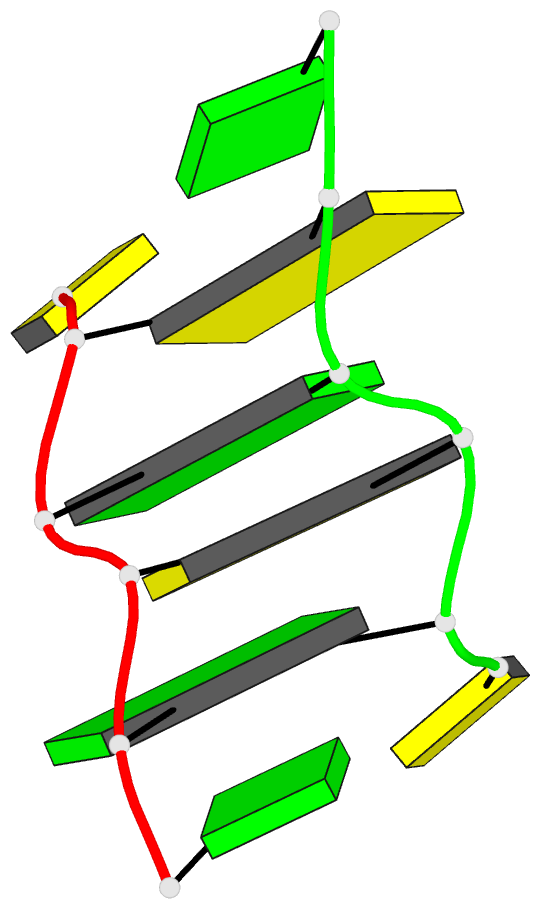
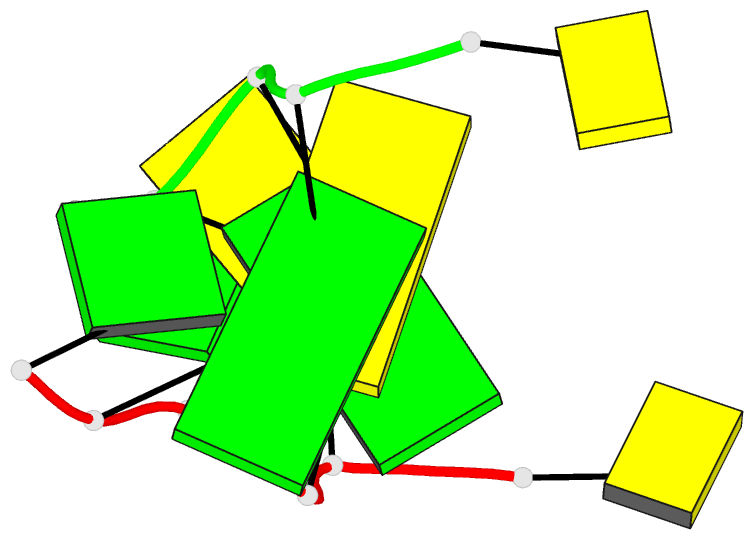
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
192d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.92 Å)
- Summary
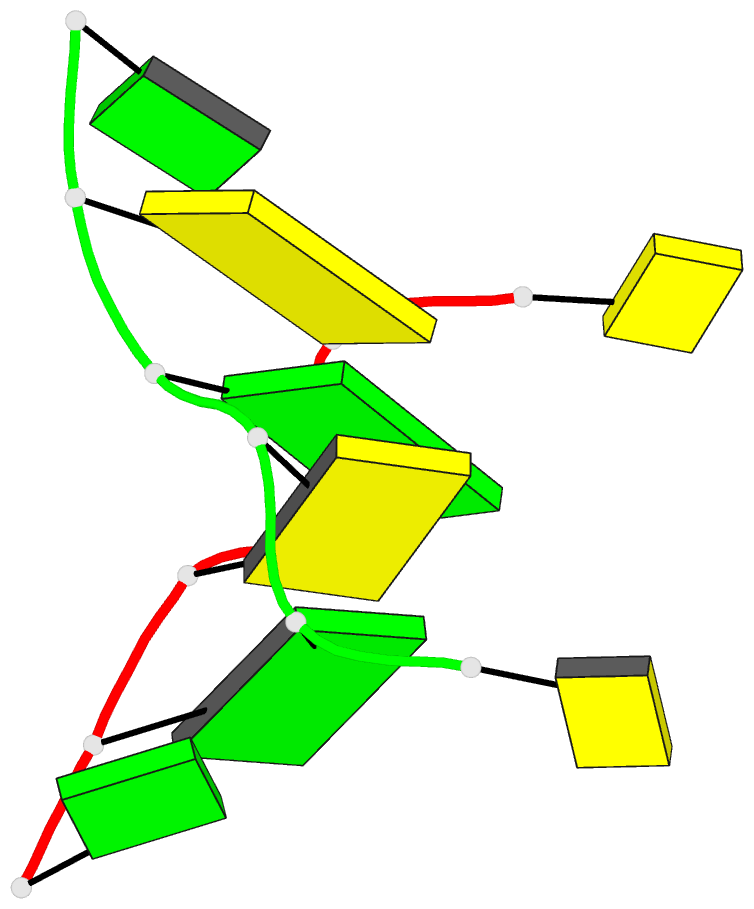
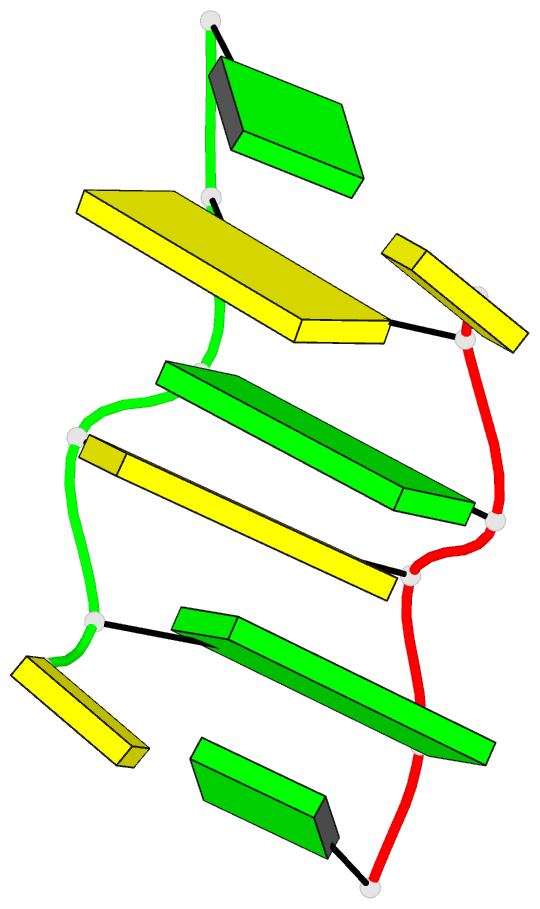
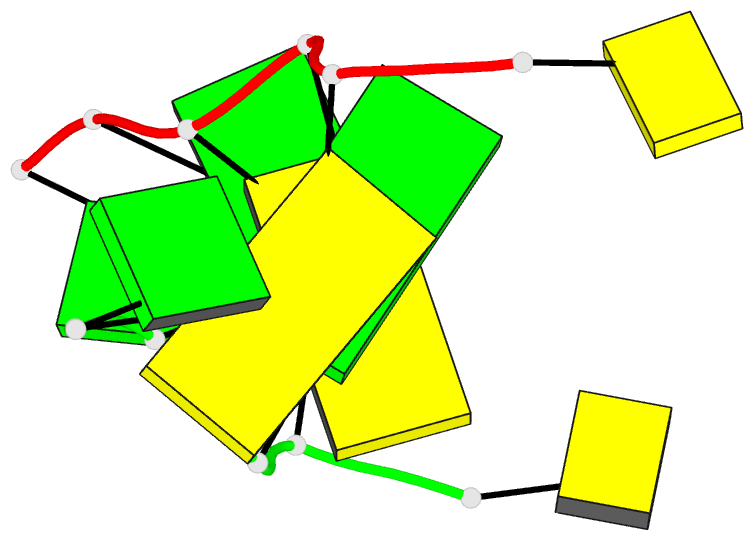
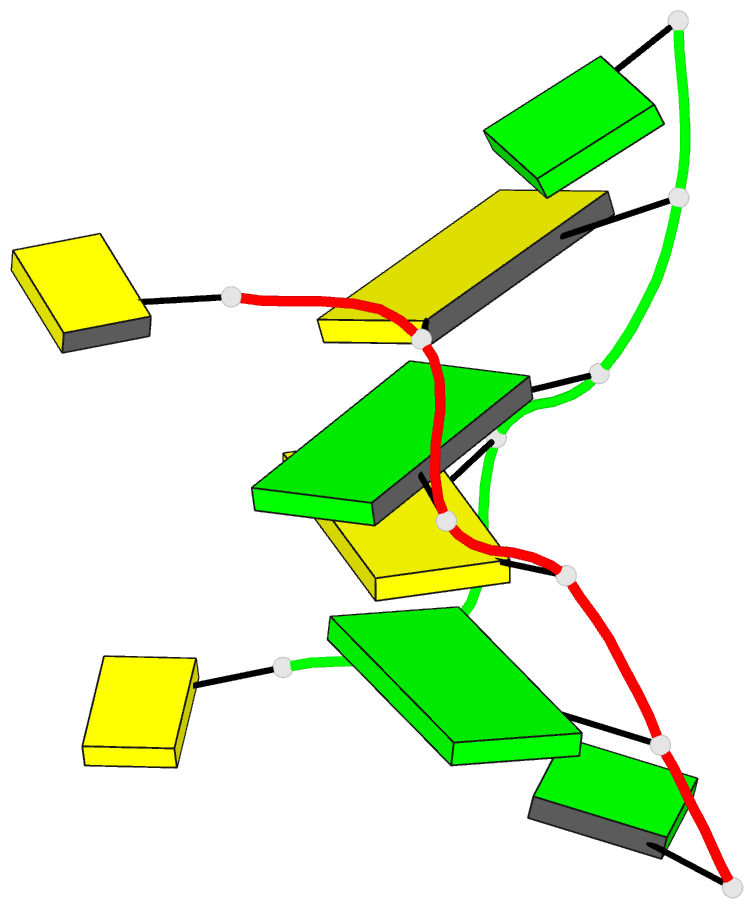
- Recombination-like structure of d(ccgcgg)
- Reference
-
Malinina L, Urpi L, Salas X, Huynh-Dinh T, Subirana JA
(1994): "Recombination-like
structure of d(CCGCGG)." J.Mol.Biol.,
243, 484-493. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1674.
- Abstract
- We have solved the single crystal X-ray structure of
the synthetic DNA hexamer d(CCGCGG). The central
alternating tetramer forms a Z-DNA duplex. The initial
cytosine of each strand of the duplex swings out and forms
a Watson-Crick base-pair with the terminal guanine of a
symmetry-related molecule. Thus, two symmetry-related DNA
molecules form a twin with intermolecular base-pairs at
both ends. Such a twin is additionally stabilized by a
sodium ion located on a dyad axis between two DNA duplexes.
The total structure has recombination-like features. It
also provides a model for B/Z junctions. The crystal used
in this study belongs to space group C222(1) with a = 34.33
A, b = 44.04 A and c = 38.27 A. The structure was solved by
molecular replacement using partial models, and refined by
molecular dynamics simulated annealing and positional
treatment. The refinement has been concluded with an
R-factor of 18.5% for 2377 reflections with F > or = 2
sigma (F) in the resolution region 8.0 to 1.92 A. The
asymmetric unit contains two strands of d(CCGCGG) and 38
water molecules.