Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
185d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA-antibiotic
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
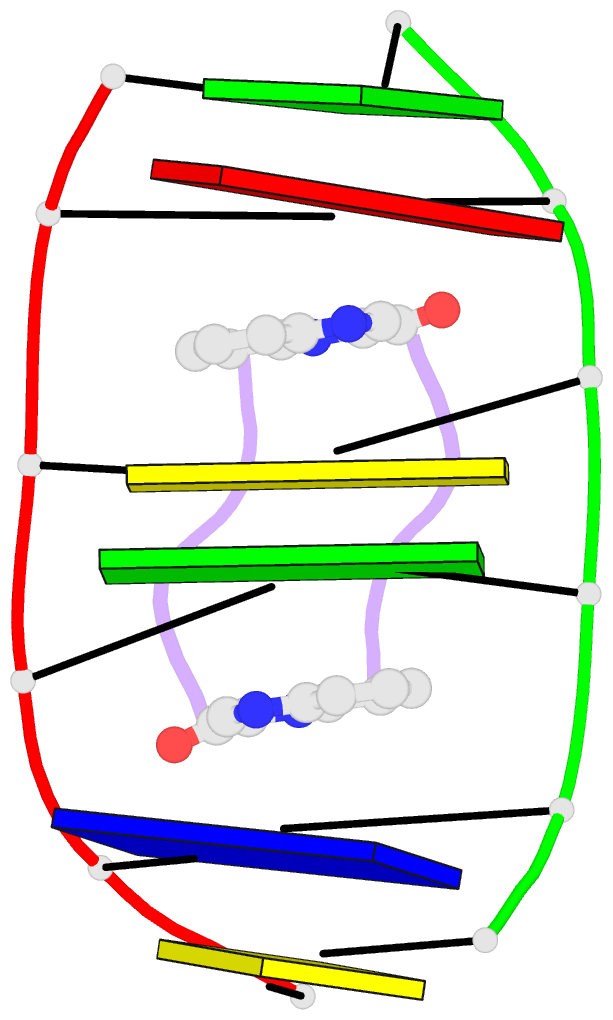
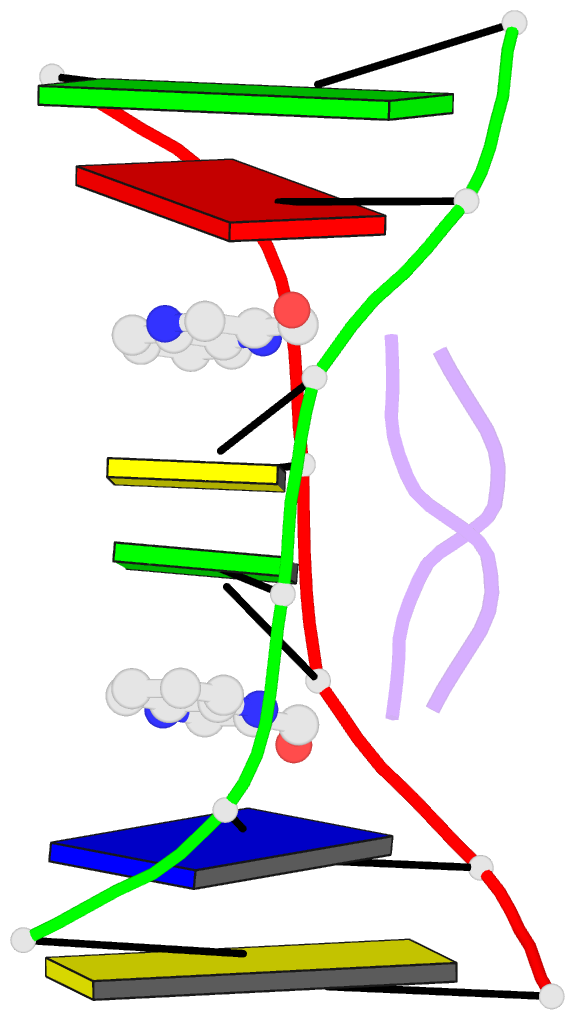
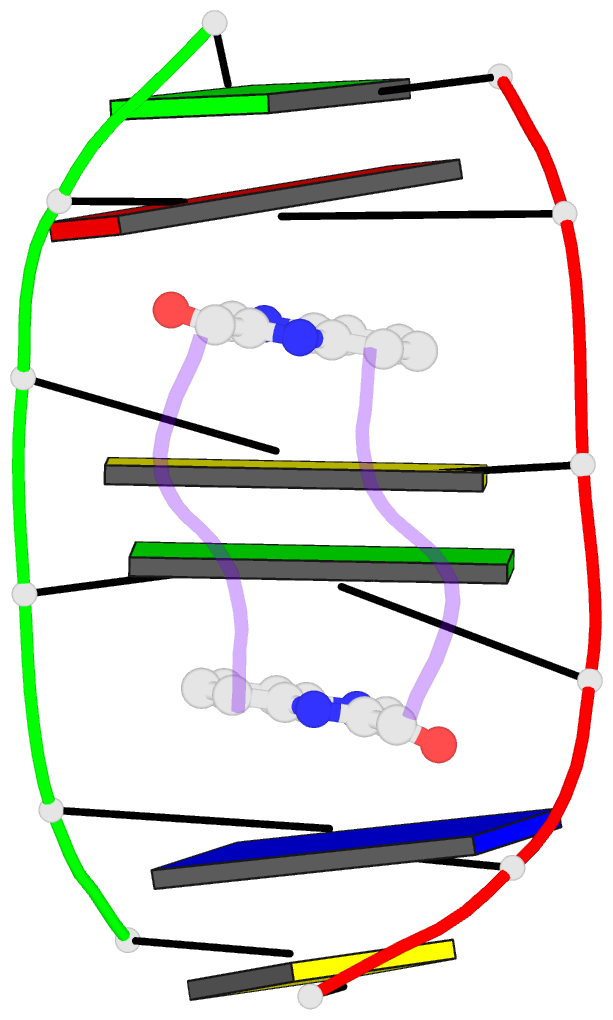
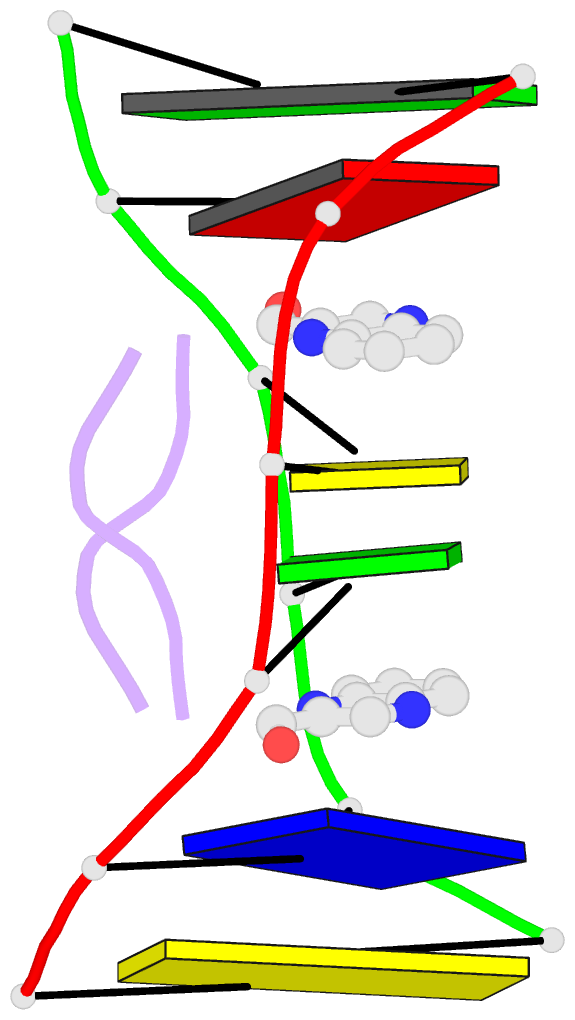
- Sequence specificity of quinoxaline antibiotics. 1.
solution structure of a 1:1 complex between triostin a and
[d(gacgtc)]2 and comparison with the solution structure of
the [n-mecys3, n-mecys7]tandem-[d(gatatc)]2 complex
- Reference
-
Addess KJ, Feigon J (1994): "Sequence
Specificity of Quinoxaline Antibiotics. 1. Solution
Structure of a 1:1 Complex between Triostin a and
[D(Gacgtc)]2 and Comparison with the Solution Structure
of the [N-Mecys3,N-Mecys7]Tandem-[D(Gatatc)]2
Complex." Biochemistry, 33,
12386. doi: 10.1021/BI00207A005.
- Abstract
- Triostin A, a naturally occurring quinoxaline
antibiotic that contains N-methyl groups on the valine and
cysteine residues, binds sequence specifically to DNA at
NCGN sites. [N-MeCys3,N-MeCys7]-TANDEM (CysMeTANDEM), a
synthetic quinoxaline antibiotic, differs in its chemical
structure from triostin A only at the valine residues,
which contain no N-methyl substituents. CysMeTANDEM has a
sequence specificity different from triostin A, binding
specifically to DNA at NTAN sites. To understand the
factors that determine the sequence specificity of these
quinoxaline antibiotics, the solution structure of a 1:1
complex of triostin A with the DNA hexamer [d(GACGTC)]2 has
been determined using NMR-derived distance and dihedral
angle restraints. The solution structure of the triostin
A-[d(GACGTC)]2 complex is compared directly to the solution
structure of a 1:1 complex of CysMeTANDEM with [d(GATATC)]2
and is also compared to the crystal structure of 2:1
complex of triostin A with [d(CGTACG)]2. Triostin A binds
to [d(GACGTC)]2 as a bis-intercalator around the CpG step,
and the peptide ring of the drug binds in the minor groove
of the DNA. The central C.G base pairs of the complex are
underwound with an average helical twist angle of
approximately -9.0 degrees and buckle inward by about 25
degrees. There are intermolecular hydrogen bonds between
each of the Ala NH and the GN3 protons of the CpG binding
site. Similar structural features are observed in the
solution structure of the CysMeTANDEM-[d(GATATC)]2 complex.
However, in the structure of the triostin A-[d(GACGTC)]2
complex, two intermolecular hydrogen bonds between each of
the Ala CO oxygens of the drug and the 2-amino protons of
guanine are observed. These hydrogen bonds do not form in
the CysMeTANDEM-DNA complex. Instead, CysMeTANDEM contains
two intramolecular hydrogen bonds between the Ala CO atoms
and the Val amide protons, making the Ala CO atoms
unavailable to form two intermolecular hydrogen bonds. The
role of these intermolecular hydrogen bonds in the CpG
specificity of triostin A is discussed.