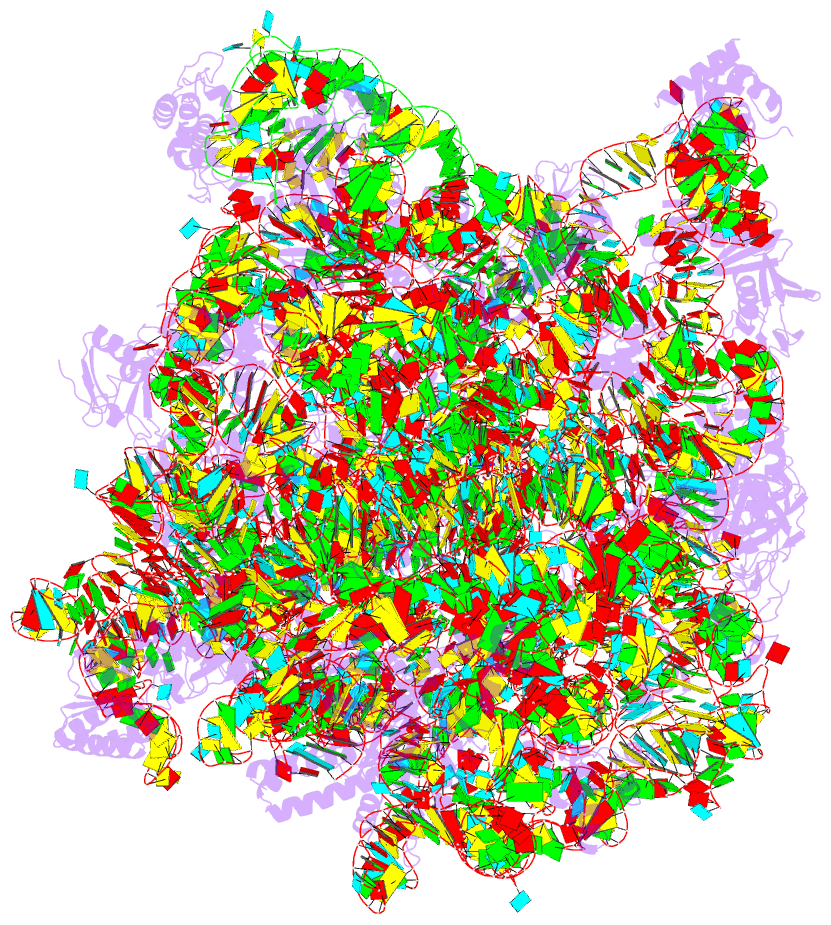
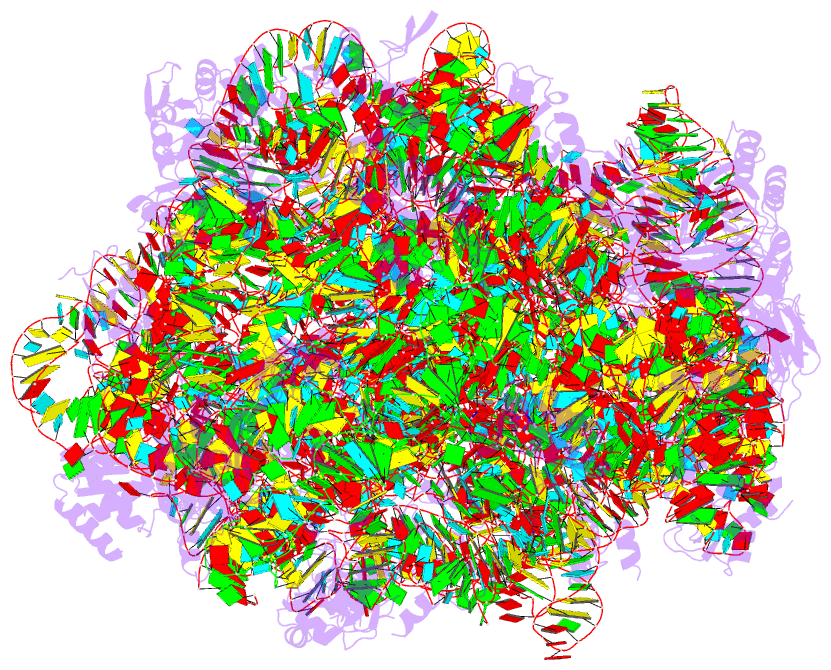
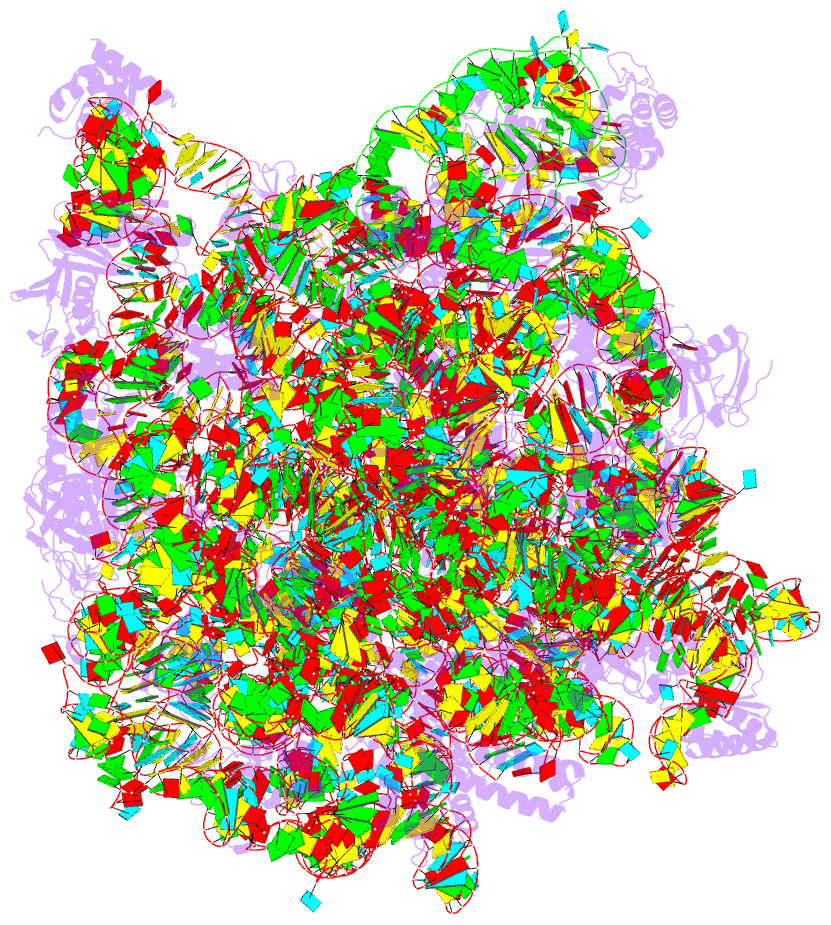
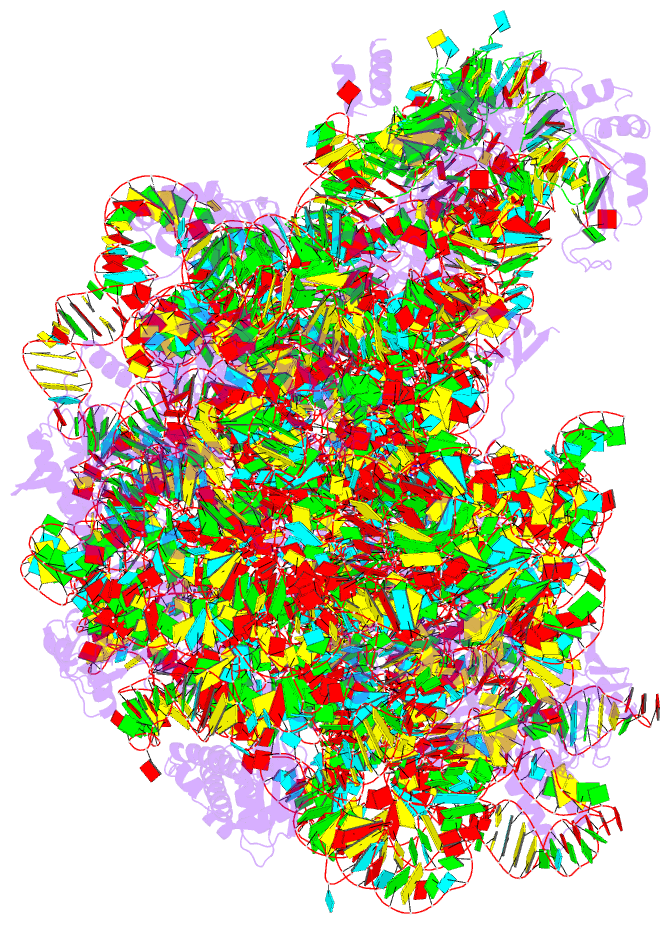
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1vqm; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- X-ray (2.3 Å)
- Summary
- The structure of the transition state analogue "dan" bound to the large ribosomal subunit of haloarcula marismortui
- Reference
- Schmeing TM, Huang KS, Kitchen DE, Strobel SA, Steitz TA (2005): "Structural Insights into the Roles of Water and the 2' Hydroxyl of the P Site tRNA in the Peptidyl Transferase Reaction." Mol.Cell, 20, 437-448. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.09.006.
- Abstract
- Peptide bond formation is catalyzed at the peptidyl transferase center (PTC) of the large ribosomal subunit. Crystal structures of the large ribosomal subunit of Haloarcula marismortui (Hma) complexed with several analogs that represent either the substrates or the transition state intermediate of the peptidyl transferase reaction show that this reaction proceeds through a tetrahedral intermediate with S chirality. The oxyanion of the tetrahedral intermediate interacts with a water molecule that is positioned by nucleotides A2637 (E. coli numbering, 2602) and (methyl)U2619(2584). There are no Mg2+ ions or monovalent metal ions observed in the PTC that could directly promote catalysis. The A76 2' hydroxyl of the peptidyl-tRNA is hydrogen bonded to the alpha-amino group and could facilitate peptide bond formation by substrate positioning and by acting as a proton shuttle between the alpha-amino group and the A76 3' hydroxyl of the peptidyl-tRNA.