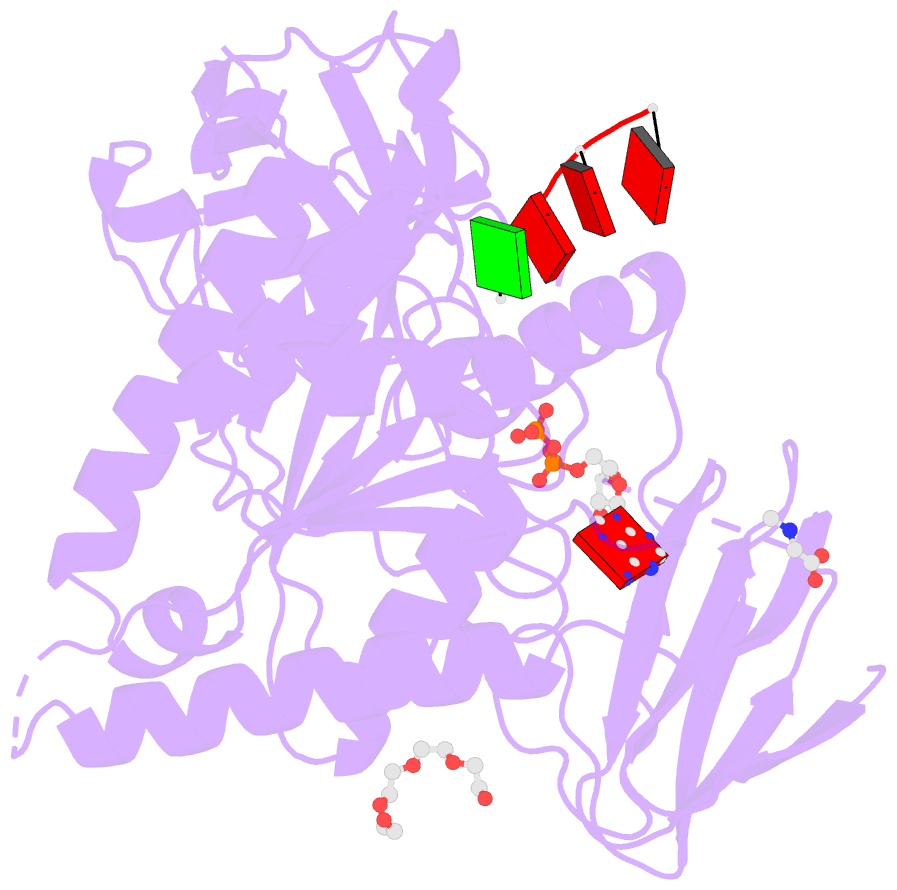
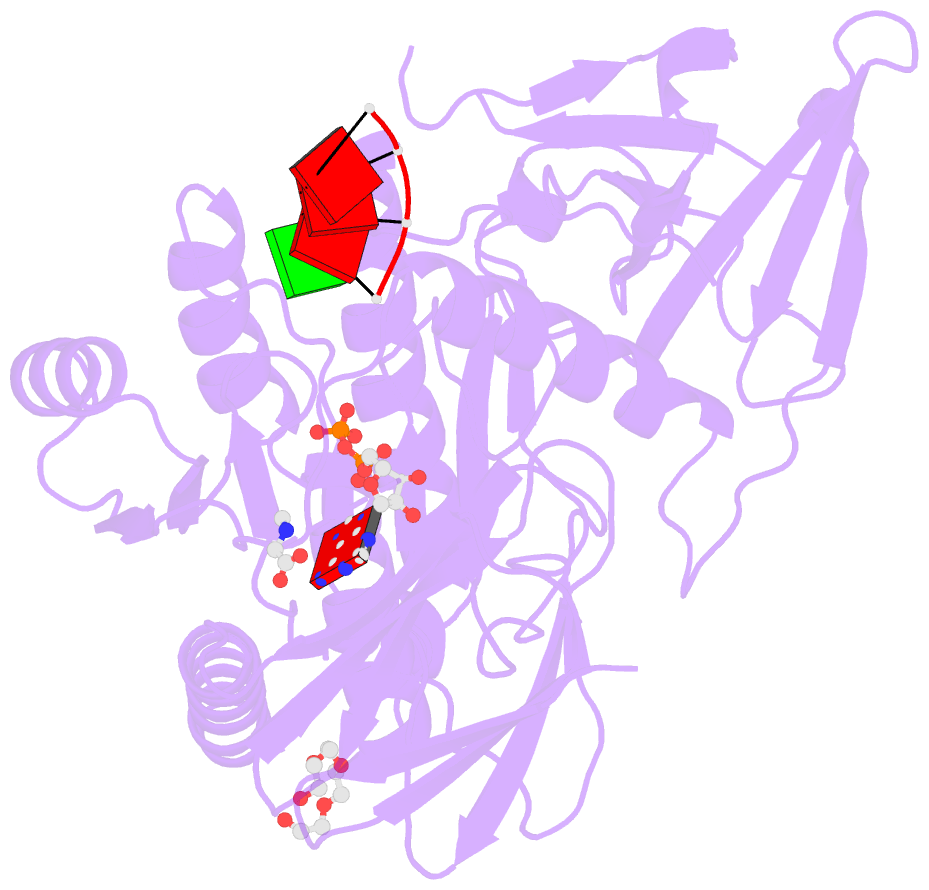
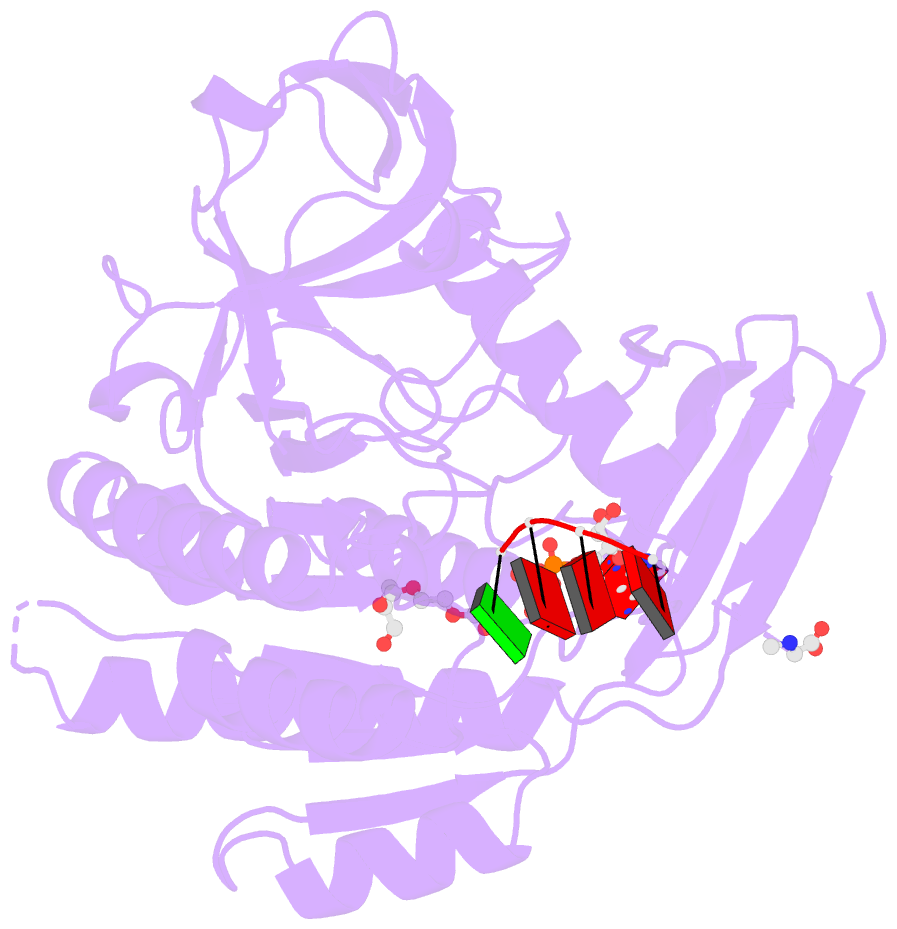
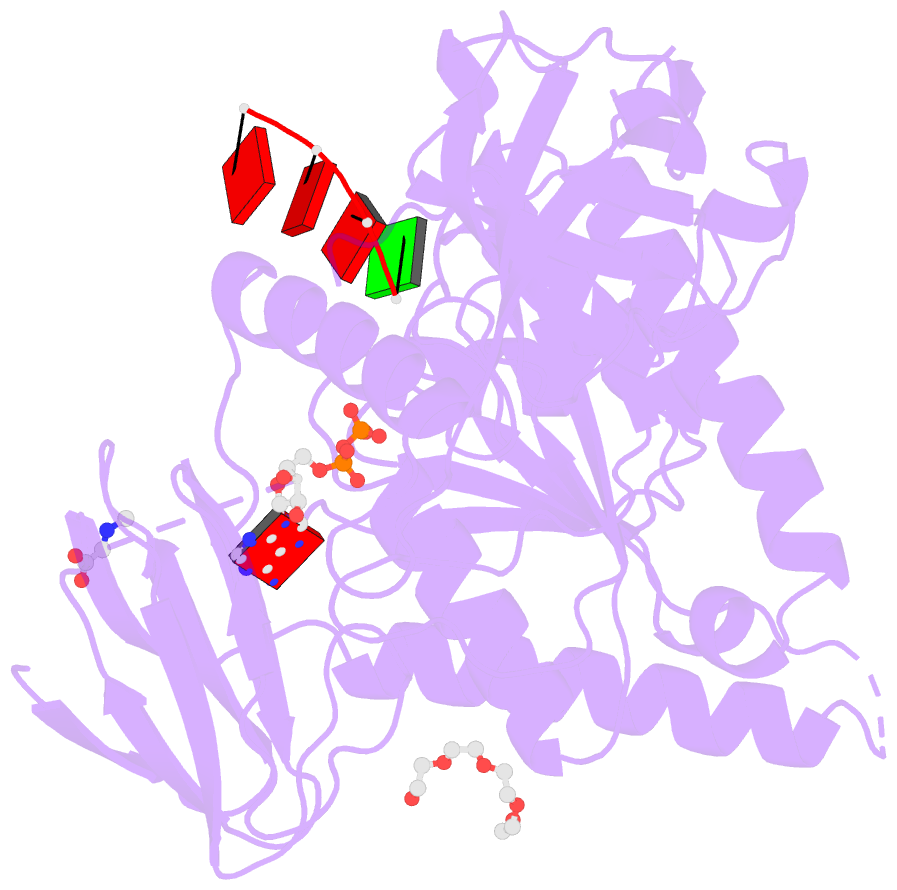
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
4ohz;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.4 Å)
- Summary
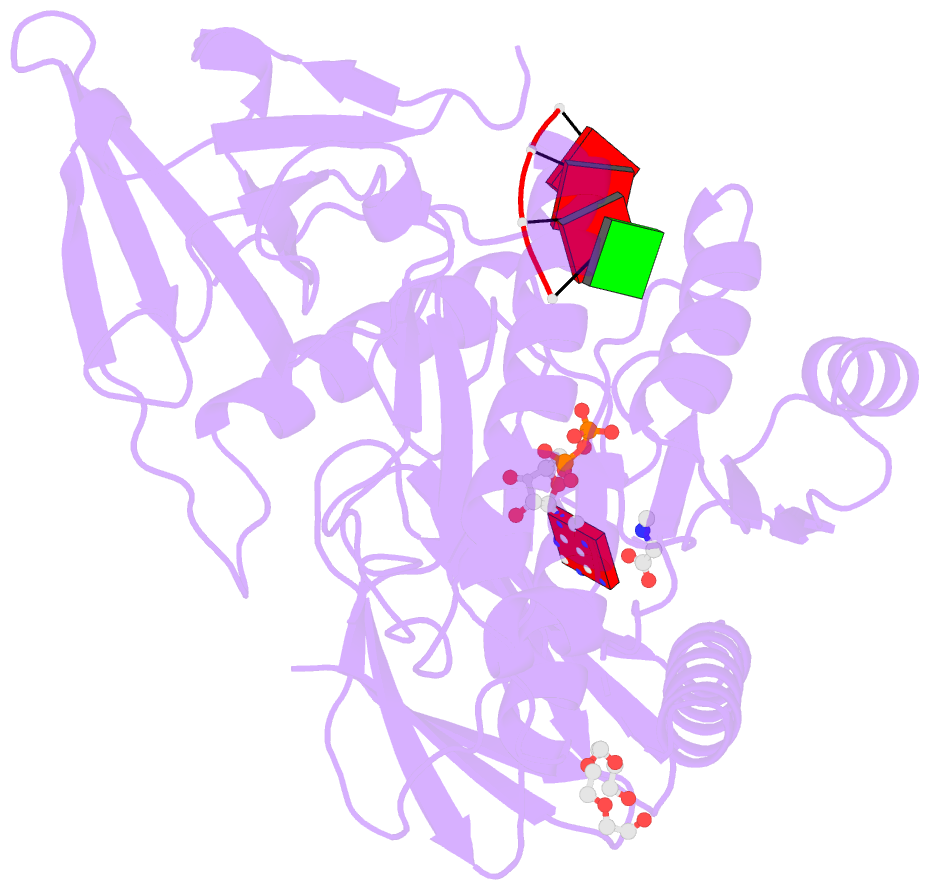
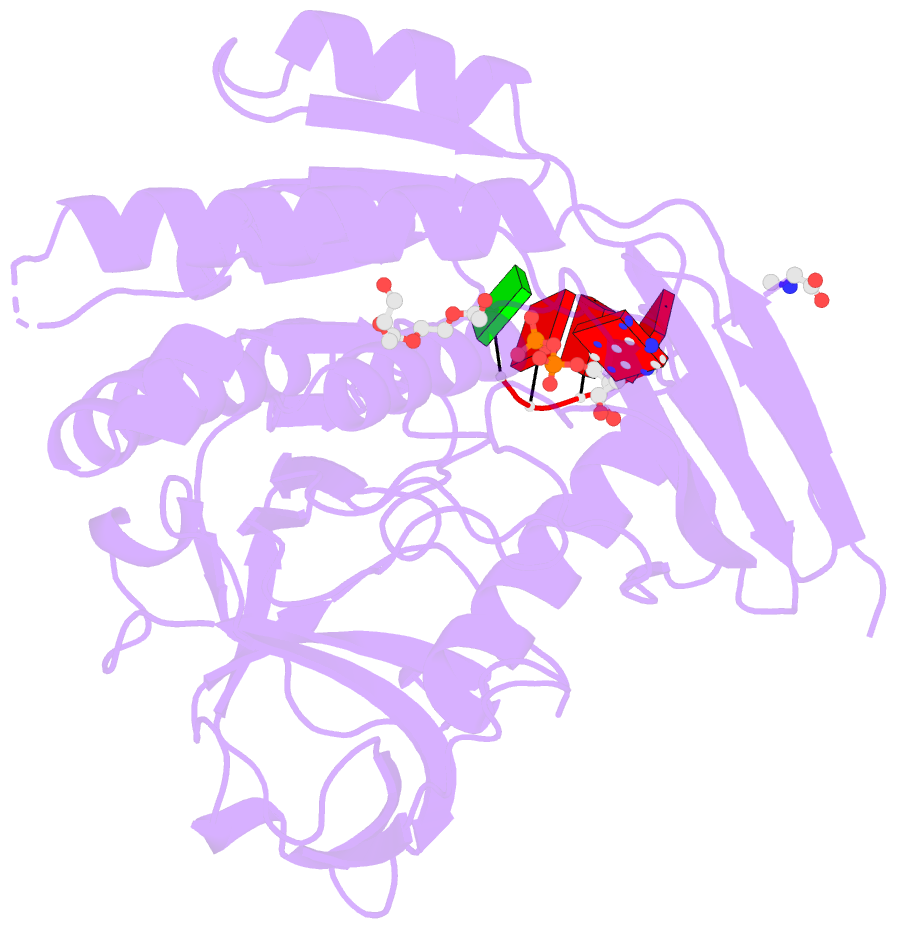
- Bound to ssrna tetranucleotide gaaa, adp, and mg2+
- Reference
-
Dikfidan A, Loll B, Zeymer C, Magler I, Clausen T,
Meinhart A (2014): "RNA
specificity and regulation of catalysis in the eukaryotic
polynucleotide kinase clp1." Mol.Cell,
54, 975-986. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.04.005.
- Abstract
- RNA-specific polynucleotide kinases of the Clp1
subfamily are key components of various RNA maturation
pathways. However, the structural basis explaining their
substrate specificity and the enzymatic mechanism is
elusive. Here, we report crystal structures of Clp1 from
Caenorhabditis elegans (ceClp1) in a number of nucleotide-
and RNA-bound states along the reaction pathway. The
combined structural and biochemical analysis of ceClp1
elucidates the RNA specificity and lets us derive a general
model for enzyme catalysis of RNA-specific polynucleotide
kinases. We identified an RNA binding motif referred to as
"clasp" as well as a conformational switch that involves
the essential Walker A lysine (Lys127) and regulates the
enzymatic activity of ceClp1. Structural comparison with
other P loop proteins, such as kinases, adenosine
triphosphatases (ATPases), and guanosine triphosphatases
(GTPases), suggests that the observed conformational switch
of the Walker A lysine is a broadly relevant mechanistic
feature.