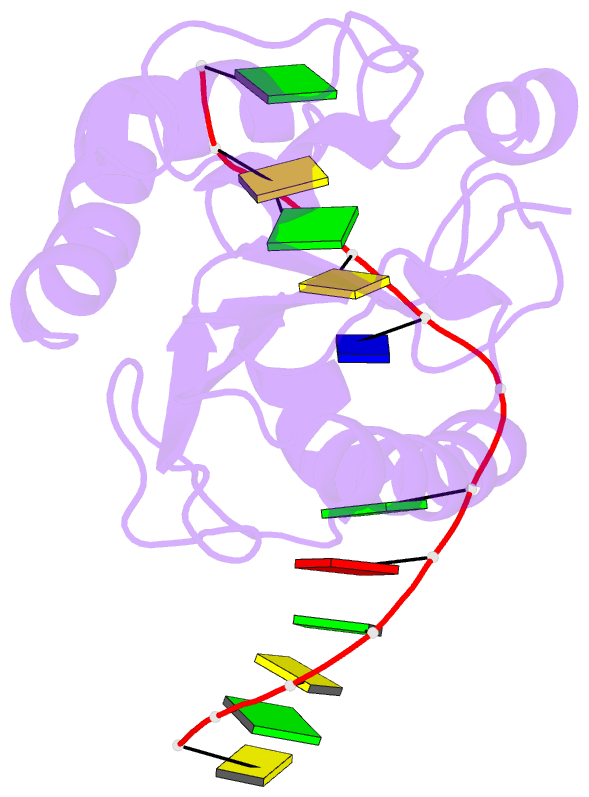
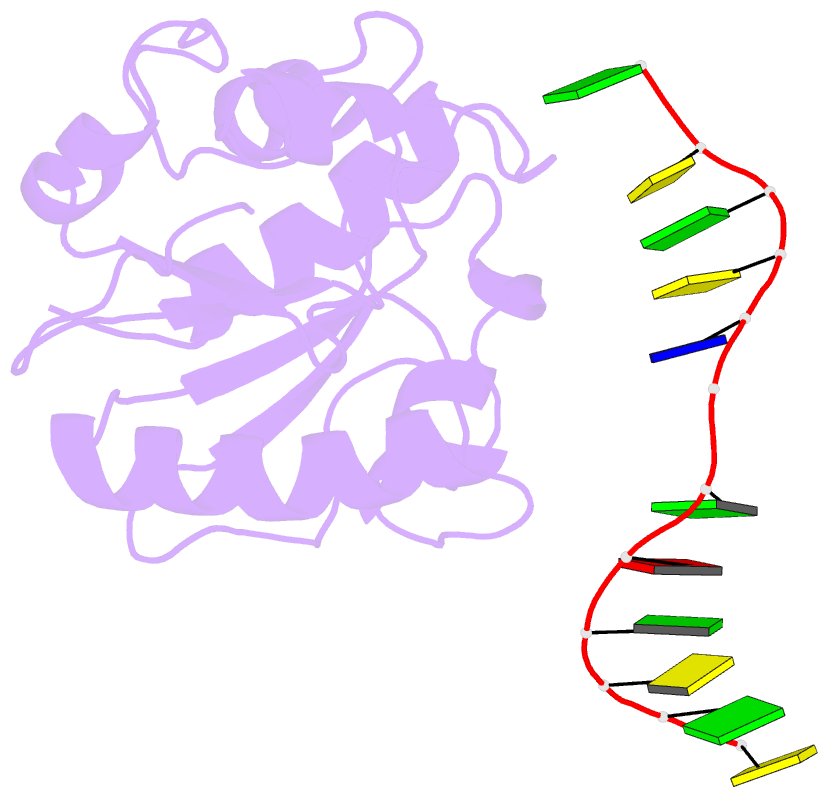
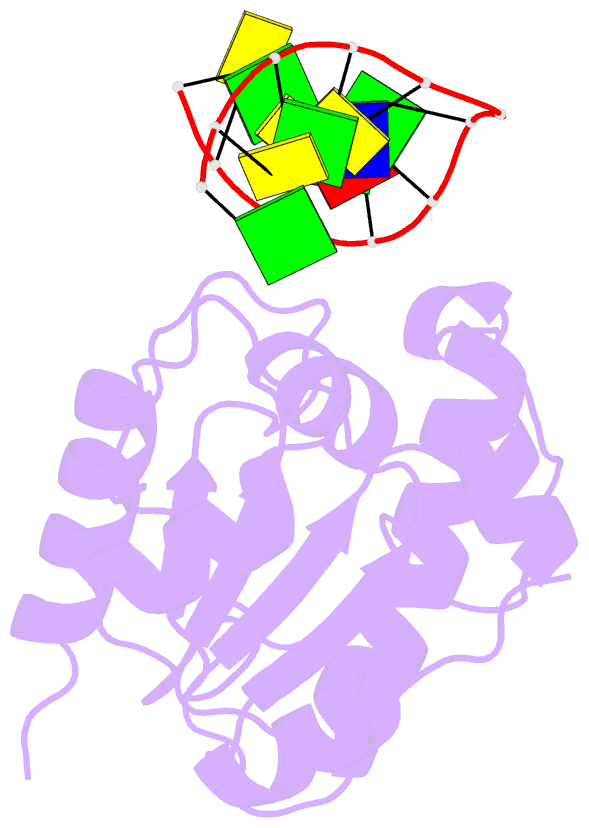
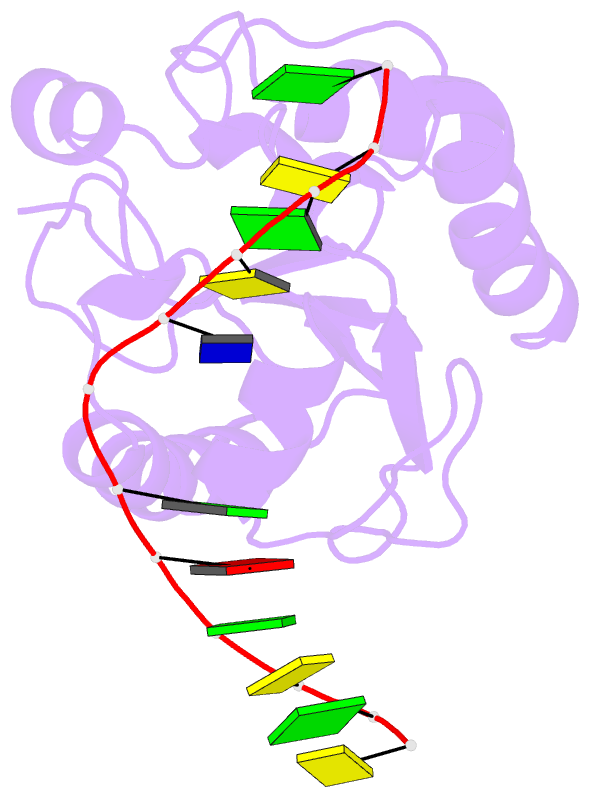
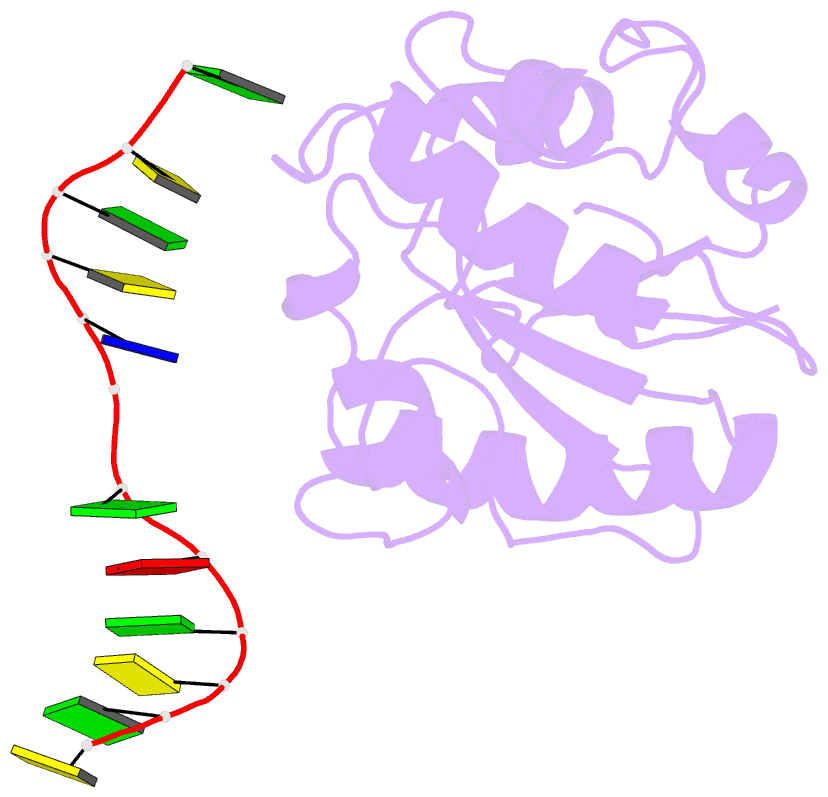
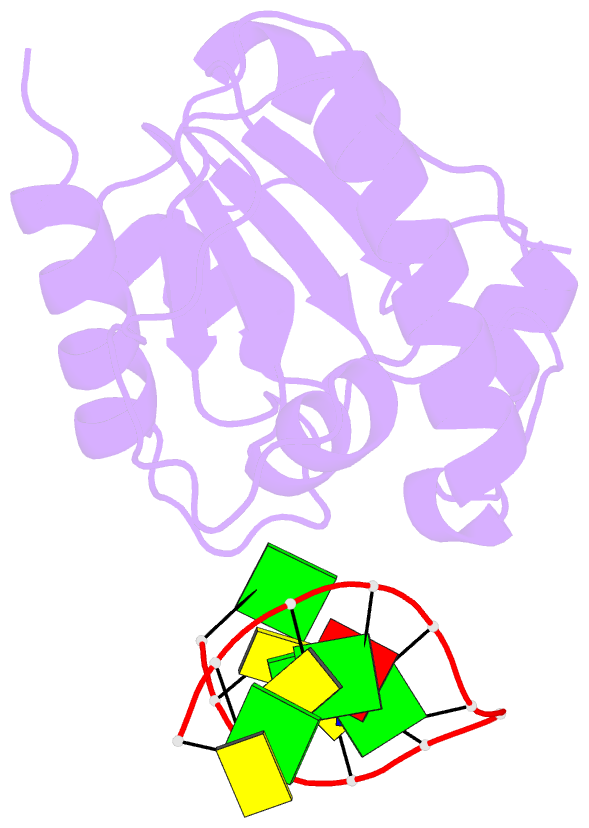
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1mwi; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.35 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of a mug-DNA product complex
- Reference
- Barrett TE, Savva R, Panayotou G, Barlow T, Brown T, Jiricny J, Pearl LH (1998): "Crystal structure of a G:T/U mismatch-specific DNA glycosylase: mismatch recognition by complementary-strand interactions." Cell(Cambridge,Mass.), 92, 117-129. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80904-6.
- Abstract
- G:U mismatches resulting from deamination of cytosine are the most common promutagenic lesions occurring in DNA. Uracil is removed in a base-excision repair pathway by uracil DNA-glycosylase (UDG), which excises uracil from both single- and double-stranded DNA. Recently, a biochemically distinct family of DNA repair enzymes has been identified, which excises both uracil and thymine, but only from mispairs with guanine. Crystal structures of the mismatch-specific uracil DNA-glycosylase (MUG) from E. coli, and of a DNA complex, reveal a remarkable structural and functional homology to UDGs despite low sequence identity. Details of the MUG structure explain its thymine DNA-glycosylase activity and the specificity for G:U/T mispairs, which derives from direct recognition of guanine on the complementary strand.