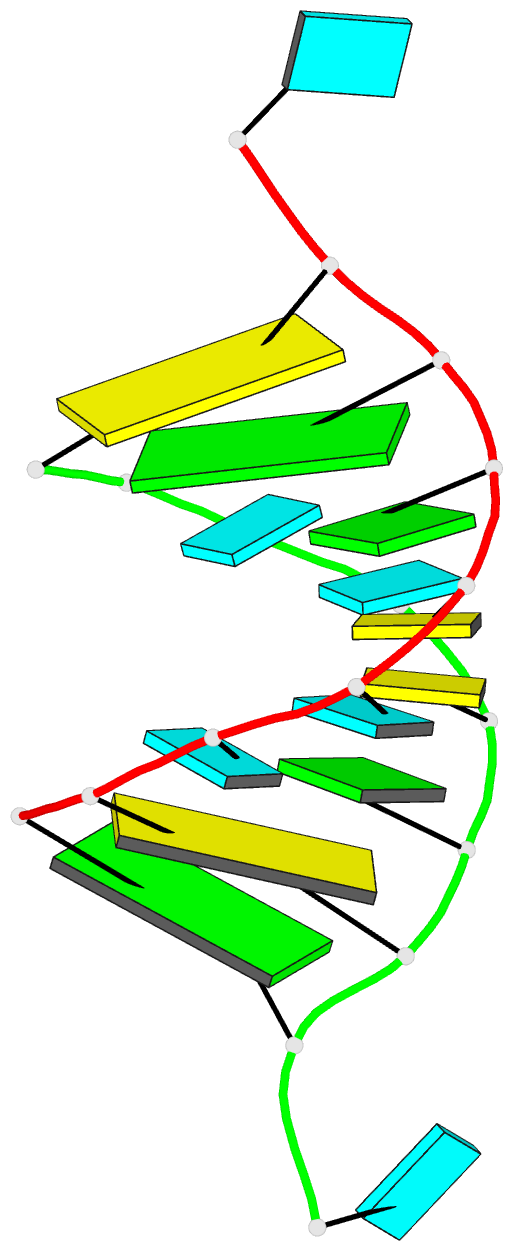
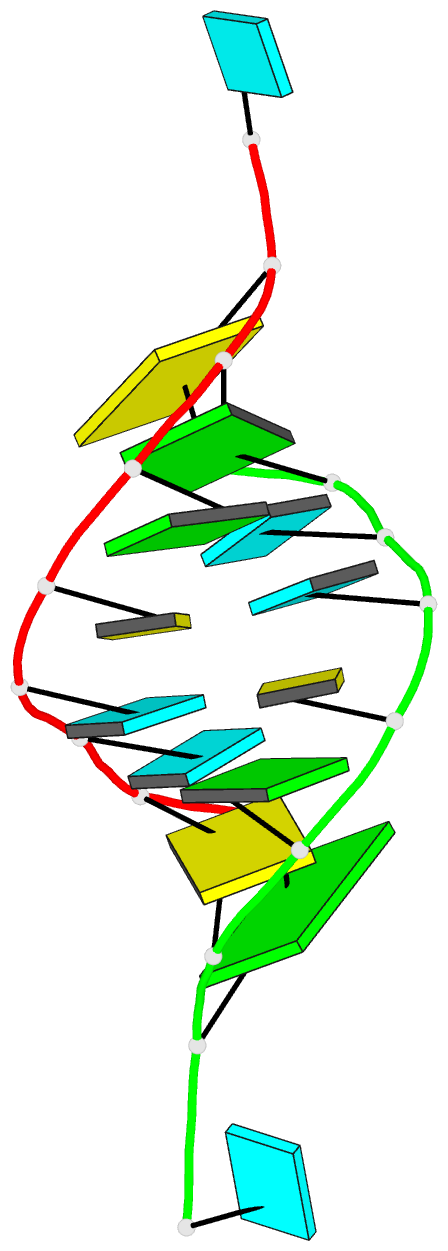
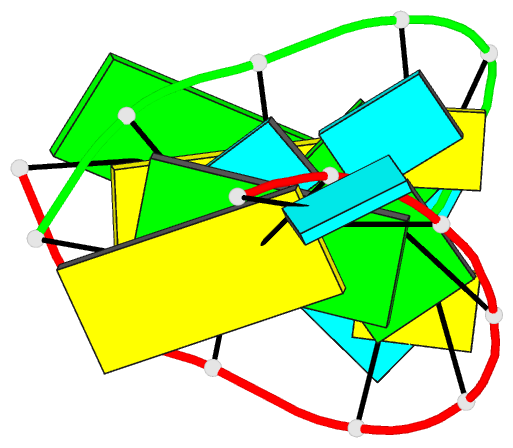
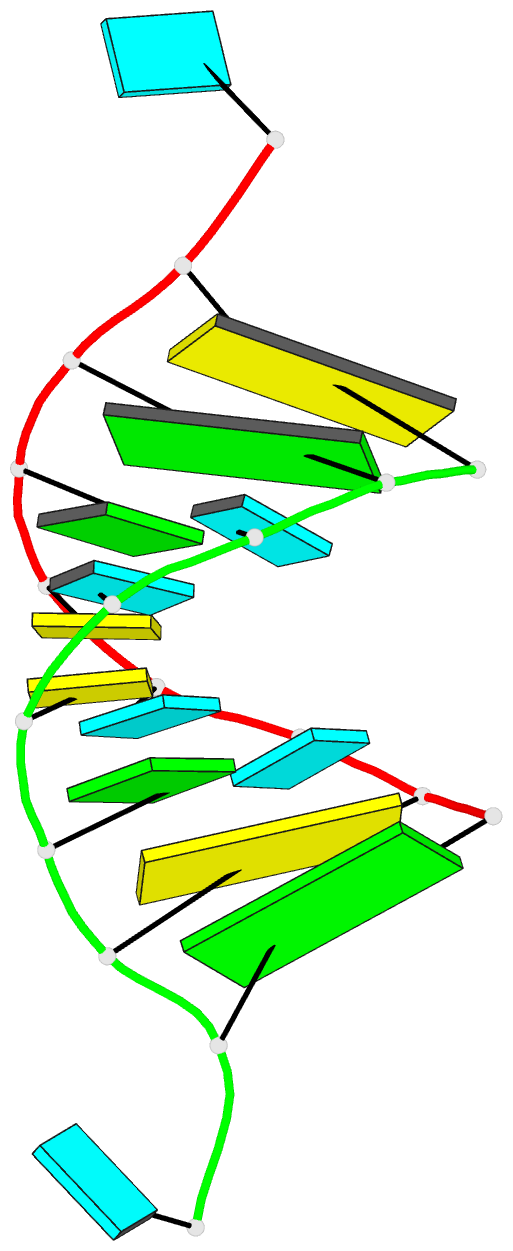
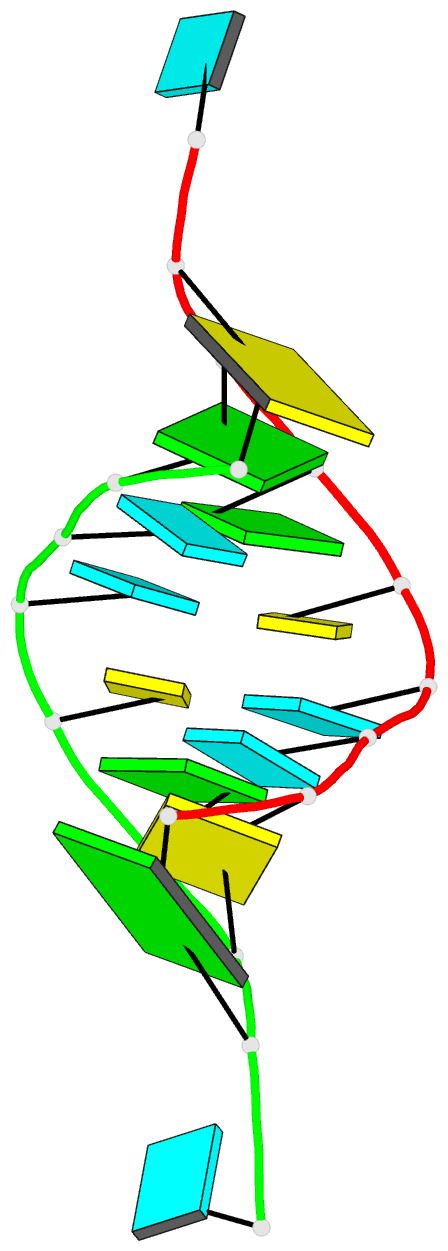
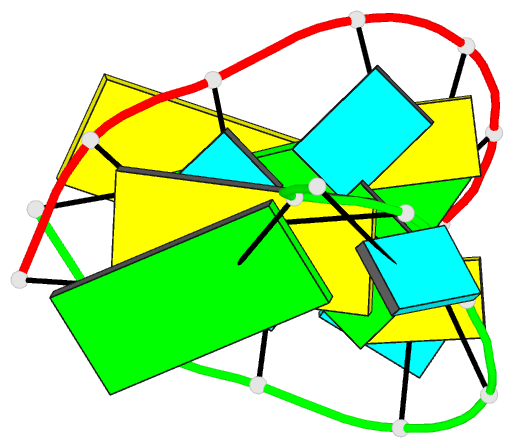
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 1id9; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- DNA-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.6 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of the hybrid RNA-DNA r-gcuucggc-d[f]u in presence of rh(nh3)6+++
- Reference
- Cruse W, Saludjian P, Neuman A, Prange T (2001): "Destabilizing effect of a fluorouracil extra base in a hybrid RNA duplex compared with bromo and chloro analogues." Acta Crystallogr.,Sect.D, 57, 1609-1613. doi: 10.1107/S0907444901012318.
- Abstract
- In the presence of cobalt, rhodium or iridium hexammine salts, the RNA/DNA hybrid r-GCUUCGGC-d(X)U (with X = F, Cl or Br) crystallizes as a double-stranded helix with four consecutive G-U and C-U mismatches. The deoxy chloro- and bromouracil derivatives are isomorphous, space group C2, unit-cell parameters a = 53.80, b = 19.40, c = 50.31 A, beta = 109.9 degrees, with the same infinite helix arrangement in the packing along the c axis with one extra DNA halogenouracil base included in the stacking. However, the fluorouracil derivative, with unit-cell parameters a = 53.75, b = 19.40, c = 45.84 A, beta = 105.7 degrees, is not isomorphous. The corresponding extra DNA base d(F)U of the second strand is ejected out of the helical stack, leading to a shortening of the c axis. The specific destabilization of the fluorouracil for the duplex building is analyzed in terms of the polarization effect of the halogen atom attached to the 3'-terminal base that modulates its interactions.