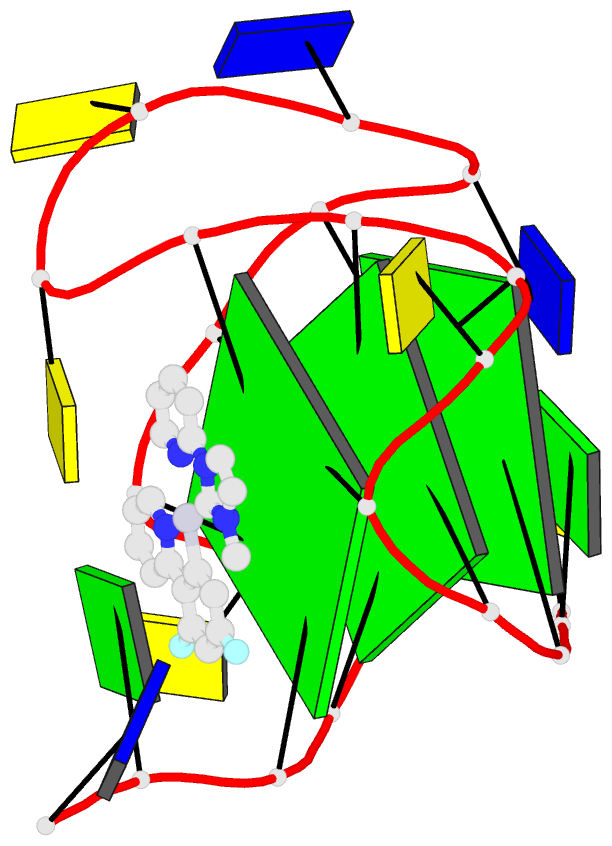
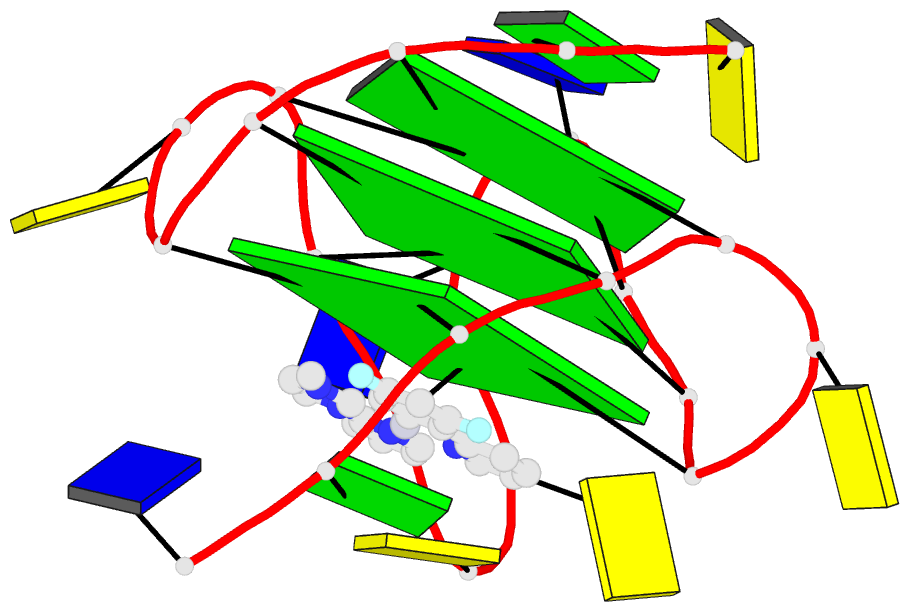
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
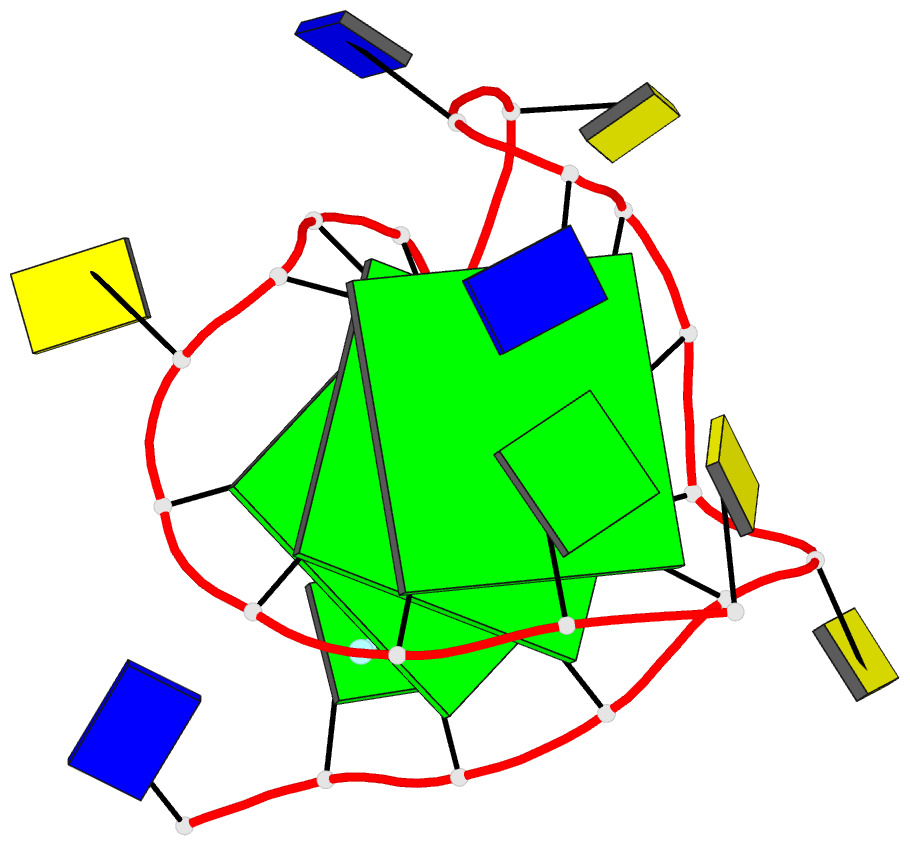
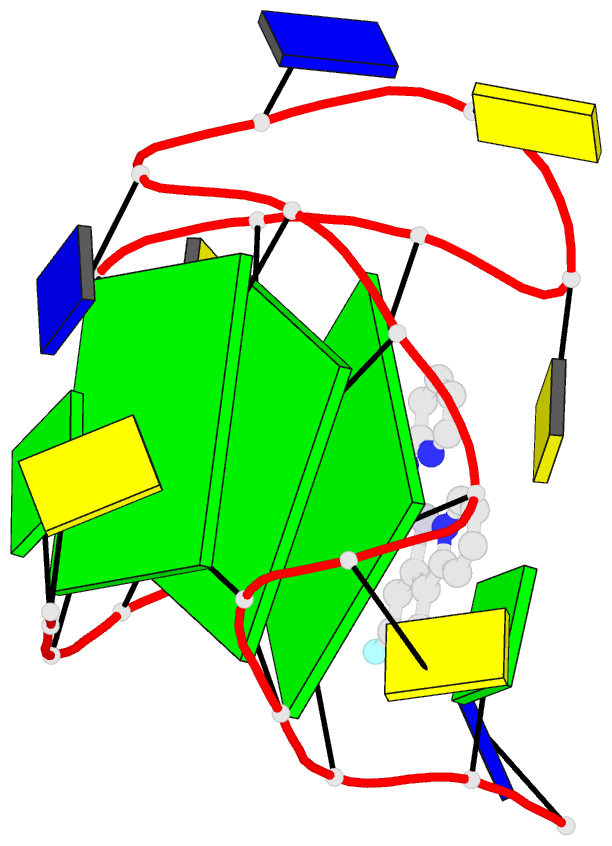
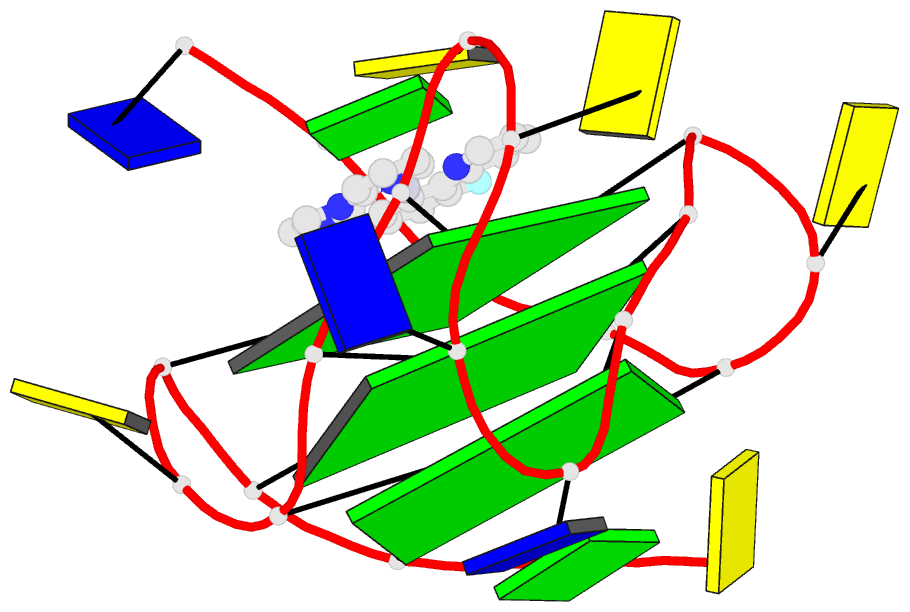
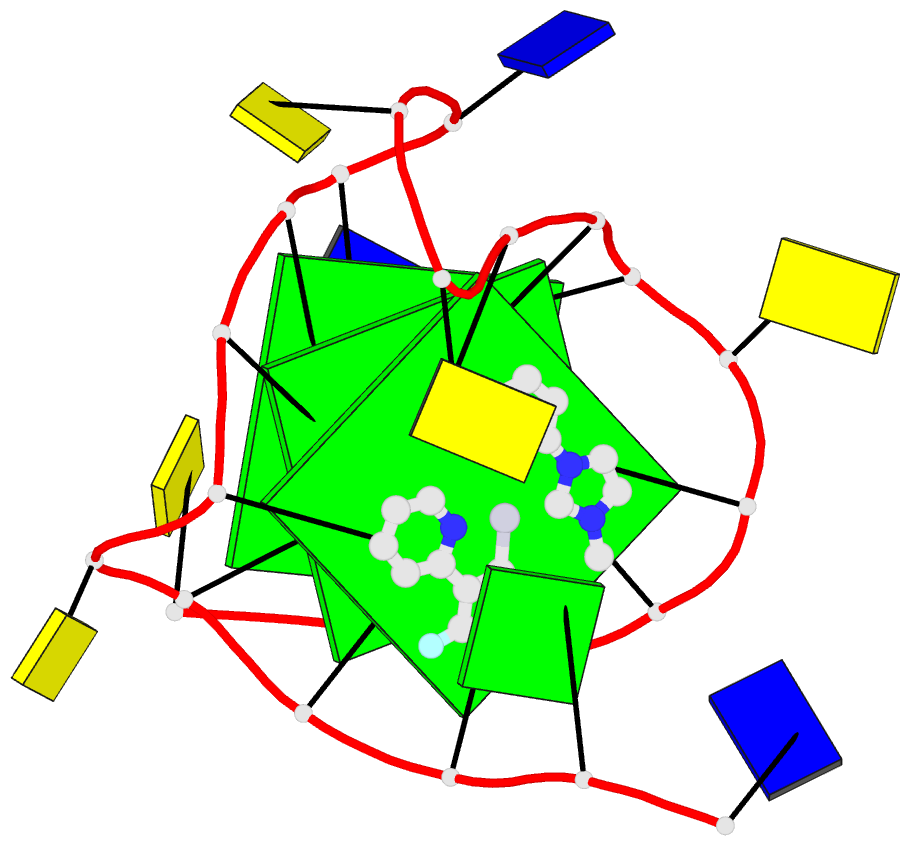
- 6lnz; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- NMR solution structure of vegf g-quadruplex bound a non-planar cyclometalated-carbene platinum(ii) complex
- Reference
- Zhu BC, He J, Liu W, Xia XY, Liu LY, Liang BB, Yao HG, Liu B, Ji LN, Mao ZW (2021): "Selectivity and Targeting of G-Quadruplex Binders Activated by Adaptive Binding and Controlled by Chemical Kinetics." Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl., 60, 15340-15343. doi: 10.1002/anie.202104624.
- Abstract
- G-quadruplexes (G4s) are prevalent in oncogenes and are potential antitumor drug targets. However, binding selectivity of compounds to G4s still faces challenges. Herein, we report a platinum(II) complex (Pt1), whose affinity to G4-DNA is activated by adaptive binding and selectivity controlled by binding kinetics. The resolved structure of Pt1/VEGF-G4 (a promoter G4) shows that Pt1 matches 3'-G-tetrad of VEGF-G4 through Cl- -dissociation and loop rearrangement of VEGF-G4. Binding rate constants are determined by coordination bond breakage/formation, correlating fully with affinities. The selective rate-determining binding step, Cl- -dissociation upon G4-binding, is 2-3 orders of magnitude higher than dsDNA. Pt1 potently targets G4 in living cells, effectively represses VEGF expression, and inhibits vascular growth in zebrafish. We show adaptive G4-binding activation and controlled by kinetics, providing a complementary design principle for compounds targeting G4 or similar biomolecules.