Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
156d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
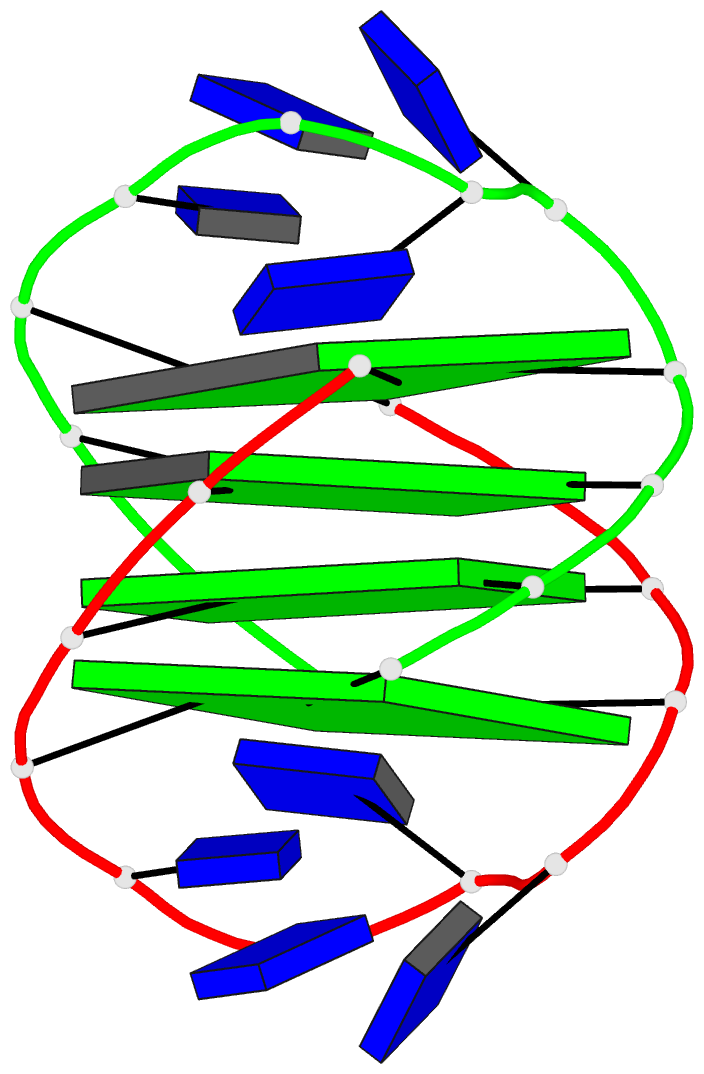
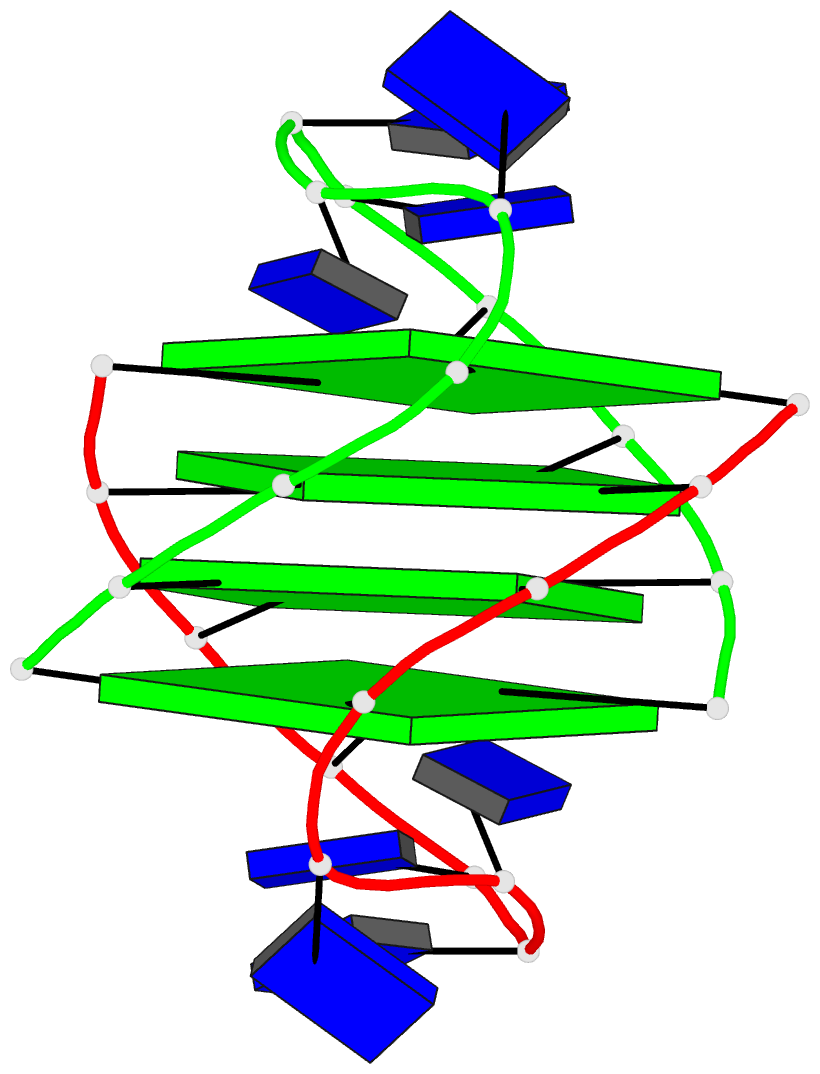
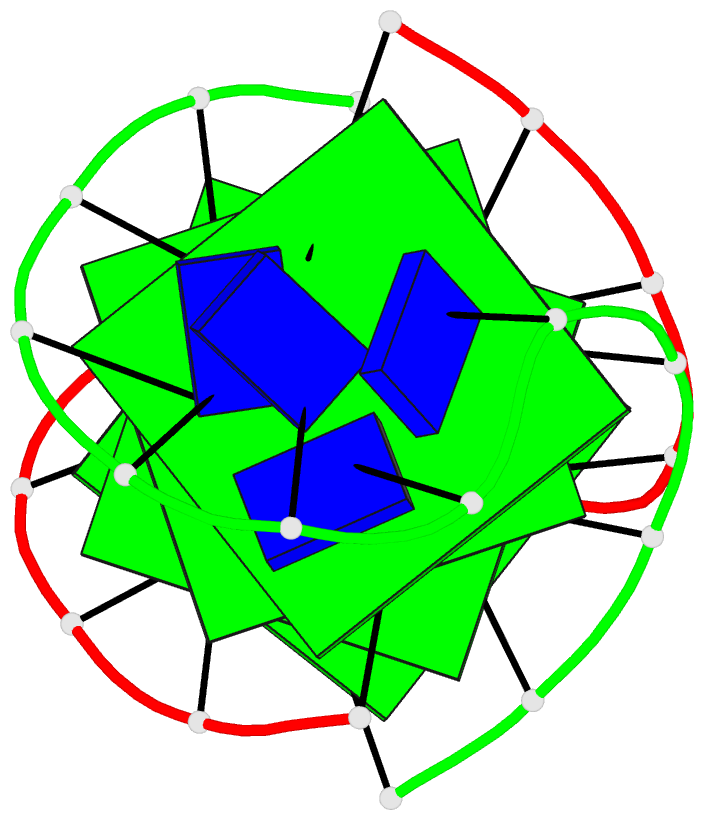
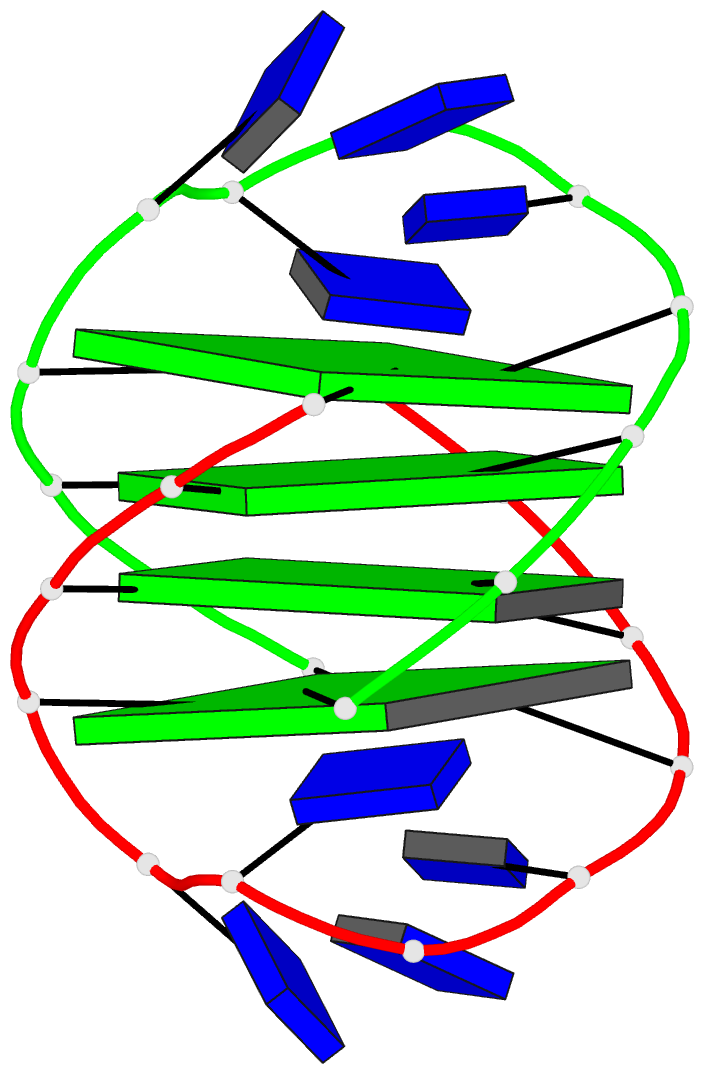
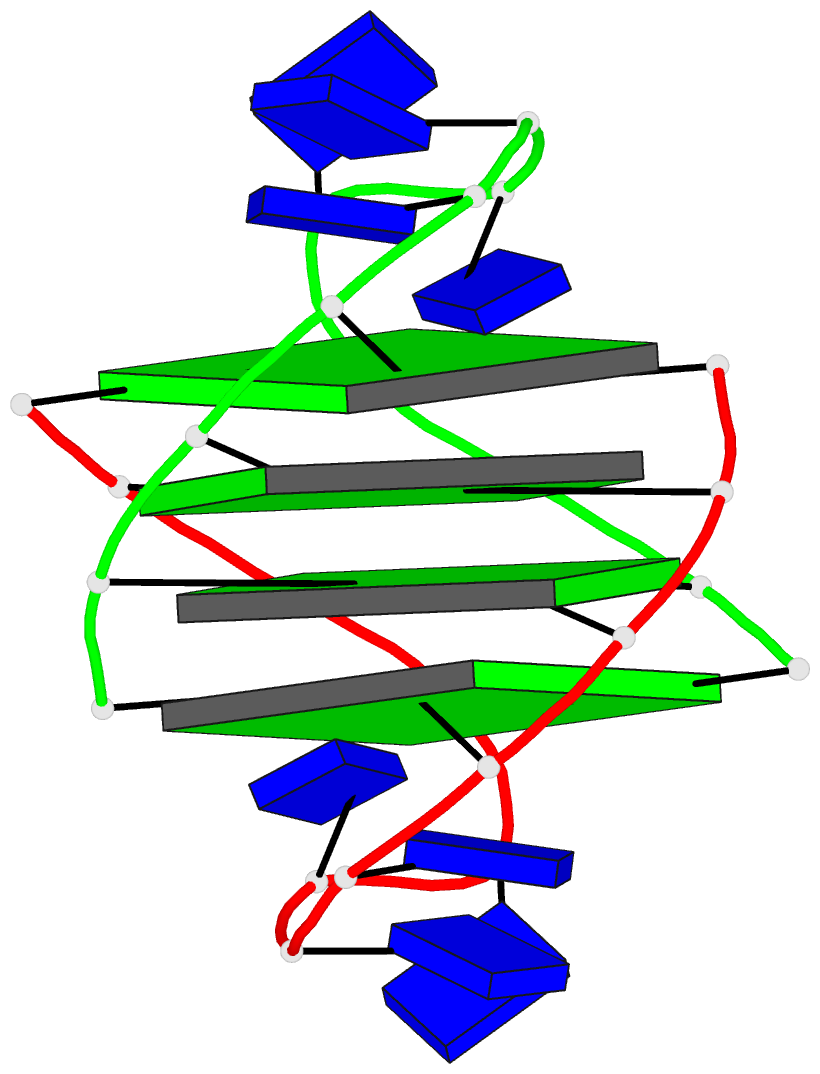
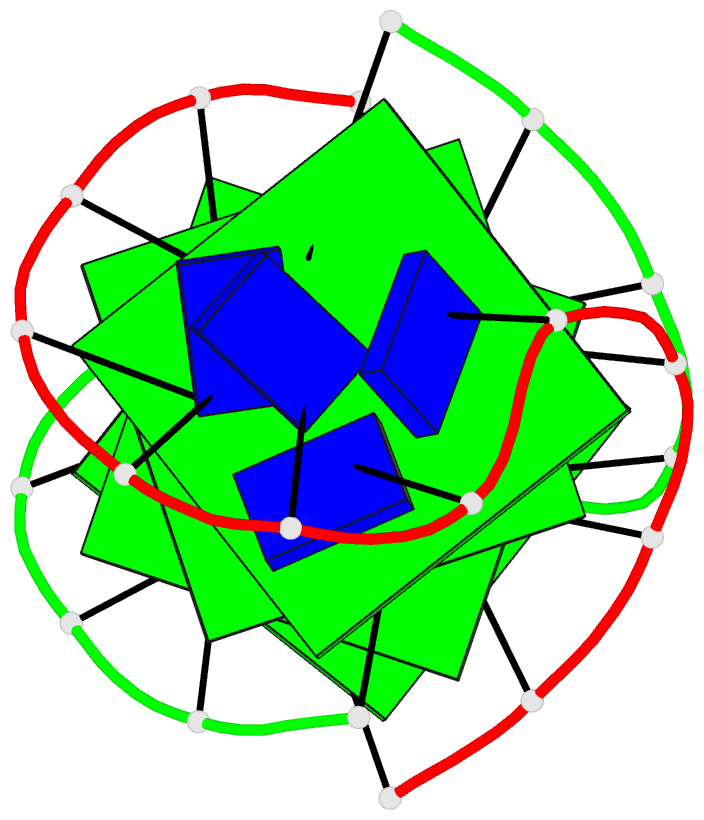
- Refined solution structure of the dimeric quadruplex
formed from the oxytricha telomeric oligonucleotide
d(ggggttttgggg)
- Reference
-
Schultze P, Smith FW, Feigon J (1994): "Refined
solution structure of the dimeric quadruplex formed from
the Oxytricha telomeric oligonucleotide
d(GGGGTTTTGGGG)." Structure,
2, 221-233. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00023-X.
- Abstract
- Background: Telomeres, the structures at the ends of
linear eukaryotic chromosomes, are essential for chromosome
replication and stability. The telomeres of the unicellular
ciliate Oxytricha contain a 3' single strand overhang
composed of two repeats of the telomere repeat sequence
d(TTTTGGGG). It has been proposed that oligonucleotides
containing this repeat can form DNA quadruplexes via
hydrogen bonding of the guanines into quartets. Such
structures may be relevant to the biological function of
the telomere, and in G-rich sequences elsewhere in the
genome.
Results: We have previously determined from solution NMR
data that the Oxy-1.5 Oxytricha repeat oligonucleotide
d(GGGGTTTTGGGG) dimerizes to form an intermolecular
quadruplex composed of four guanine quartets and with the
thymines in loops across the diagonal at opposite ends of
the quadruplex. We report here the refined solution
structure of Oxy-1.5. This structure is compared with the
previously published crystal structure of the same
oligonucleotide.
Conclusions: Oxy-1.5 forms a well-defined, symmetrical
structure with ordered thymine loops. Both the solution and
crystal structures of Oxy-1.5 are quadruplexes with
alternating syn and anti glycosyl conformation of guanines
along each strand of the helix and have thymine loops at
opposite ends. However, the topology of the two structures
is fundamentally different, leading to significant
structural differences. A topological pathway for the
formation and interconversion of the two structures is
proposed.