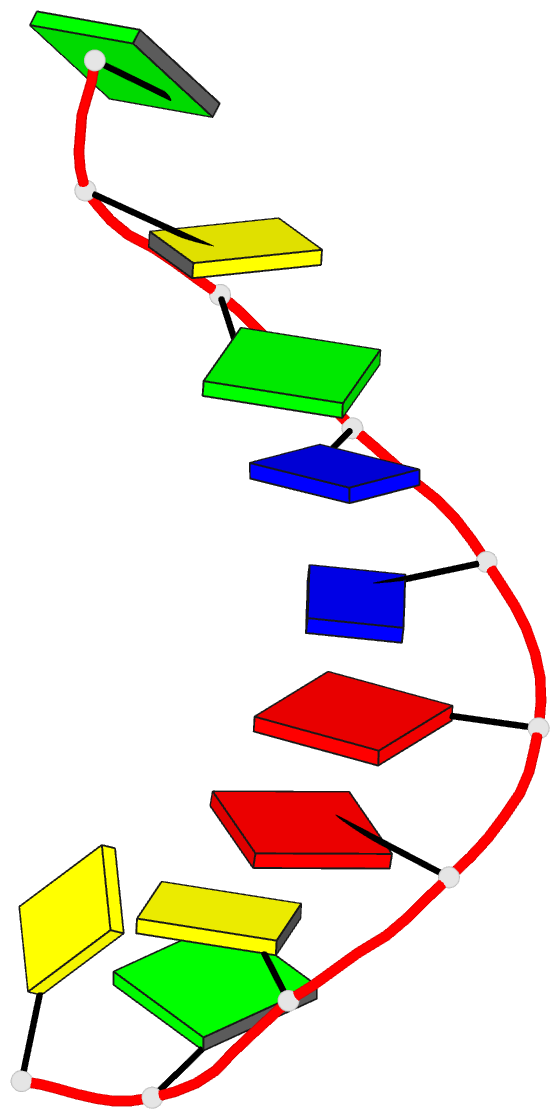
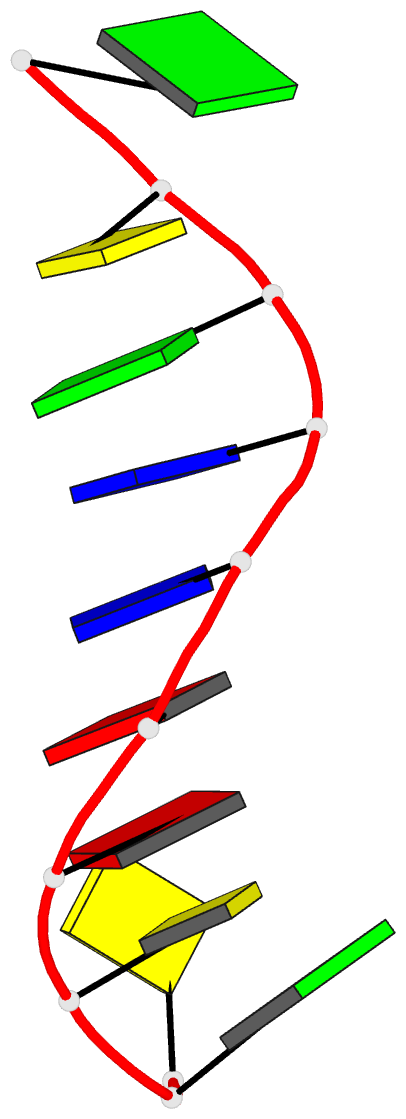
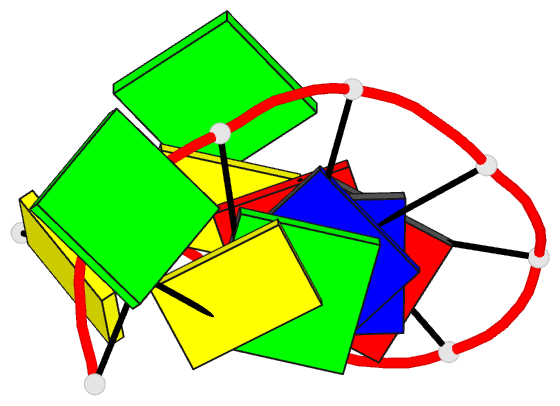
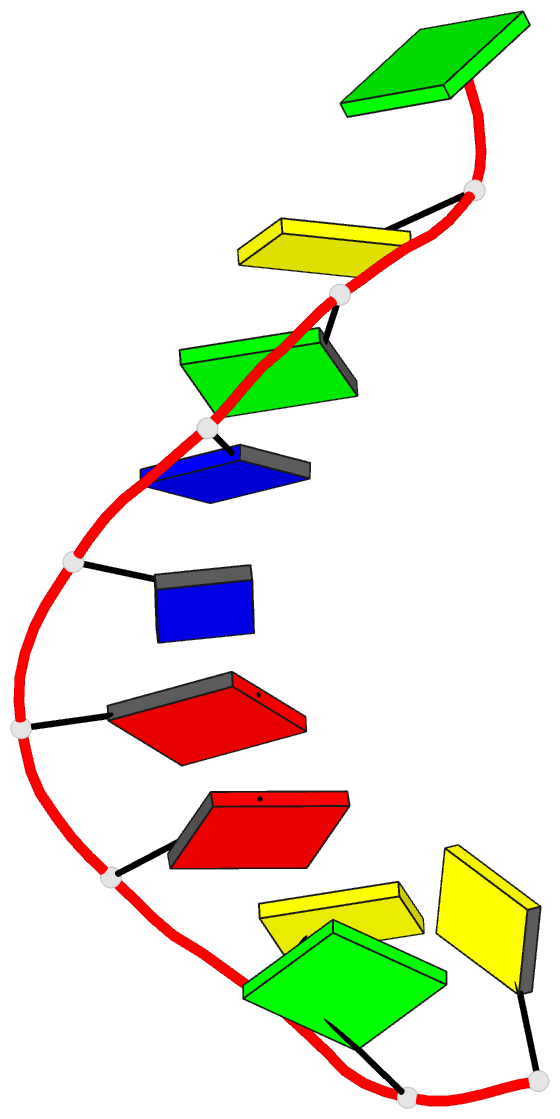
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
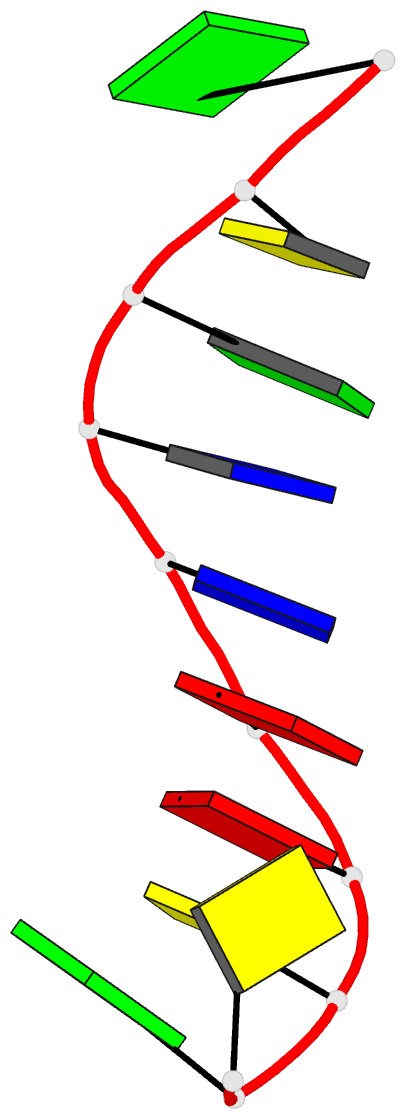
- 1g6d; DSSR-derived features in text and JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.9 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of peptidyl-d(cgcaattgcg) in the presence of zinc ions
- Reference
- Soler-Lopez M, Malinina L, Tereshko V, Zarytova V, Subirana JA (2002): "Interaction of zinc ions with d(CGCAATTGCG) in a 2.9 A resolution X-ray structure." J.Biol.Inorg.Chem., 7, 533-538. doi: 10.1007/s00775-001-0333-z.
- Abstract
- We have synthesized and crystallized in the presence of Zn(2+) ions the peptidyl-oligonucleotide adduct CH(3)CO-(Arg)(4)-NH-(CH(2))(6)-NH-p-d(CGCAATTGCG). This is the first structure obtained from a deoxyoligonucleotide crystallized in the presence of zinc ions. Zn ions are clearly visible in the 2.9 A resolution map. On the other hand, the peptide tail is not visible in the crystal structure as determined by X-ray diffraction. The terminal bases C1 and G10 are found in extra-helical positions. Their phosphates are ligands of a Zn(2+) ion, located in a special position of the unit cell. This ion plays an important role in the packing arrangement, since it binds four different DNA molecules. Two other Zn(2+) ions are also important for DNA packing. They interact specifically with the N7 atoms of the terminal G2 and G10 bases, but not with the internal G8. This result supports the hypothesis that transition metals do not interact with the bases of duplex DNA in the B form.