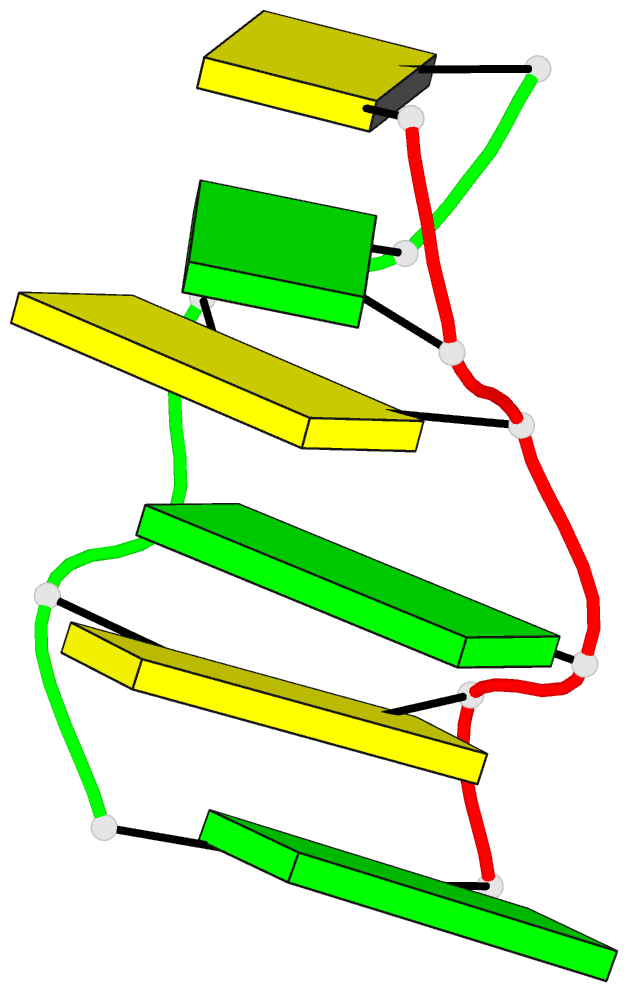
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
133d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.8 Å)
- Summary
- The crystal structure of n4-methylcytosine.guanosin
base-pairs in the synthetic hexanucleotide
d(cgcgm(4)cg)
- Reference
-
Cervi AR, Guy A, Leonard GA, Teoule R, Hunter WN (1993):
"The crystal
structure of N4-methylcytosine.guanosine base-pairs in
the synthetic hexanucleotide d(CGCGm4CG)."
Nucleic Acids Res., 21,
5623-5629. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.24.5623.
- Abstract
- The structure of d(CGCGm4CG) were m4C =
N4-methylcytosine has been determined by crystallographic
methods. The crystals are multifaced prisms, with
orthorhombic space group P2(1)2(1)2(1) and unit cell
dimensions of a = 17.98, b = 30.77 and c = 44.75A. The
asymmetric unit consists of one duplex of hexanucleotide
and 49 waters. The R-factor is 0.189 for 1495 reflections
with F > or = sigma(F) to a resolution limit of 1.8A.
The double helix has a Z-DNA type structure which appears
to be intermediate in structure to the two previously
characterised structure types for Z-DNA hexamers. The two
m4C.G base-pairs adopt structures that are very similar to
those of the equivalent base-pairs in the structure of the
native sequence d(CGCGCG) except for the presence of the
methyl groups which are trans to the N3 atoms of their
parent nucleotides and protrude into the solvent region.
The introduction of the modified base-pairs into the
d(CGCGCG) duplex appears to have a minimal effect on the
overall base-pair morphology of the Z-DNA duplex.