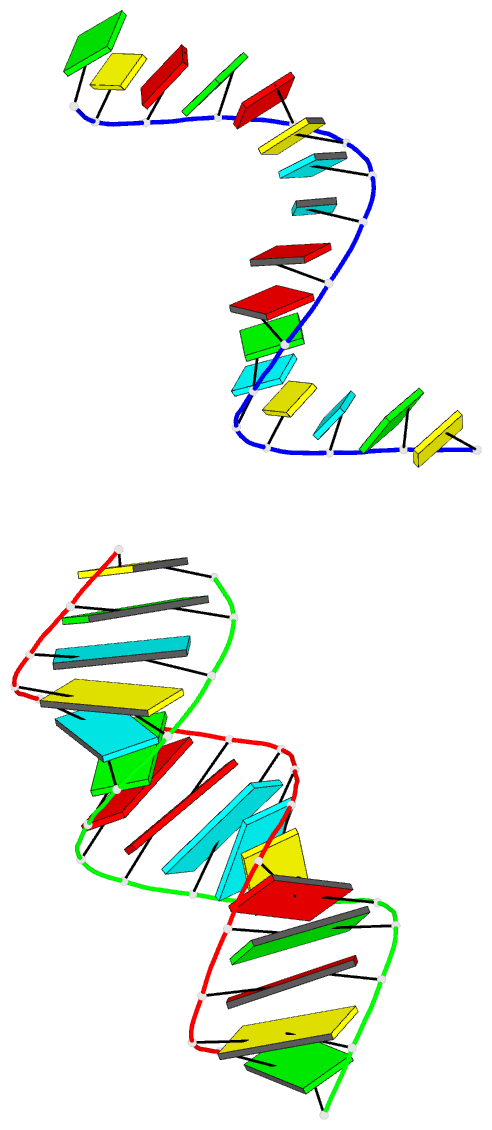
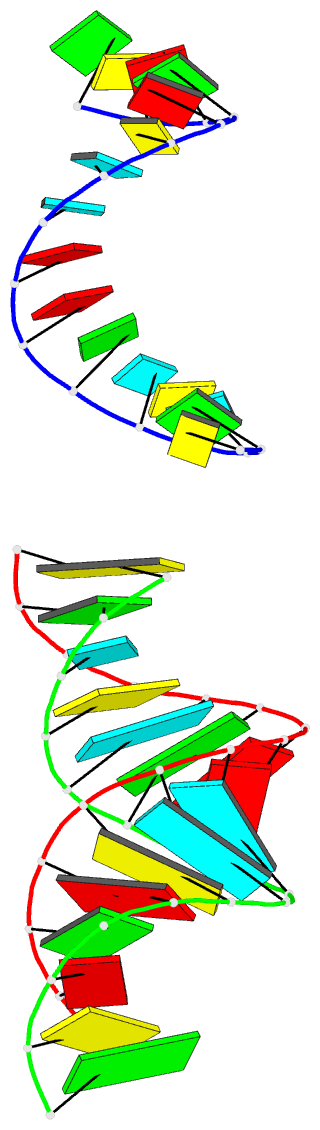
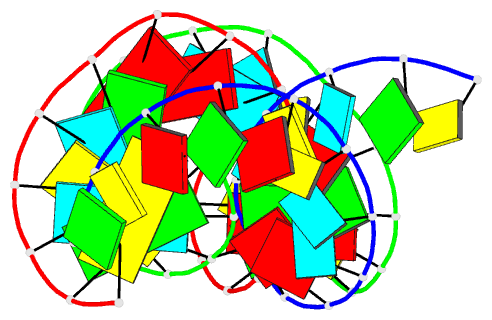
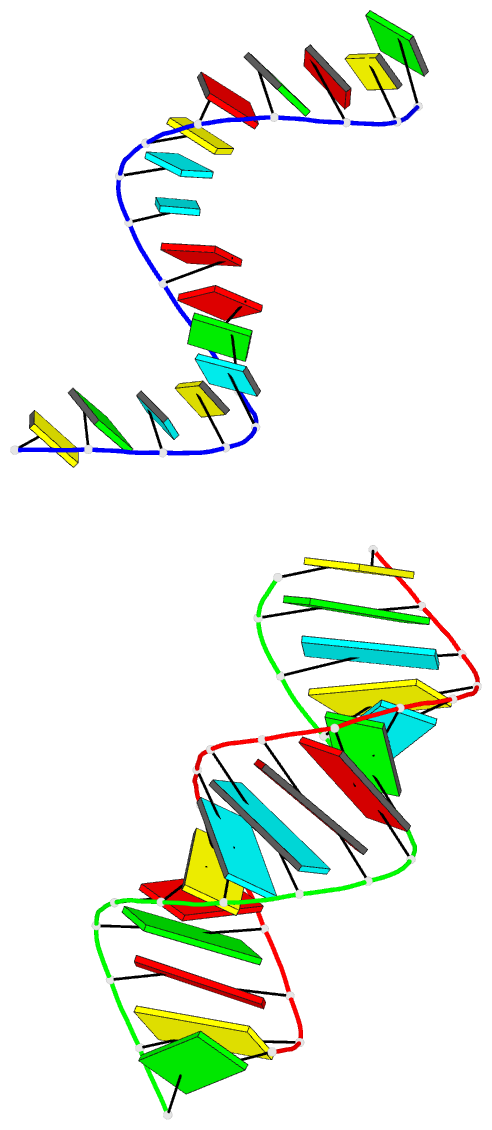
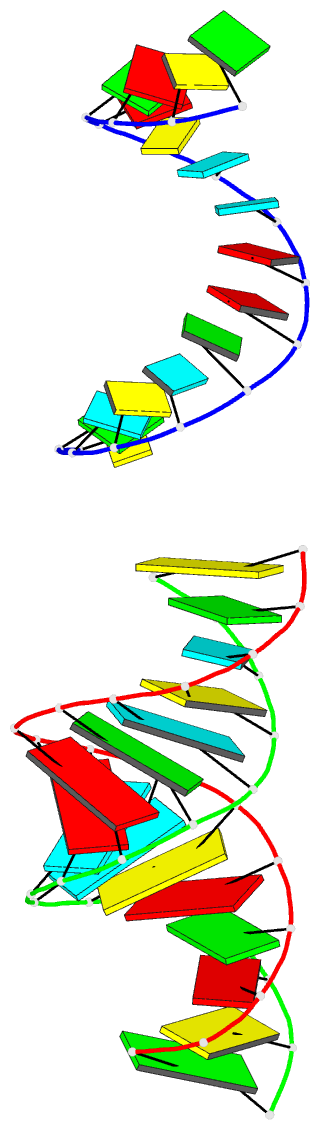
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1yzd; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.35 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of an RNA duplex containing a site specific 2'-amine substitution at a c-g watson-crick base pair
- Reference
- Gherghe CM, Krahn JM, Weeks KM (2005): "Crystal structures, reactivity and inferred acylation transition States for 2'-amine substituted RNA." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 127, 13622-13628. doi: 10.1021/ja053647y.
- Abstract
- Ribose 2'-amine substitutions are broadly useful as structural probes in nucleic acids. In addition, structure-selective chemical reaction at 2'-amine groups is a robust technology for interrogating local nucleotide flexibility and conformational changes in RNA and DNA. We analyzed crystal structures for several RNA duplexes containing 2'-amino cytidine (C(N)) residues that form either C(N)-G base pairs or C(N)-A mismatches. The 2'-amine substitution is readily accommodated in an A-form RNA helix and thus differs from the C2'-endo conformation observed for free nucleosides. The 2'-amide product structure was visualized directly by acylating a C(N)-A mismatch in intact crystals and is also compatible with A-form geometry. To visualize conformations able to facilitate formation of the amide-forming transition state, in which the amine nucleophile carries a positive partial charge, we analyzed crystals of the C(N)-A duplex at pH 5, where the 2'-amine is protonated. The protonated amine moves to form a strong electrostatic interaction with the 3'-phosphodiester. Taken together with solution-phase experiments, 2'-amine acylation is likely facilitated by either of two transition states, both involving precise positioning of the adjacent 3'-phosphodiester group.