Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
179d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
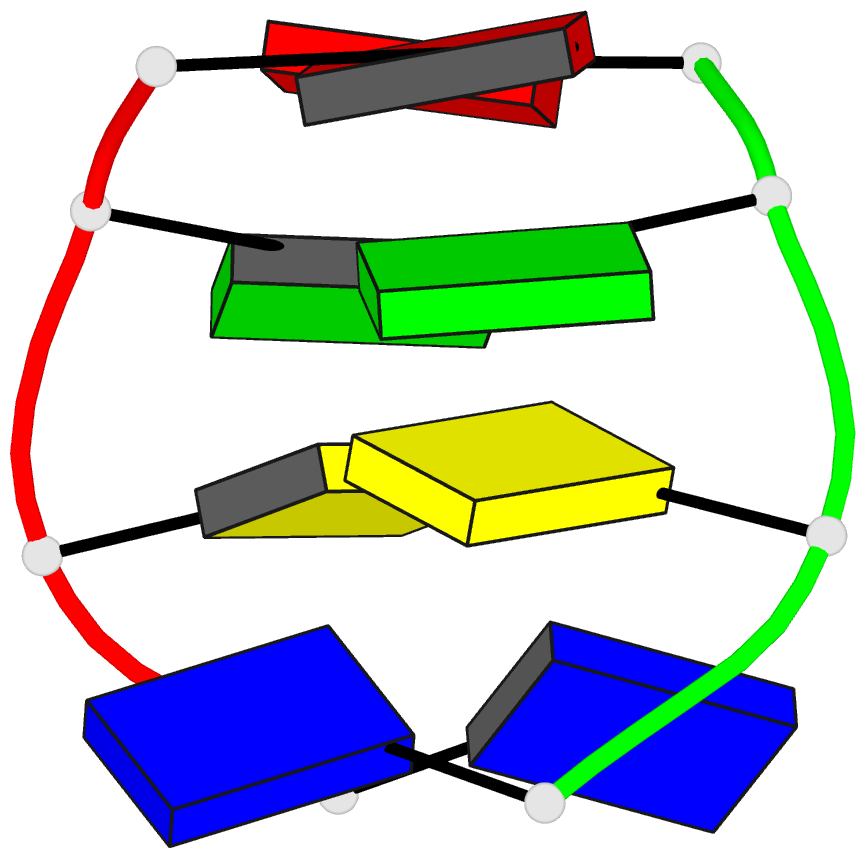
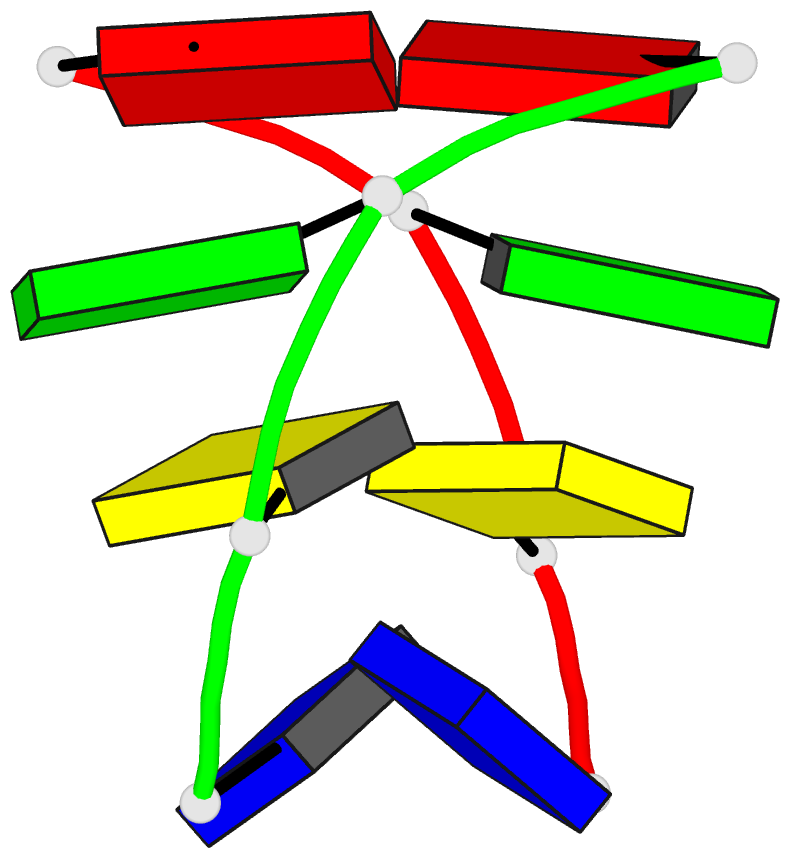
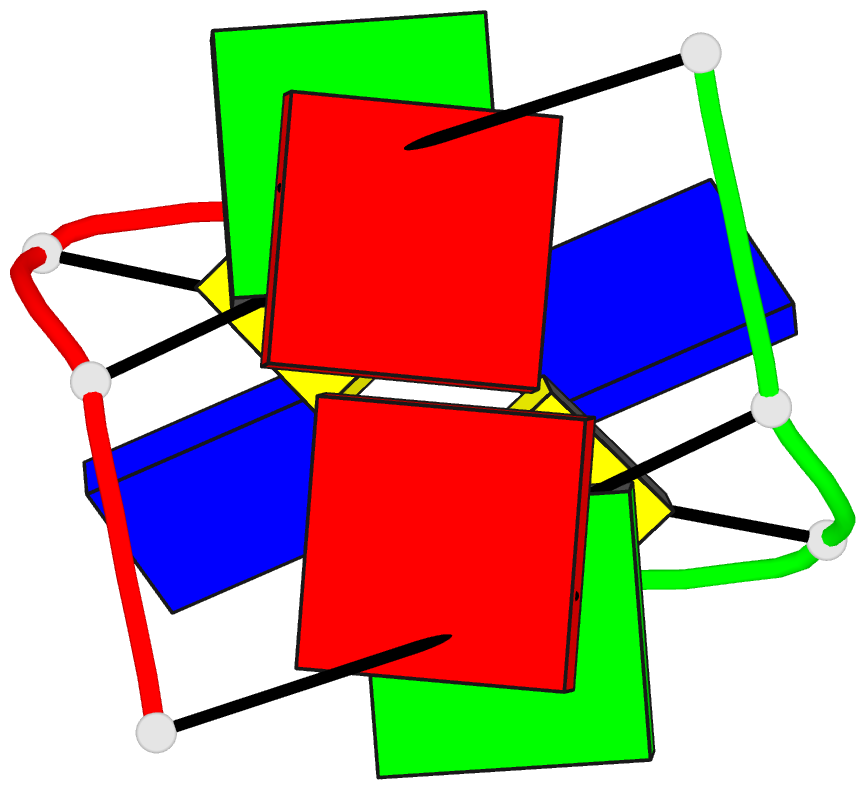
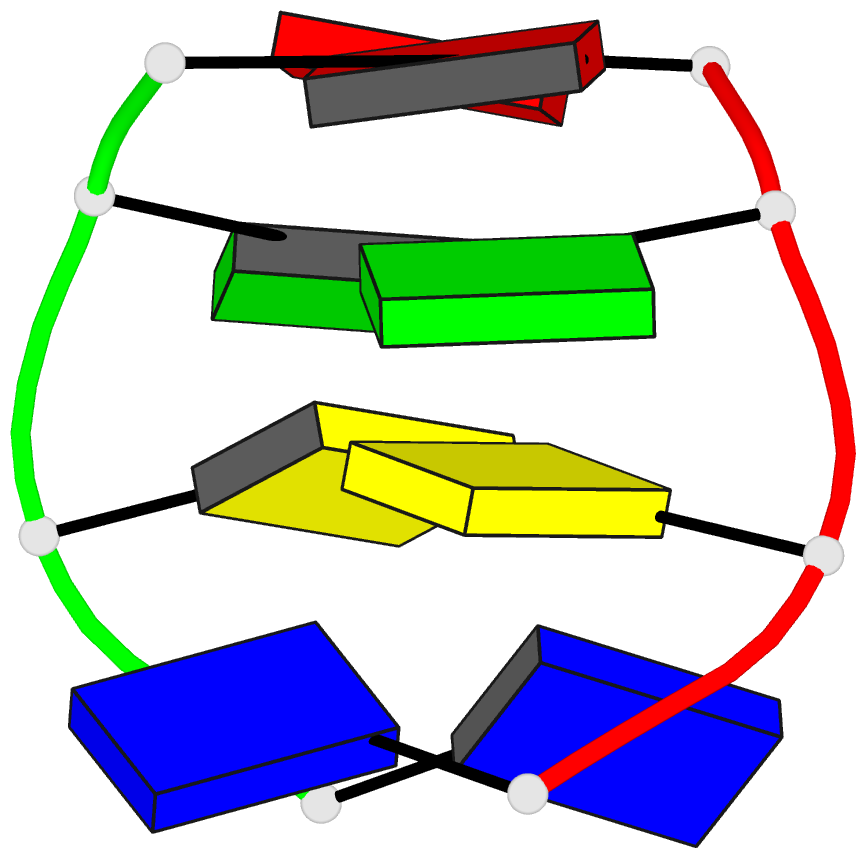
- Solution structure of the d(t-c-g-a) duplex at acidic
ph: a parallel-stranded helix containing c+.c, g.g and a.a
pairs
- Reference
-
Wang Y, Patel DJ (1994): "Solution
structure of the d(T-C-G-A) duplex at acidic pH. A
parallel-stranded helix containing C+ .C, G.G and A.A
pairs." J.Mol.Biol., 242,
508-526.
- Abstract
- The solution structure of the d(T-C-G-A) sequence at
acidic pH has been determined by a combination of NMR and
molecular dynamics calculations including NOE intensity
based refinements. This sequence forms a right-handed
parallel-stranded duplex with C+ .C (three hydrogen bonds
along Watson-Crick edge), G.G (two symmetry related N2-H..
N3 hydrogen bonds) and A.A (two symmetry related N6-H..N7
hydrogen bonds) homo base-pair formation at acidic pH. The
duplex is stabilized by intra-strand base stacking at the
C2-G3 step and cross-strand base stacking at the G3-A4
step. The thymine residues on partner strands are directed
towards each other and are positioned over the C+ .C
base-pair. All four residues adopt anti glycosidic torsion
angles and C2'-endo type sugar conformations in the
parallel-stranded d(T-C-G-A) duplex which exhibits large
changes in twist angles between adjacent steps along the
duplex. This study rules out previously proposed models for
the structure of the d(T-C-G-A) duplex at acidic pH and
supports earlier structural contributions, which
established that d(C-G) and d(C-G-A) containing sequences
at acidic pH pair through parallel-stranded alignment. We
have also monitored hydration patterns in the symmetry
related grooves of the parallel-stranded d(T-C-G-A)
duplex.