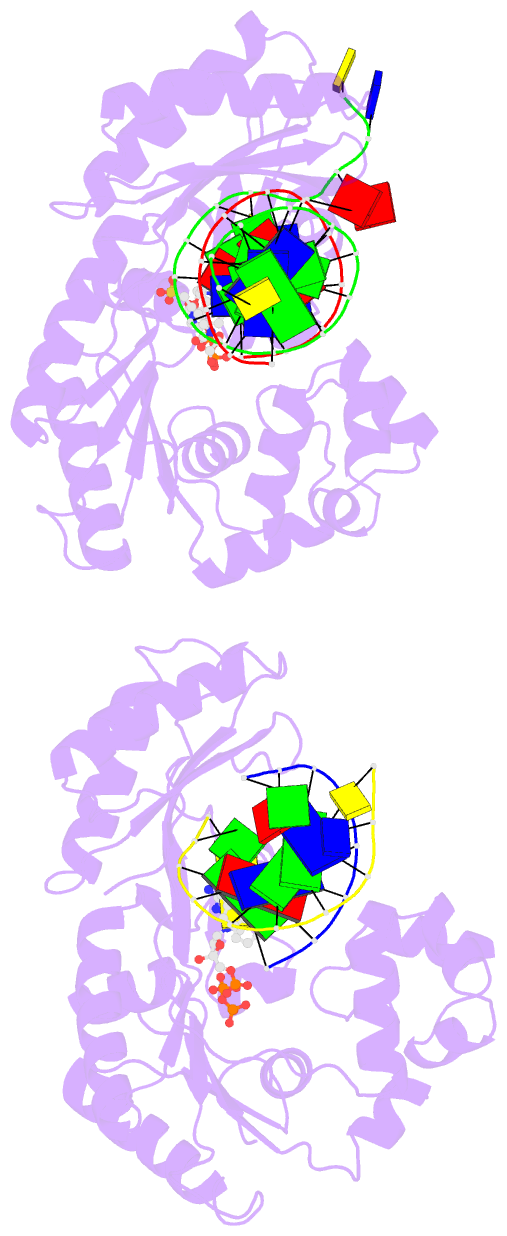
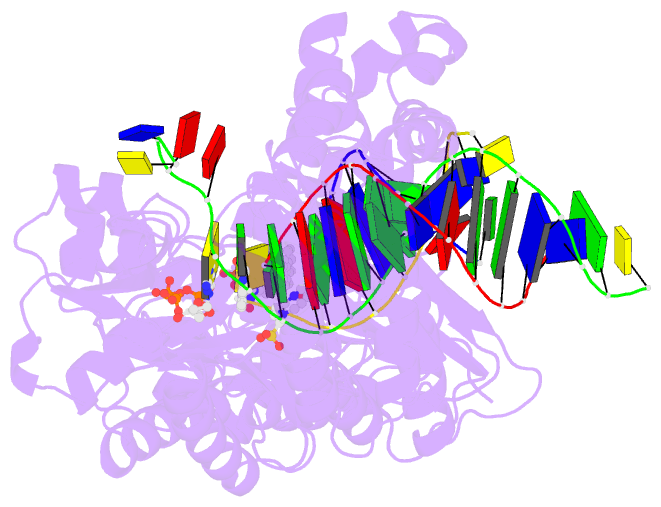
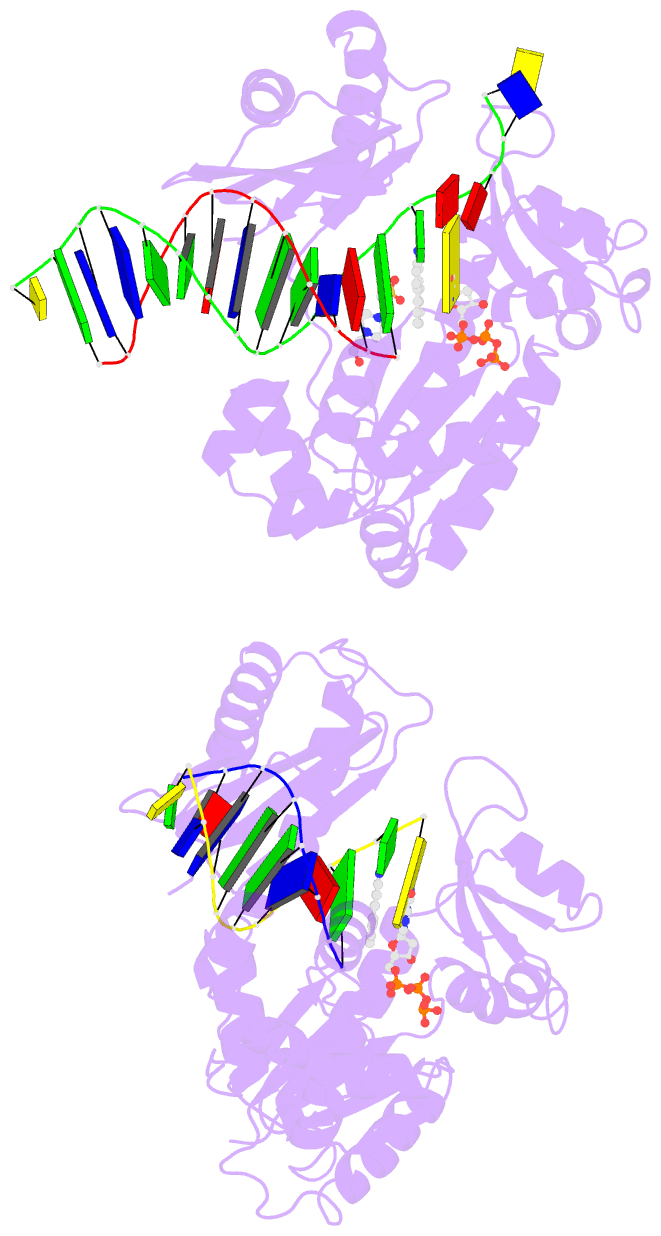
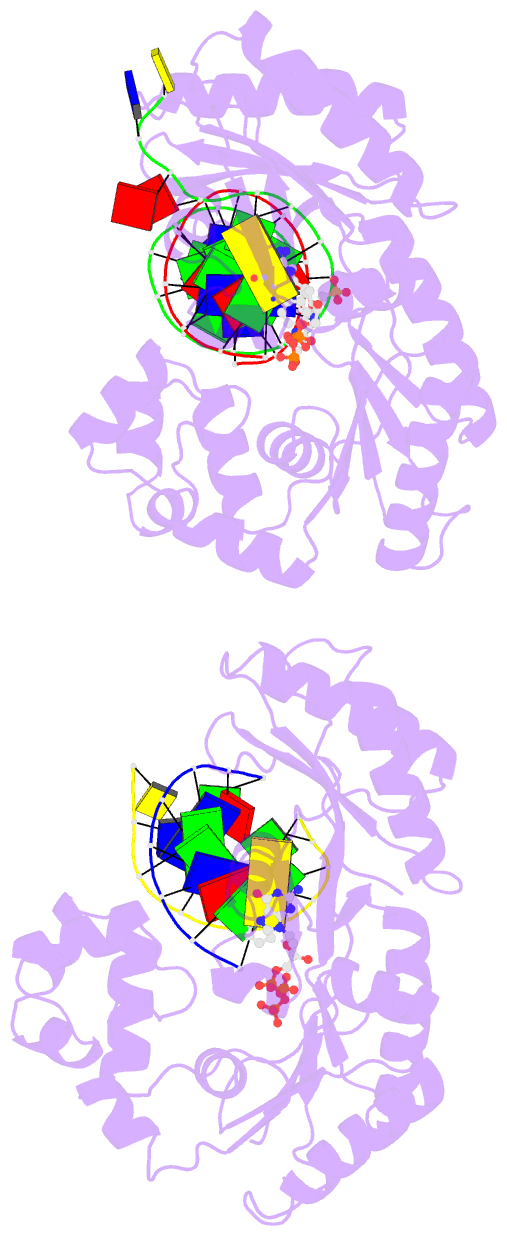
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
3khg;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.96 Å)
- Summary
- Dpo4 extension ternary complex with misinserted a
opposite the 2-aminofluorene-guanine [af]g lesion
- Reference
-
Rechkoblit O, Kolbanovskiy A, Malinina L, Geacintov NE,
Broyde S, Patel DJ (2010): "Mechanism
of error-free and semitargeted mutagenic bypass of an
aromatic amine lesion by Y-family polymerase Dpo4."
Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 17,
379-388. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1771.
- Abstract
- The aromatic amine carcinogen 2-aminofluorene (AF)
forms covalent adducts with DNA, predominantly with guanine
at the C8 position. Such lesions are bypassed by Y-family
polymerases such as Dpo4 via error-free and error-prone
mechanisms. We show that Dpo4 catalyzes elongation from a
correct 3'-terminal cytosine opposite [AF]G in a
nonrepetitive template sequence with low efficiency. This
extension leads to cognate full-length product, as well as
mis-elongated products containing base mutations and
deletions. Crystal structures of the Dpo4 ternary complex,
with the 3'-terminal primer cytosine base opposite [AF]G in
the anti conformation and with the AF moiety positioned in
the major groove, reveal both accurate and
misalignment-mediated mutagenic extension pathways. The
mutagenic template-primer-dNTP arrangement is promoted by
interactions between the polymerase and the bulky lesion
rather than by a base pair-stabilized misaligment. Further
extension leads to semitargeted mutations via this proposed
polymerase-guided mechanism.