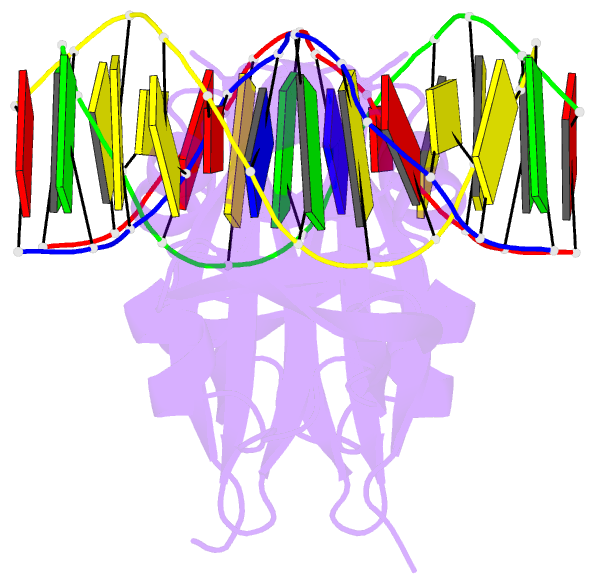
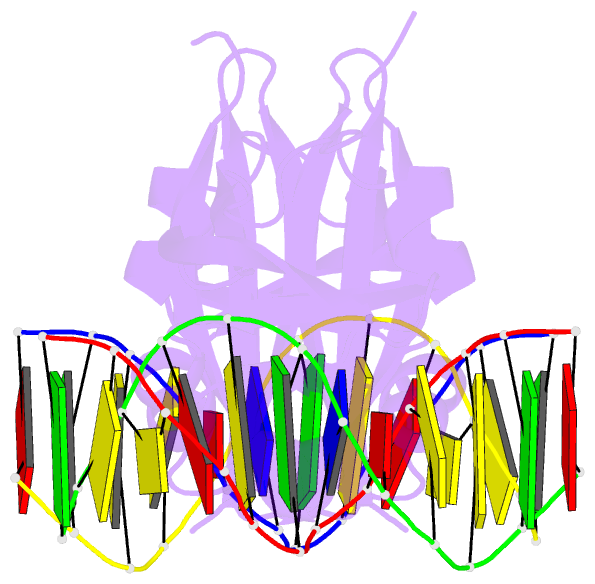
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
6fas;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (1.9 Å)
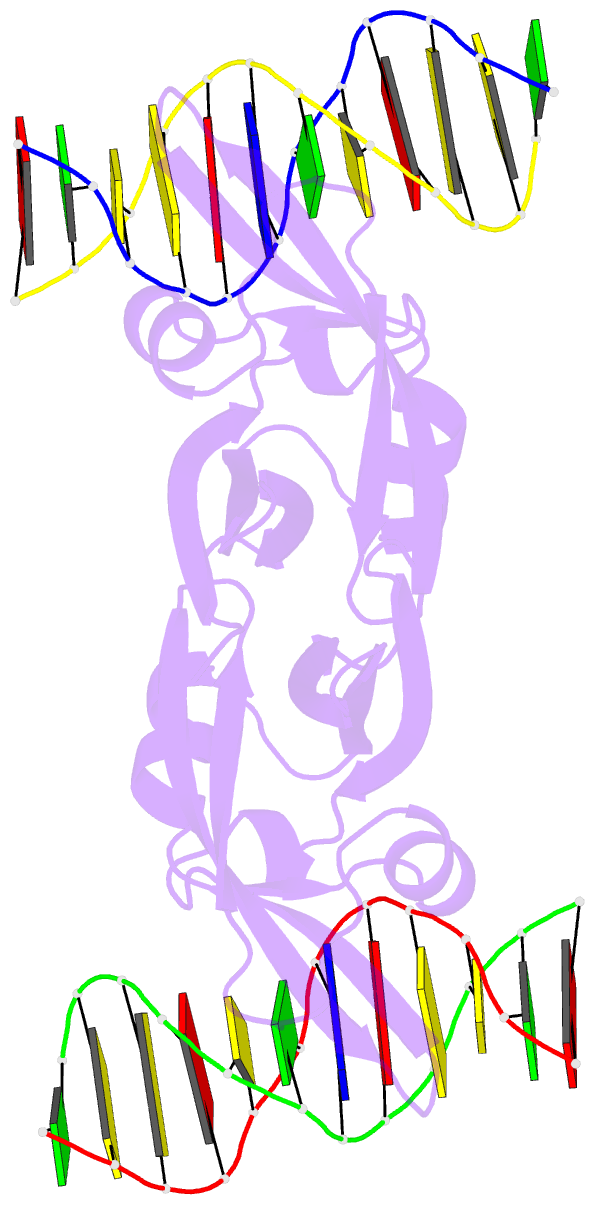
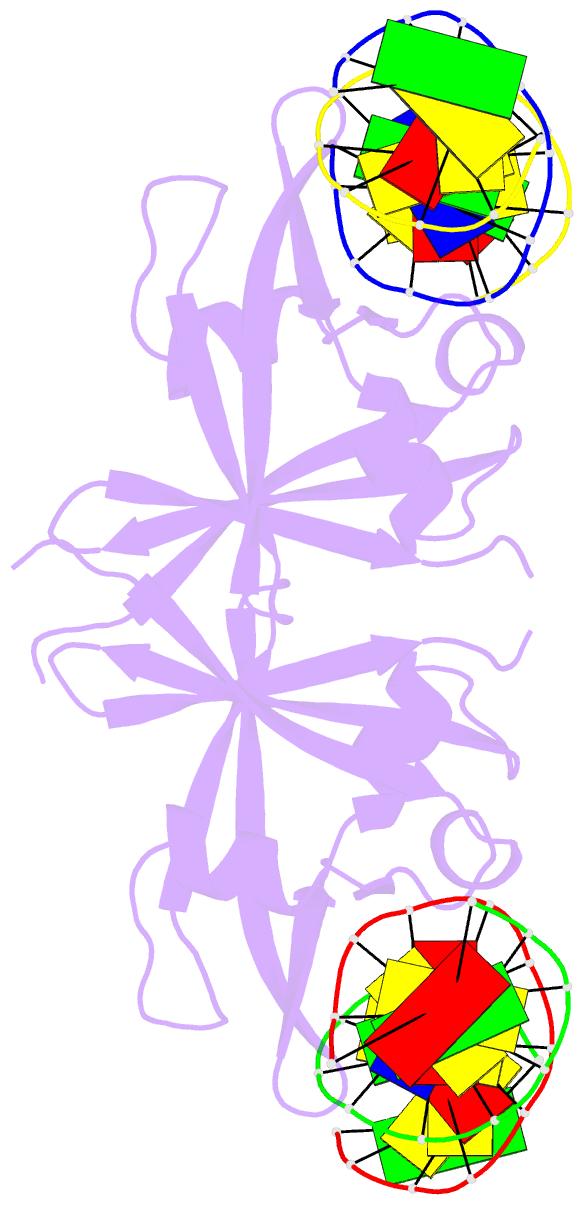
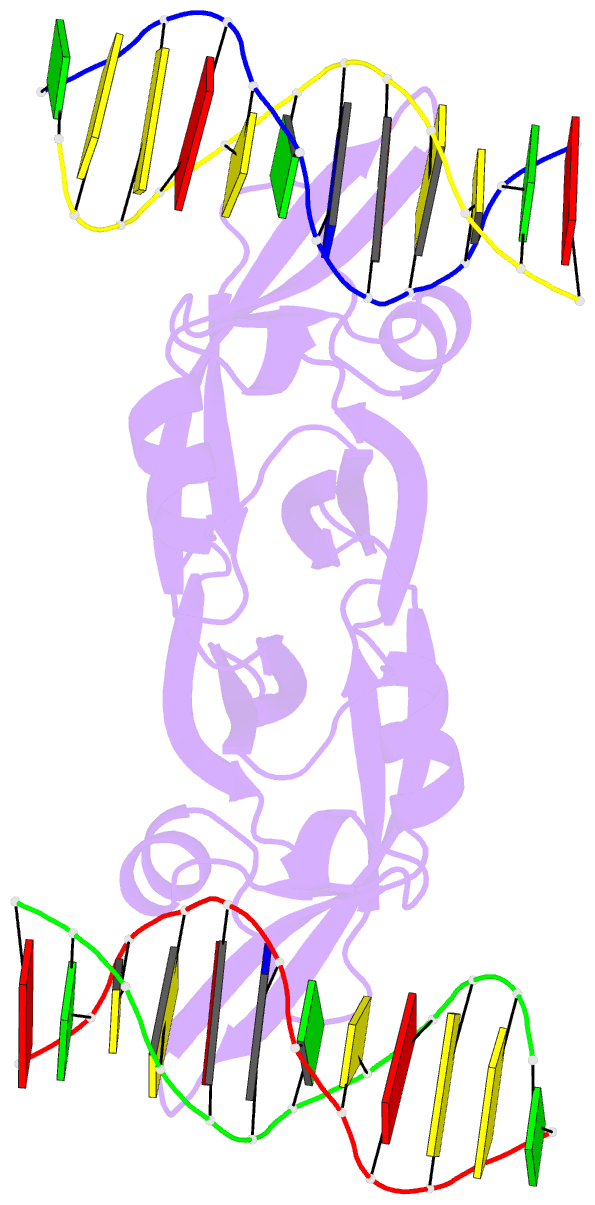
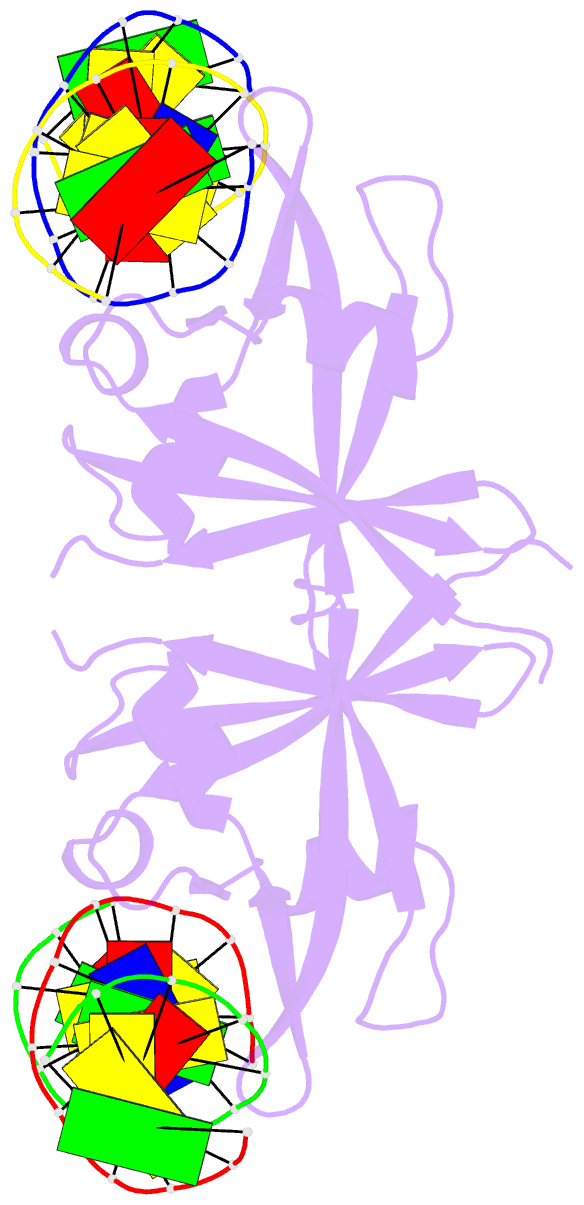
- Summary
- Crystal structure of val1 b3 domain in complex with
cognate DNA
- Reference
-
Sasnauskas G, Kauneckaite K, Siksnys V (2018): "Structural
basis of DNA target recognition by the B3 domain of
Arabidopsis epigenome reader VAL1." Nucleic Acids
Res., 46, 4316-4324. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky256.
- Abstract
- Arabidopsis thaliana requires a prolonged period of
cold exposure during winter to initiate flowering in a
process termed vernalization. Exposure to cold induces
epigenetic silencing of the FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) gene by
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins. A key role in this
epigenetic switch is played by transcriptional repressors
VAL1 and VAL2, which specifically recognize Sph/RY DNA
sequences within FLC via B3 DNA binding domains, and
mediate recruitment of PcG silencing machinery. To
understand the structural mechanism of site-specific DNA
recognition by VAL1, we have solved the crystal structure
of VAL1 B3 domain (VAL1-B3) bound to a 12 bp oligoduplex
containing the canonical Sph/RY DNA sequence
5'-CATGCA-3'/5'-TGCATG-3'. We find that VAL1-B3 makes
H-bonds and van der Waals contacts to DNA bases of all six
positions of the canonical Sph/RY element. In agreement
with the structure, in vitro DNA binding studies show that
VAL1-B3 does not tolerate substitutions at any position of
the 5'-TGCATG-3' sequence. The VAL1-B3-DNA structure
presented here provides a structural model for
understanding the specificity of plant B3 domains
interacting with the Sph/RY and other DNA sequences.