Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
4da3;
DSSR-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.4 Å)
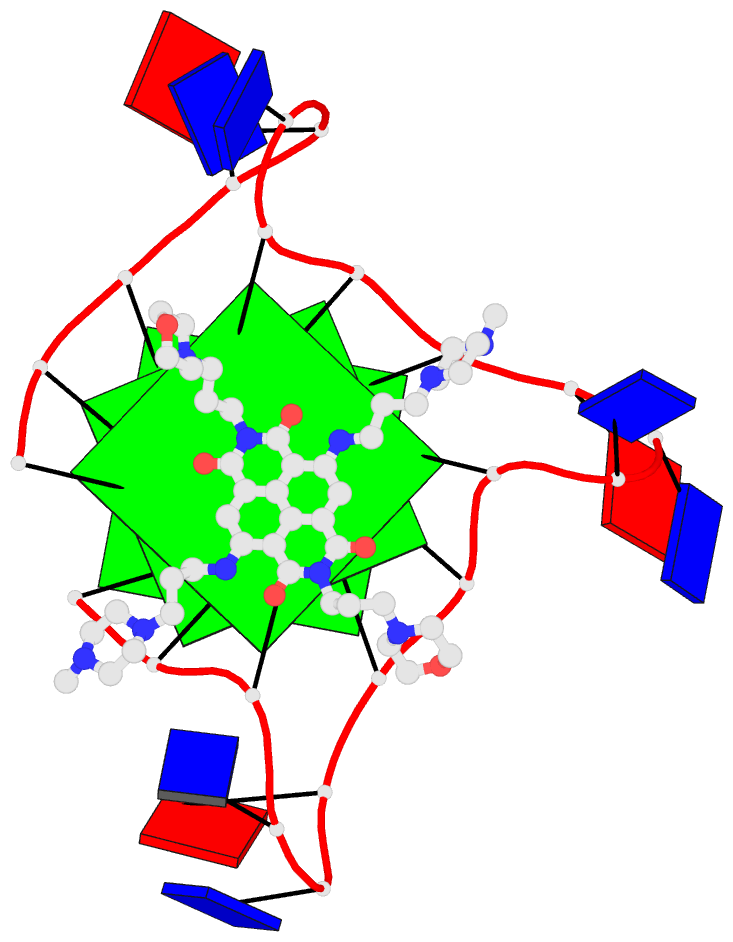
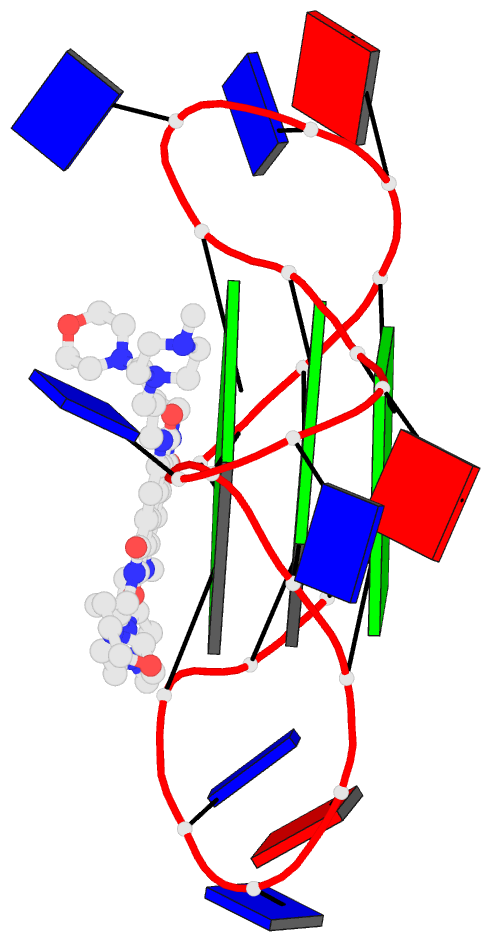
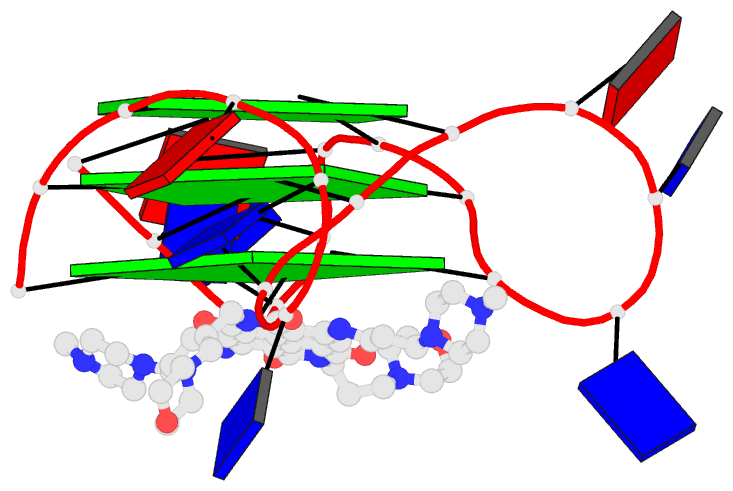
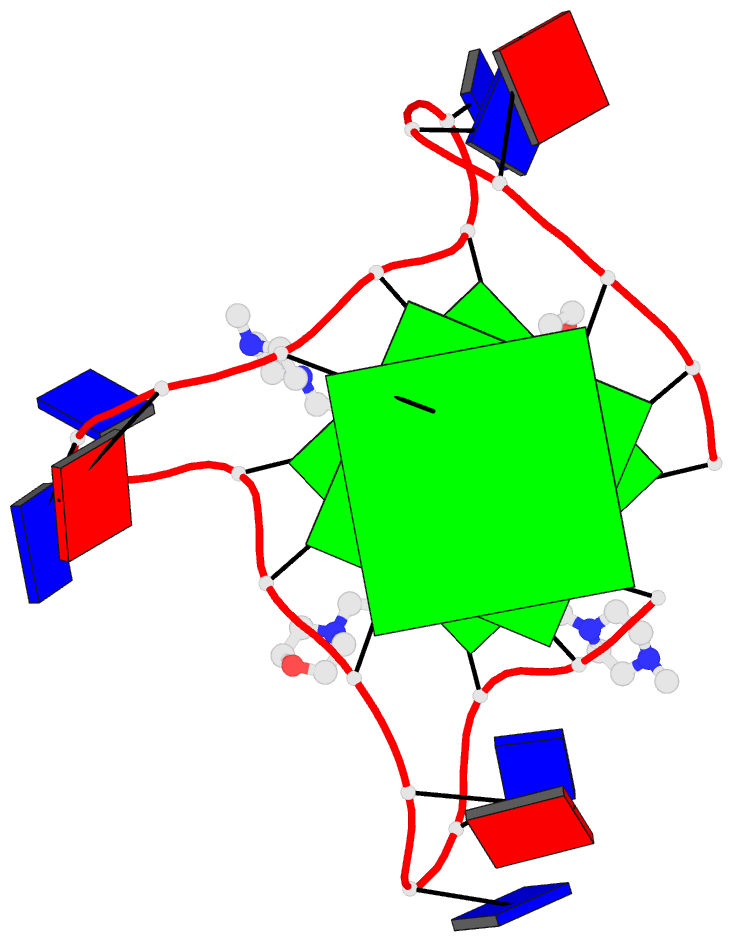
- Summary
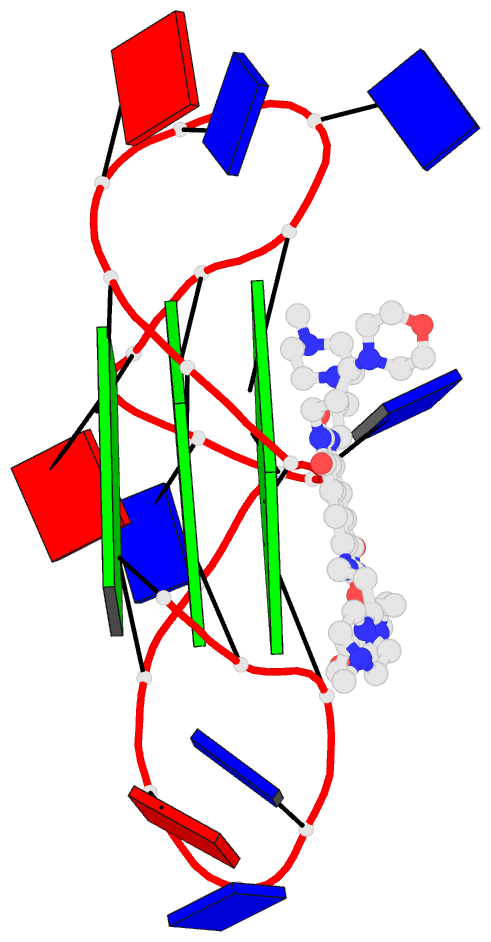
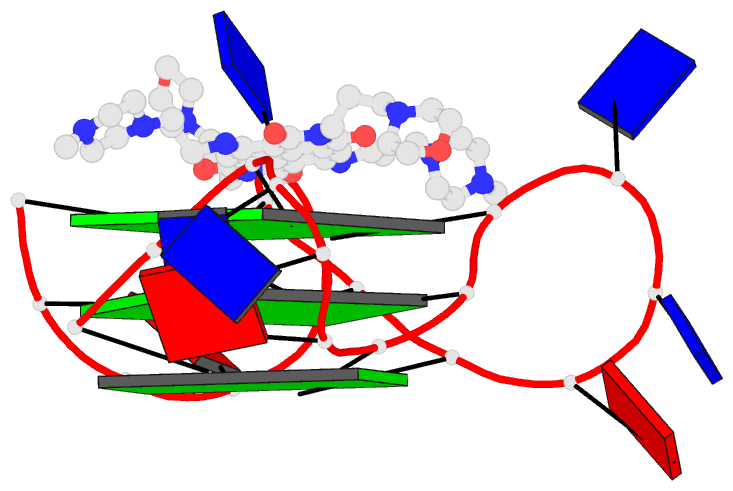
- Crystal structure of an intramolecular human telomeric
DNA g-quadruplex 21-mer bound by the naphthalene diimide
compound mm41.
- Reference
-
Micco M, Collie GW, Dale AG, Ohnmacht SA, Pazitna I,
Gunaratnam M, Reszka AP, Neidle S (2013): "Structure-based
design and evaluation of naphthalene diimide g-quadruplex
ligands as telomere targeting agents in pancreatic cancer
cells." J.Med.Chem., 56,
2959-2974. doi: 10.1021/jm301899y.
- Abstract
- Tetra-substituted naphthalene diimide (ND) derivatives
with positively charged termini are potent stabilizers of
human telomeric and gene promoter DNA quadruplexes and
inhibit the growth of human cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo. The present study reports the enhancement of the
pharmacological properties of earlier ND compounds using
structure-based design. Crystal structures of three
complexes with human telomeric intramolecular quadruplexes
demonstrate that two of the four strongly basic
N-methyl-piperazine groups can be replaced by less basic
morpholine groups with no loss of intermolecular
interactions in the grooves of the quadruplex. The new
compounds retain high affinity to human telomeric
quadruplex DNA but are 10-fold more potent against the MIA
PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cell line, with IC50 values of ~10
nM. The lead compound induces cellular senescence but does
not inhibit telomerase activity at the nanomolar dosage
levels required for inhibition of cellular proliferation.
Gene array qPCR analysis of MIA PaCa-2 cells treated with
the lead compound revealed significant dose-dependent
modulation of a distinct subset of genes, including strong
induction of DNA damage responsive genes CDKN1A, DDIT3,
GADD45A/G, and PPM1D, and repression of genes involved in
telomere maintenance, including hPOT1 and PARP1.