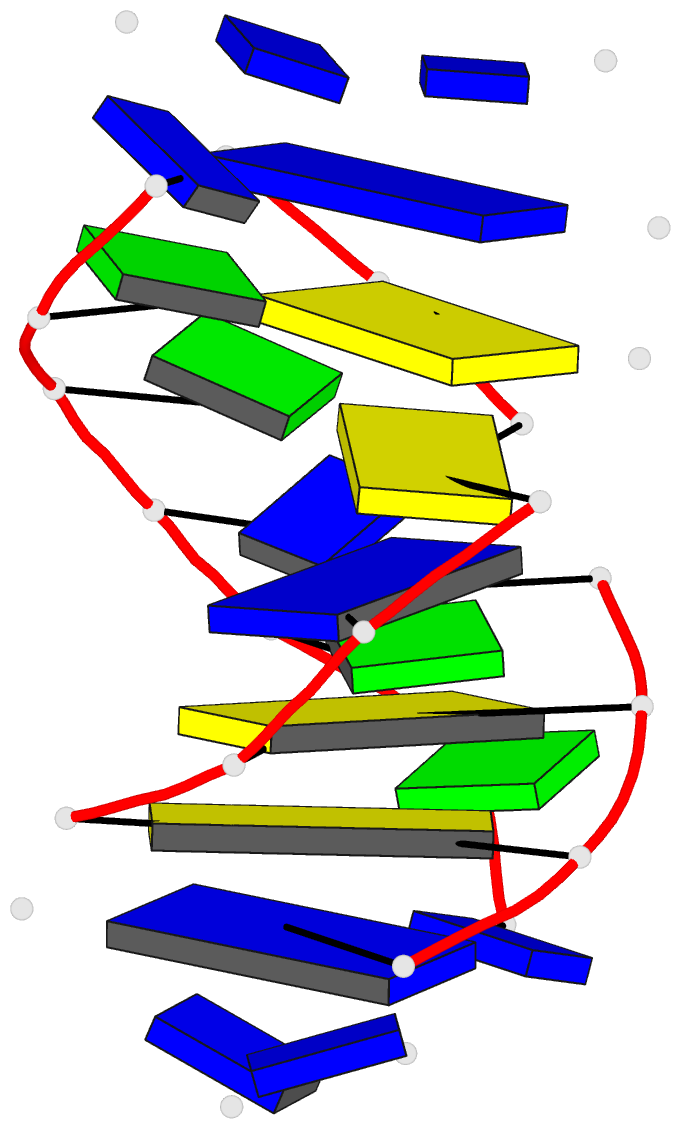
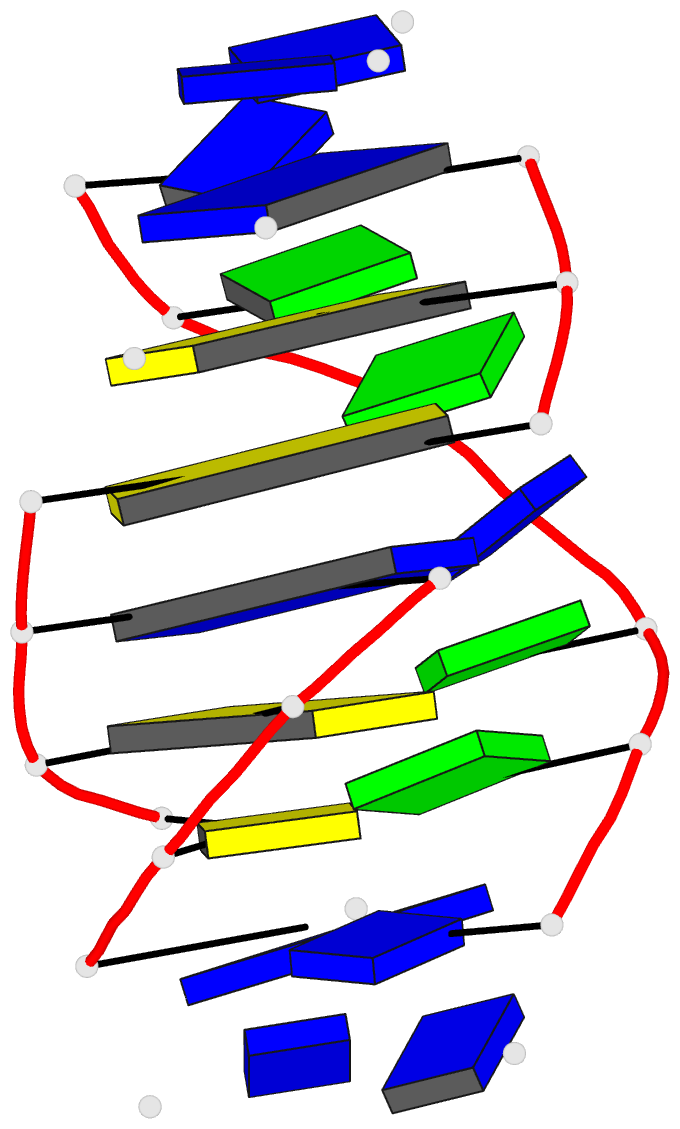
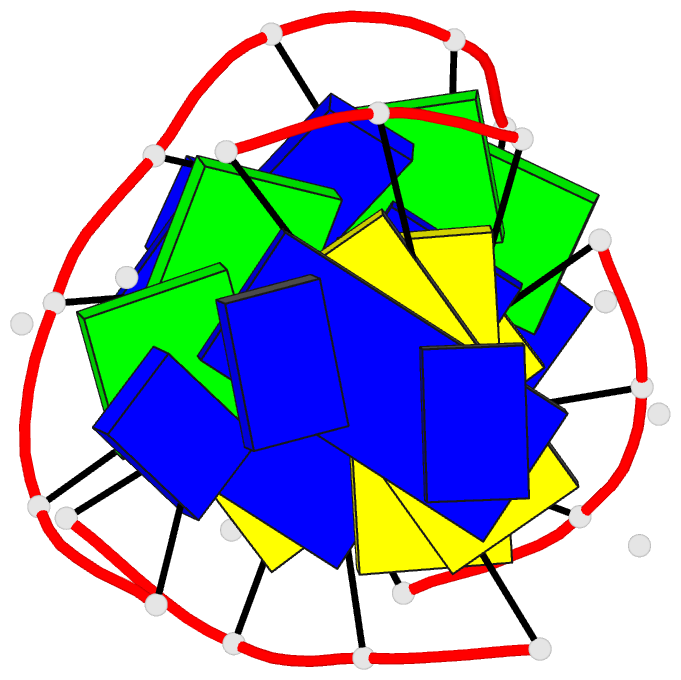
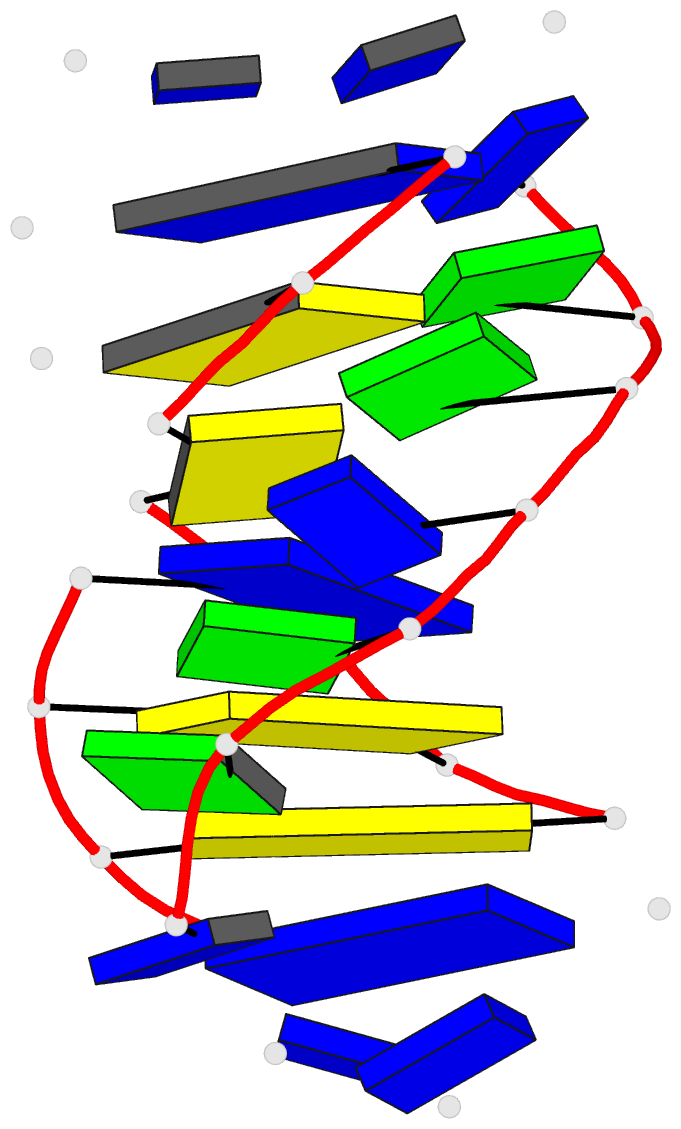
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
135d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
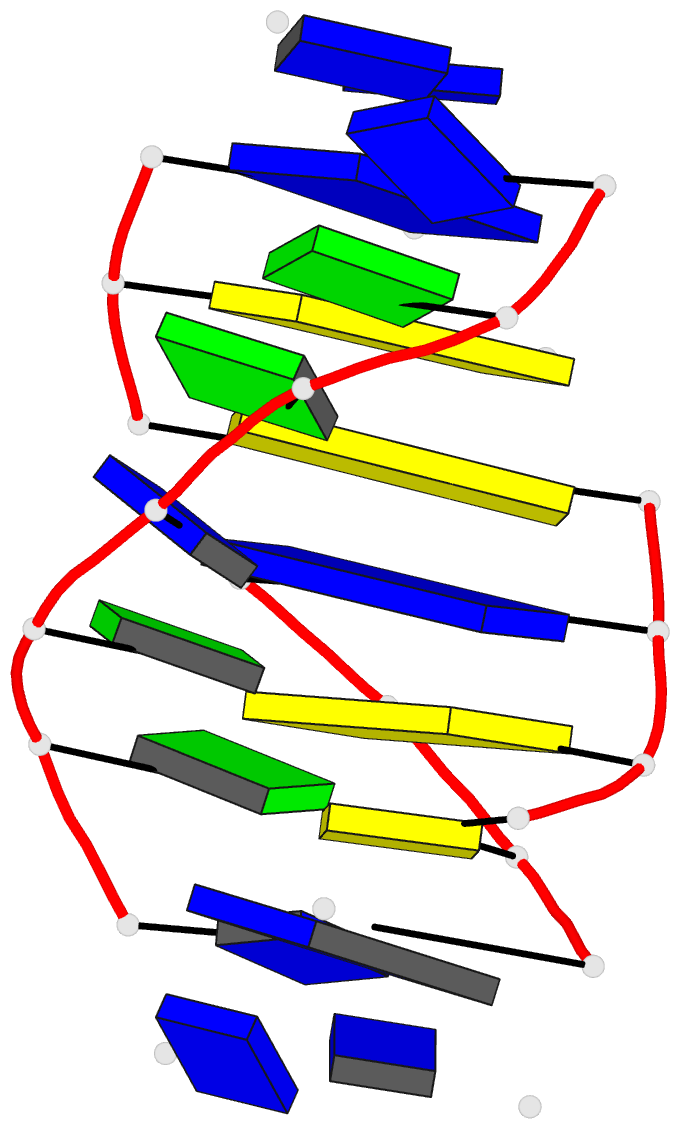
- Solution structure of a
purine(dot)purine(dot)pyrimidine DNA triplex containing
g(dot)gc and t(dot)at triples
- Reference
-
Radhakrishnan I, Patel DJ (1993): "Solution
structure of a purine.purine.pyrimidine DNA triplex
containing G.GC and T.AT triples."
Structure, 1, 135-152. doi:
10.1016/0969-2126(93)90028-F.
- Abstract
- Background: Oligonucleotide-directed triple helix
formation allows sequence specific recognition of double
helical DNA. This powerful approach has been used to
inhibit gene transcription in vitro and to mediate single
site specific cleavage of a human chromosome.
Results: Using a combined NMR and molecular dynamics
approach (including relaxation matrix refinement), we have
determined the solution structure of an intramolecular
purine.purine.pyrimidine (R.RY) DNA triplex containing
guanines and thymines in the third strand to high
resolution. Our studies define the G.GC and T.AT base
triple pairing alignments in the R.RY triplex and identify
the structural discontinuities in the third strand
associated with the non-isomorphism of the base triples.
The 5'-d(TpG)-3' base steps exhibit a pronounced increase
in axial rise and reduction in helical twist, while the
reverse is observed, to a lesser extent at 5'-d(GpT)-3'
steps. A third groove is formed between the purine-rich
third strand and the pyrimidine strand. It is wider and
deeper than the other two grooves.
Conclusions: Our structure of the R.RY DNA triplex will be
important in the design of oligonucleotide probes with
enhanced specificity and affinity for targeting in the
genome. The third groove presents a potential target for
binding additional ligands.