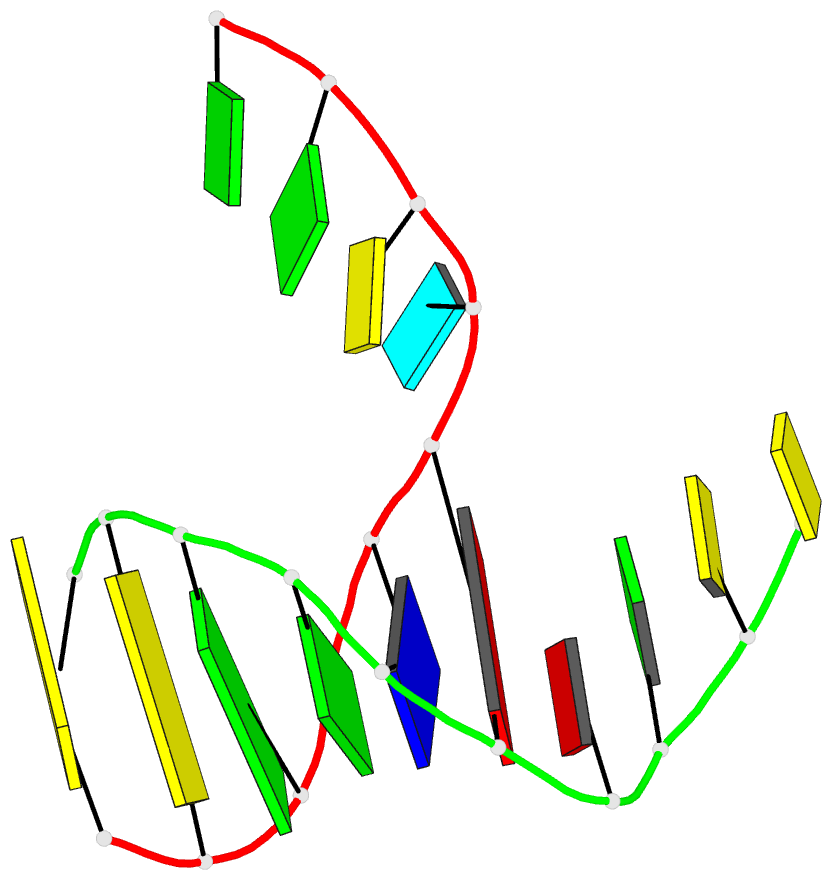
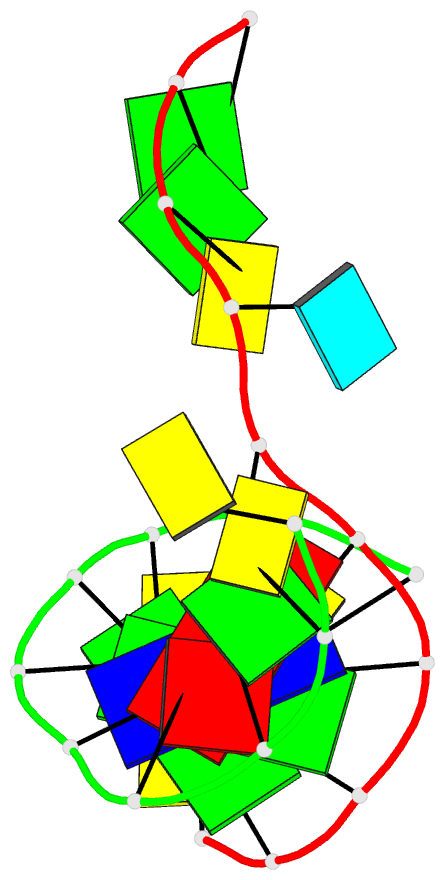
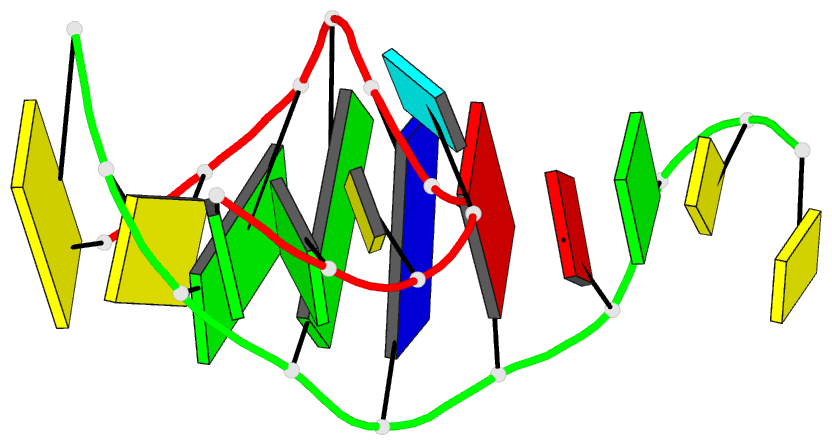
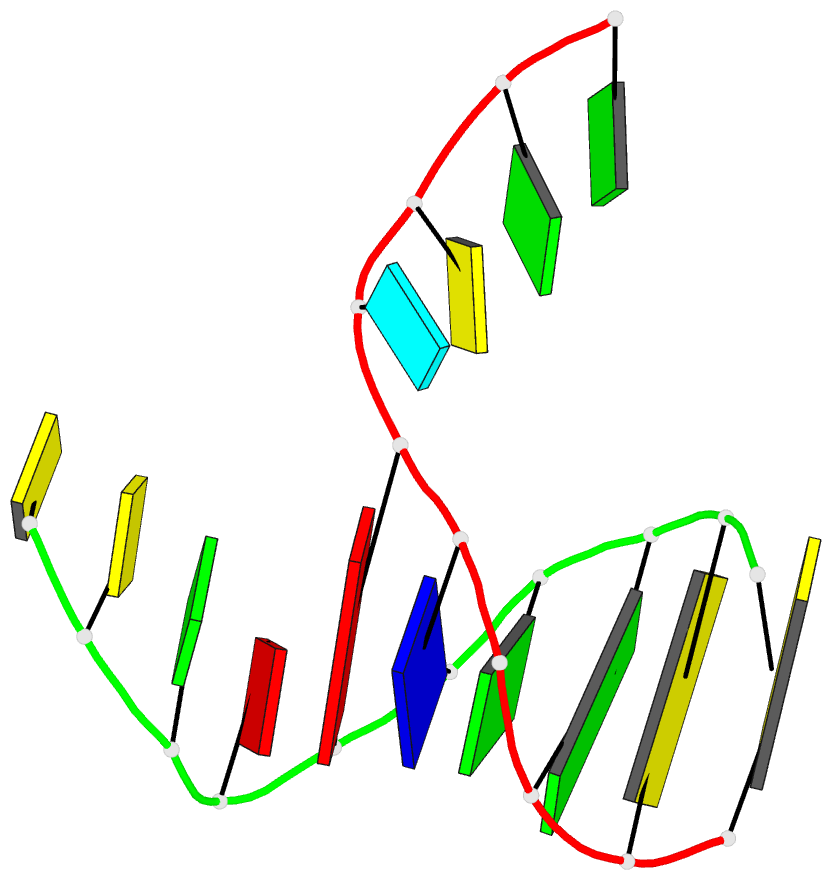
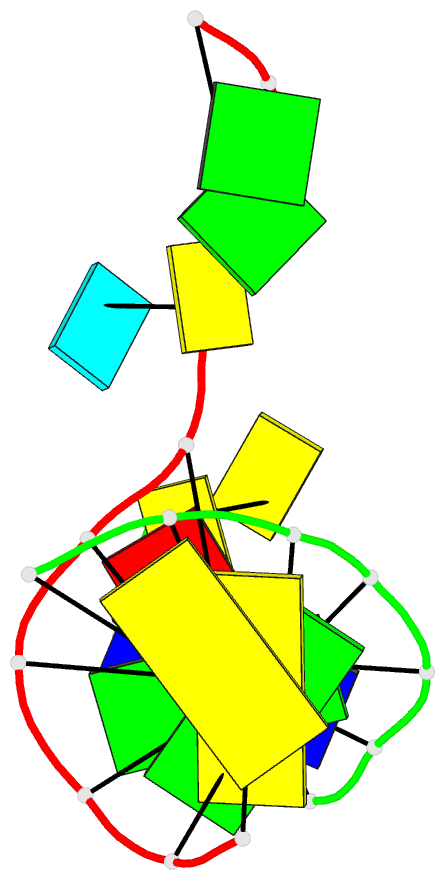
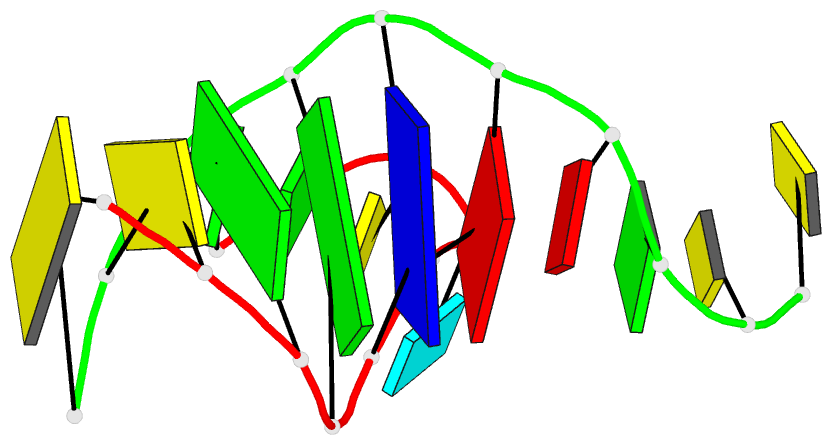
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 2org; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.0 Å)
- Summary
- Directing macromolecular conformation through halogen bonds
- Reference
- Voth AR, Hays FA, Ho PS (2007): "Directing macromolecular conformation through halogen bonds." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.Usa, 104, 6188-6193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0610531104.
- Abstract
- The halogen bond, a noncovalent interaction involving polarizable chlorine, bromine, or iodine molecular substituents, is now being exploited to control the assembly of small molecules in the design of supramolecular complexes and new materials. We demonstrate that a halogen bond formed between a brominated uracil and phosphate oxygen can be engineered to direct the conformation of a biological molecule, in this case to define the conformational isomer of a four-stranded DNA junction when placed in direct competition against a classic hydrogen bond. As a result, this bromine interaction is estimated to be approximately 2-5 kcal/mol stronger than the analogous hydrogen bond in this environment, depending on the geometry of the halogen bond. This study helps to establish halogen bonding as a potential tool for the rational design and construction of molecular materials with DNA and other biological macromolecules.