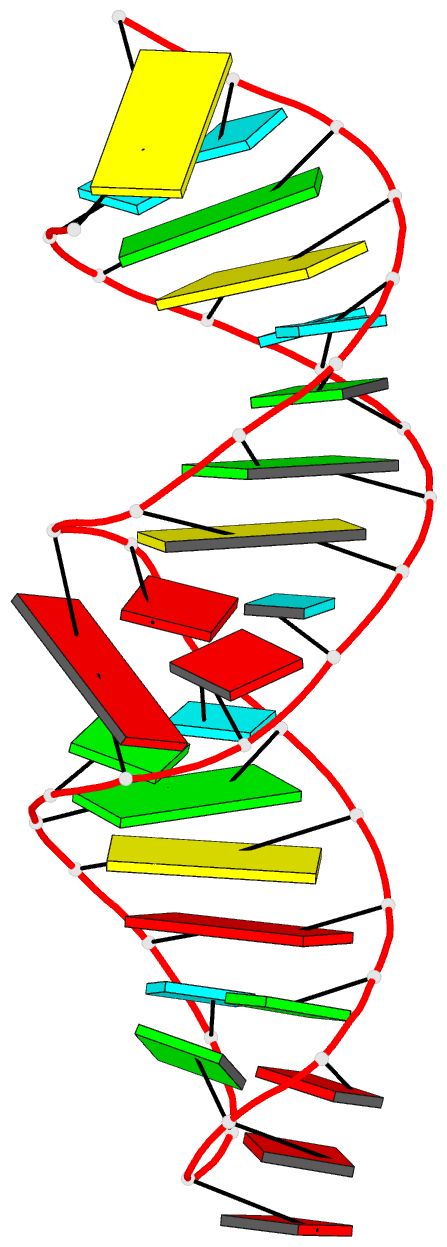
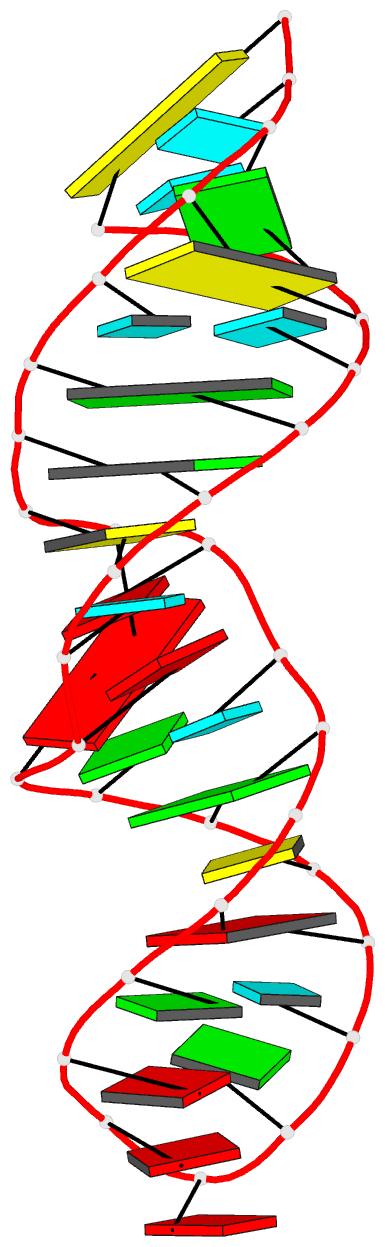
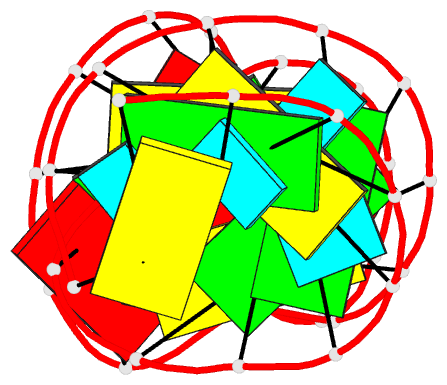
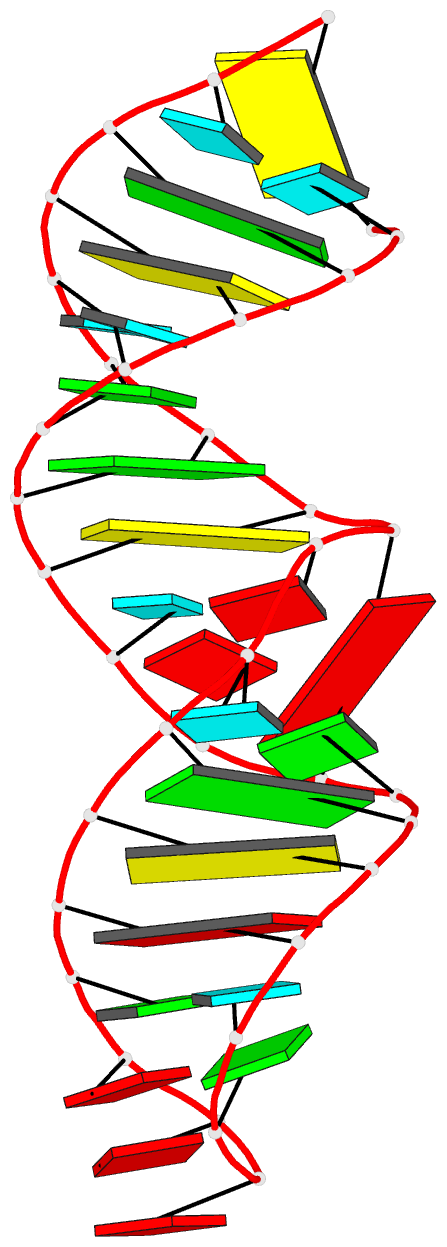
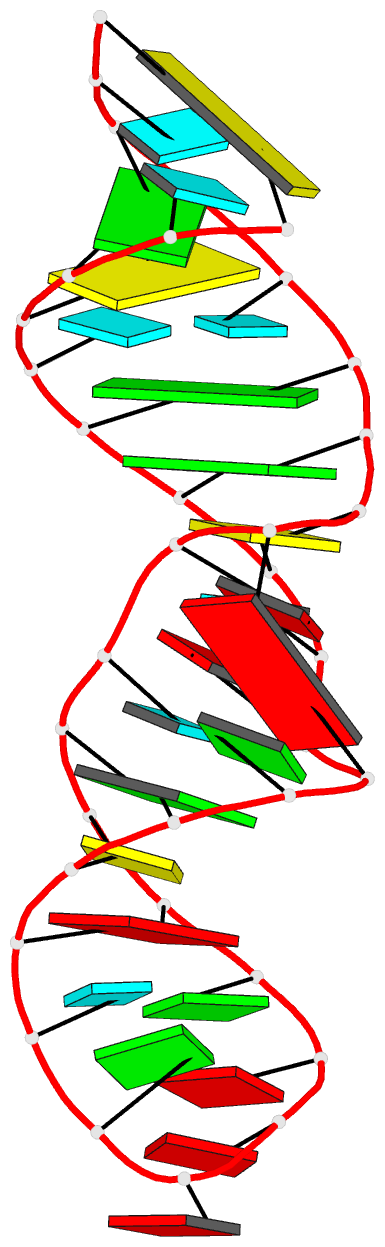
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 4fnj; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.95 Å)
- Summary
- Utilizing the gaaa tetraloop-receptor to facilitate crystal packing and structure determination of a cug RNA helix
- Reference
- Coonrod LA, Lohman JR, Berglund JA (2012): "Utilizing the GAAA Tetraloop/Receptor To Facilitate Crystal Packing and Determination of the Structure of a CUG RNA Helix." Biochemistry, 51, 8330-8337. doi: 10.1021/bi300829w.
- Abstract
- Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is a microsatellite expansion disorder caused by the aberrant expansion of CTG repeats in the 3' untranslated region of the DMPK gene. When transcribed, the toxic RNA CUG repeats sequester RNA binding proteins, which leads to disease symptoms. The expanded CUG repeats can adopt a double-stranded structure, and targeting this helix is a therapeutic strategy for DM1. In order to better understand the 5'CUG/3'GUC motif, and how it may interact with proteins and small molecules, we designed a short CUG helix attached to a GAAA tetraloop/receptor in order to facilitate crystal packing. Here we report the highest resolution structure (1.95 Å) to date of a GAAA tetraloop/receptor and the CUG helix it was used to crystallize. Within the CUG helix, we identify two different forms of non-canonical U-U pairs and reconfirm that CUG repeats are essentially A-form. An analysis of all non-canonical U-U pairs in the context of CUG repeats revealed six different classes of conformations that the non-canonical U-U pairs are able to adopt.