to severe developmental syndromes and cancers. One of a few members of the ETS family that are known to act solely as repressors, ERF, is required for normal osteogenesis and hematopoiesis. Another important function of ERF is acting as a tumor suppressor by antagonizing oncogenic fusions involving other ETS family factors. The structure of ERF and the DNA binding properties specific to this protein have not been elucidated. In this study, we determined two crystal structures of the complexes of the DNA binding domain of ERF with DNA. In one, ERF is in a distinct dimeric form, with Cys72 in a reduced state. In the other, two dimers of ERF are assembled into a tetramer that is additionally locked by two Cys72-Cys72 disulfide bonds across the dimers. In the tetramer, the ERF molecules are bound to a pseudocontinuous DNA on the same DNA face at two GGAA binding sites on opposite strands. Sedimentation velocity analysis showed that this tetrameric assembly forms on continuous DNA containing such tandem sites spaced by 7 bp. Our bioinformatic analysis of three previously reported sets of ERF binding loci across entire genomes showed that these loci were enriched in such 7 bp spaced tandem sites. Taken together, these results strongly suggest that the observed tetrameric assembly is a functional state of ERF in the human cell.