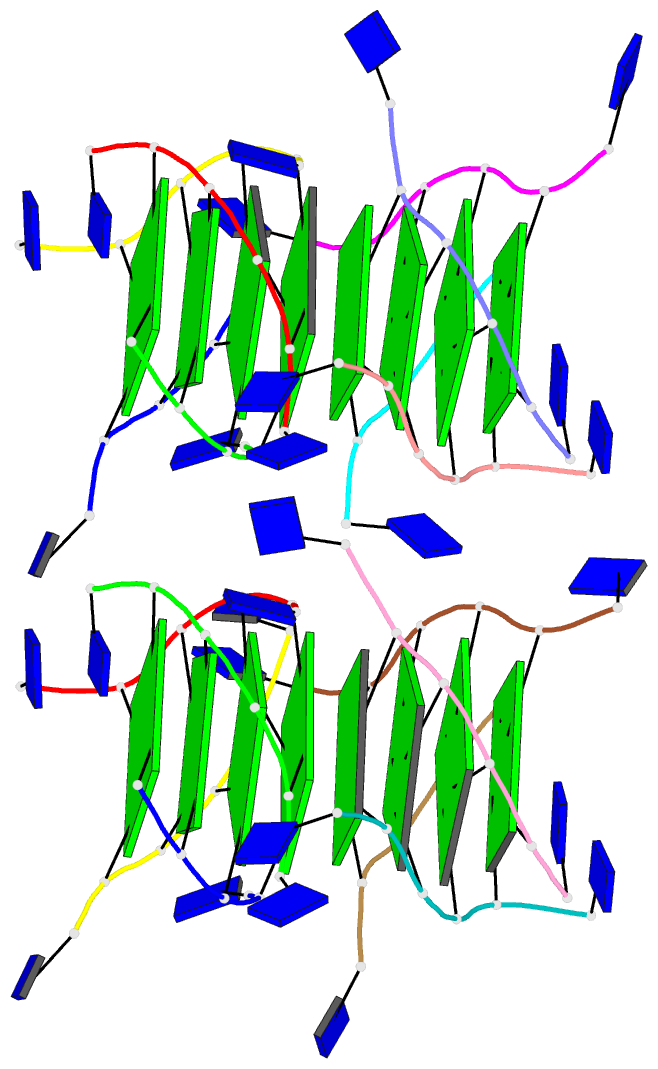
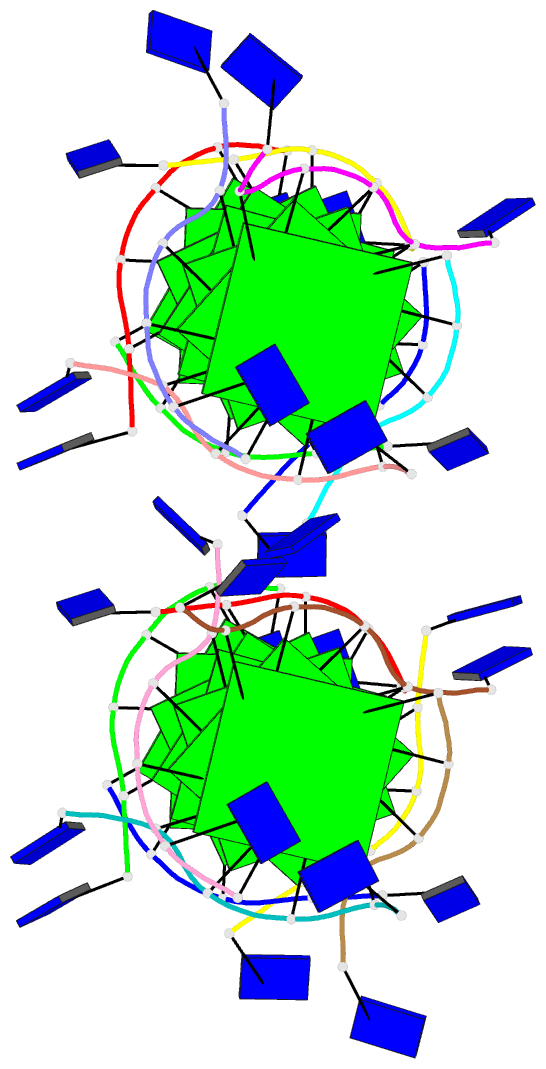
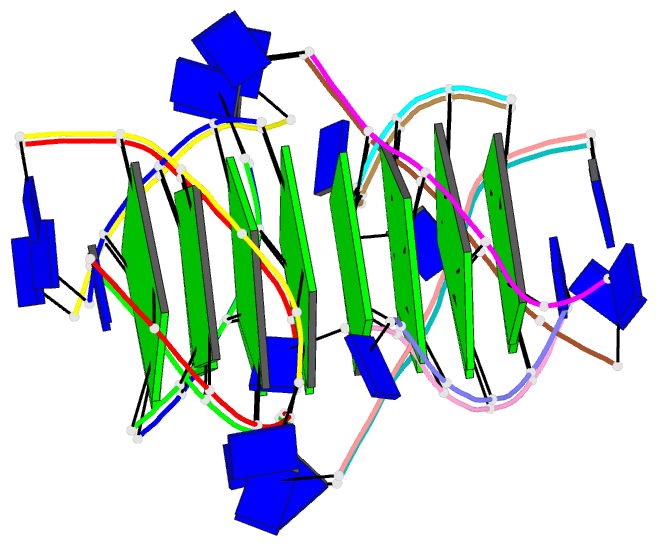
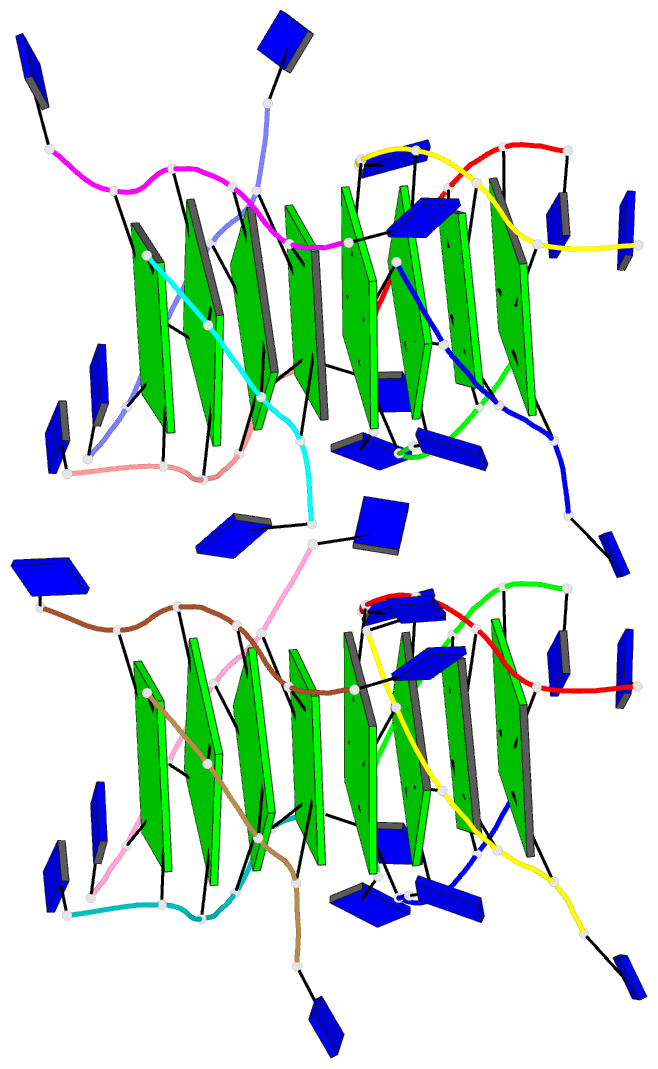
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 244d; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.2 Å)
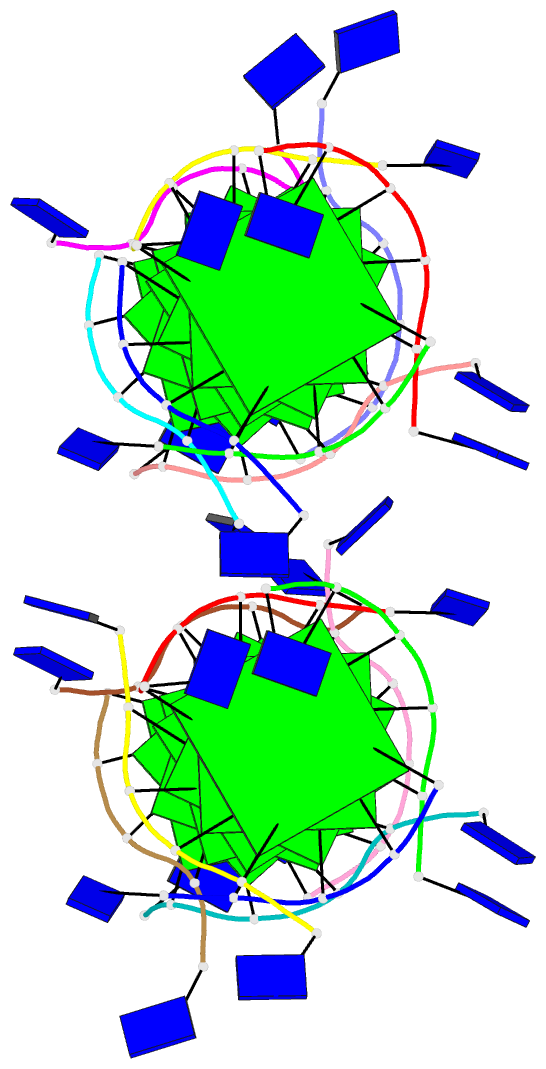
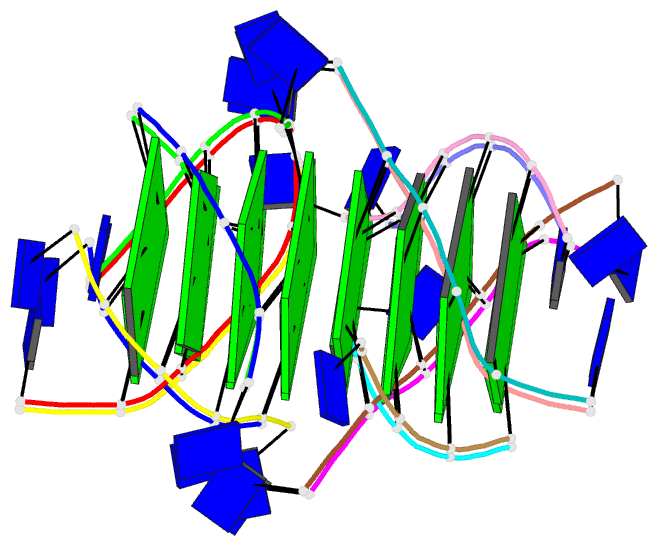
- Summary
- The high-resolution crystal structure of a parallel-stranded guanine tetraplex
- Reference
- Laughlan G, Murchie AI, Norman DG, Moore MH, Moody PC, Lilley DM, Luisi B (1994): "The high-resolution crystal structure of a parallel-stranded guanine tetraplex." Science, 265, 520-524.
- Abstract
- Repeat tracts of guanine bases found in DNA and RNA can form tetraplex structures in the presence of a variety of monovalent cations. Evidence suggests that guanine tetraplexes assume important functions within chromosomal telomeres, immunoglobulin switch regions, and the human immunodeficiency virus genome. The structure of a parallel-stranded tetraplex formed by the hexanucleotide d(TG4T) and stabilized by sodium cations was determined by x-ray crystallography to 1.2 angstroms resolution. Sharply resolved sodium cations were found between and within planes of hydrogen-bonded guanine quartets, and an ordered groove hydration was observed. Distinct intra- and intermolecular stacking arrangements were adopted by the guanine quartets. Thymine bases were exclusively involved in making extensive lattice contacts.