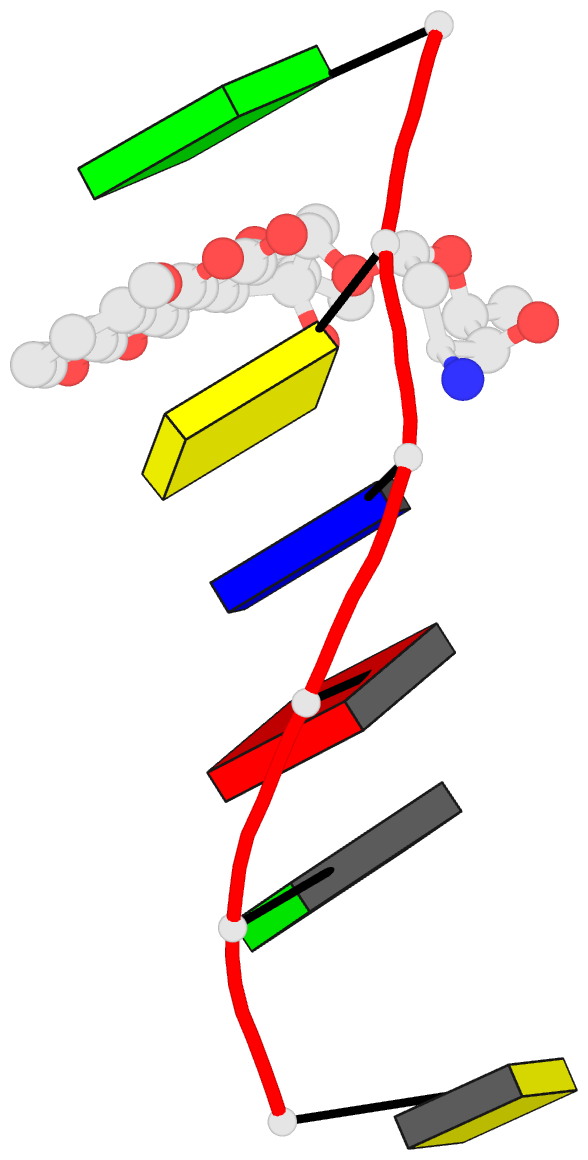
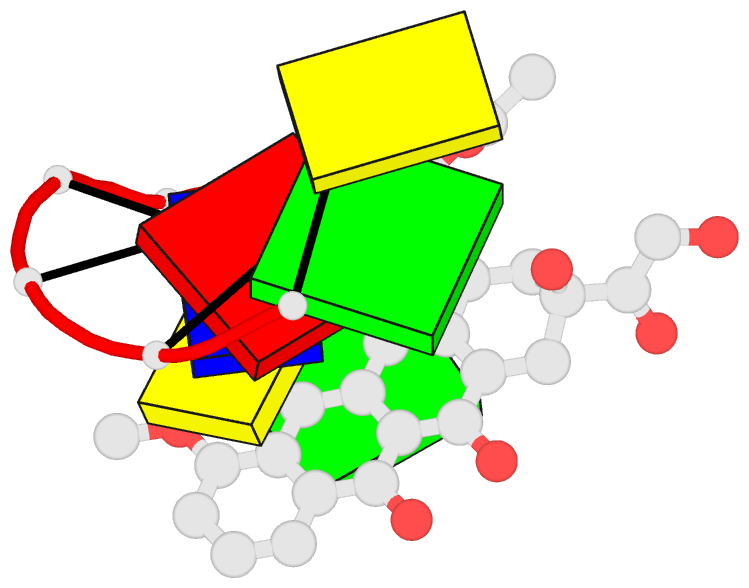
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
151d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.4 Å)
- Summary
- Diversity of water ring size at DNA interfaces:
hydration and dynamics of DNA-anthracycline complexes
- Reference
-
Lipscomb LA, Peek ME, Zhou FX, Bertrand JA, VanDerveer D,
Williams LD (1994): "Water ring
structure at DNA interfaces: hydration and dynamics of
DNA-anthracycline complexes." Biochemistry,
33, 3649-3659. doi: 10.1021/bi00178a023.
- Abstract
- In crystallographic structures of biological
macromolecules, one can observe many hydration rings that
originate at one water molecule, pass via hydrogen bonds
through several others, and return to the original water
molecule. Five-membered water rings have been thought to
occur with greater frequency than other ring sizes. We
describe a quantitative assessment of relationships between
water ring size and frequency of occurrence in the vicinity
of nucleic acid interfaces. This report focuses on
low-temperature X-ray crystallographic structures of two
anthracyclines, adriamycin (ADRI) and daunomycin (DAUN),
bound to d(CGATCG) and on several DNA structures published
previously by others. We have obtained excellent
low-temperature (-160 degrees C, LT) X-ray intensity data
for d(CGATCG)-adriamycin and d(CGATCG)-daunomycin with a
multiwire area detector. The LTX-ray data sets contain 20%
(daunomycin, LT-DAUN) and 35% (adriamycin, LT-ADRI) more
reflections than were used to derive the original
room-temperature (15 degrees C) structures [Frederick,
C.A., Williams, L.D., Ughetto, G., van der Marel, G. A.,
van Boom, J.H., Rich, A., & Wang, A.H.-J. (1990)
Biochemistry 29, 2538-2549]. The results show that
five-membered water rings are not preferred over other ring
sizes. This assessment is consistent with our observation
of broad dispersion W-W-W angles (sigma = 20 degrees). In
addition, we report that the thermal mobility, distinct
from the static disorder, of the amino sugar of daunomycin
and adriamycin is significantly greater than that of the
rest of the complex. This mobility implies that if the
central AT base pair is switched to a CG base pair, there
should be a low energy cost in avoiding the guanine amino
group. The energy difference (for the sugar-binding
preference) between d(CGTACG) and d(CGCGCG) could be
considerably less than 20 kcal/mol, a value proposed
previously from computation.