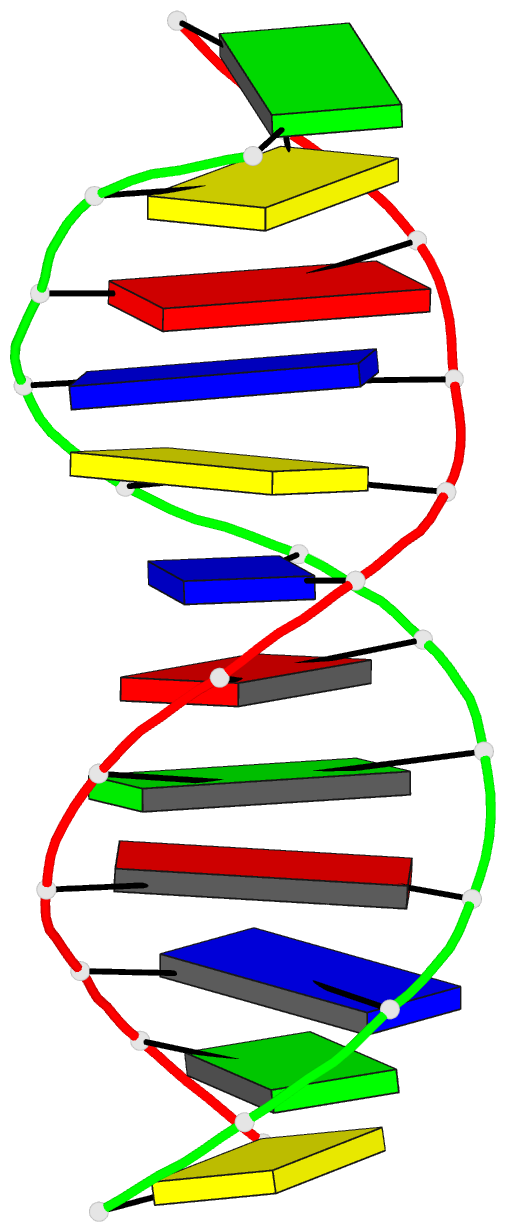
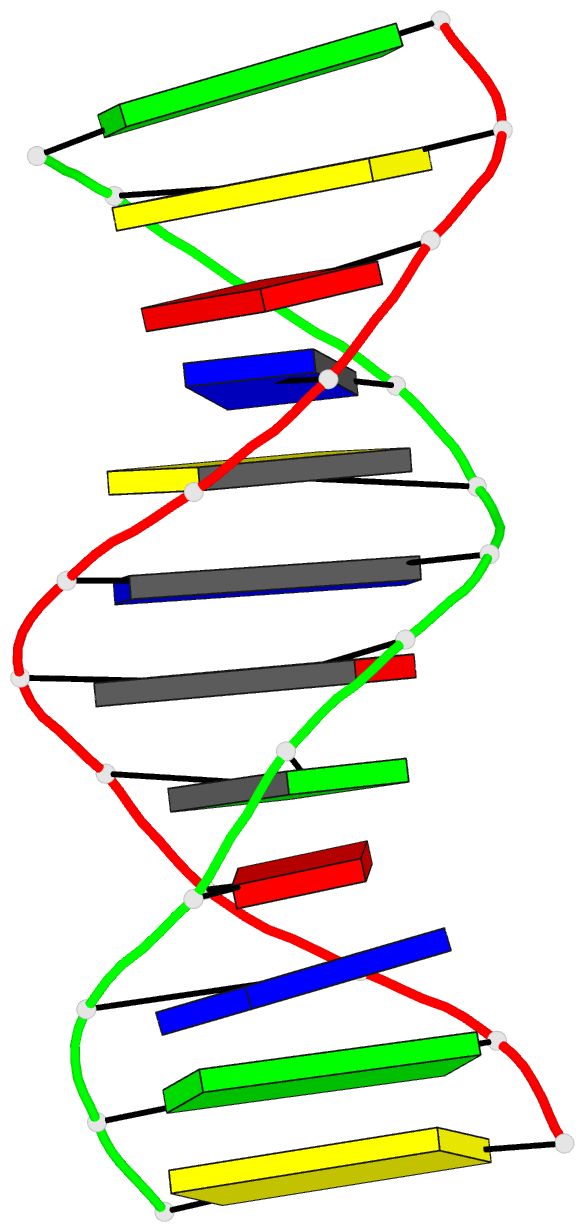
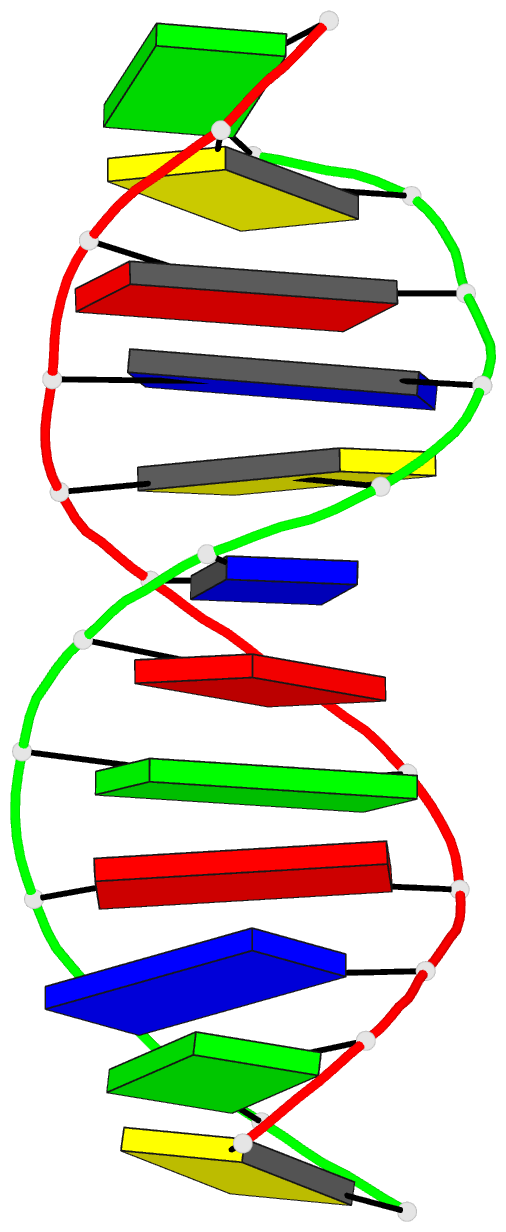
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
119d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.25 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal and molecular structure of d(cgtagatctacg) at
2.25 angstroms resolution
- Reference
-
Leonard GA, Hunter WN (1993): "Crystal and
molecular structure of d(CGTAGATCTACG) at 2.25 A
resolution." J.Mol.Biol.,
234, 198-208. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1574.
- Abstract
- Single crystal X-ray diffraction methods have been used
to determine the structure of the synthetic DNA dodecamer
d(CGTAGATCTACG). The dodecamer presents a new crystal form
of B-DNA in the monoclinic system, space group C2 with a =
64.83 A, b = 35.36 A, c = 25.35 A and beta = 92.24 degrees.
Structure solution was by molecular replacement and the
refinement used a combination of rigid body treatment,
molecular dynamics simulated annealing and restrained
least-squares methods. The refinement has been concluded
with an R-factor of 13.8% for 2120 reflections (78% of what
is theoretically available) with F > or = 2 sigma (F) in
the resolution range 7.0 to 2.25 A. The asymmetric unit
comprises a B-form duplex (24 nucleotides, molecular weight
7.2 kDa), 136.5 water molecules and a single magnesium ion
at 50% occupancy. The DNA model has root-mean-square
derivations from standard bond lengths of 0.011 A. The
central part of the structure is d(GATC), a tetrad sequence
involved in methylation and mismatch repair. A comparison
with other structures containing such a tetrad indicates
polymorphism at the tetrad level. In our structure a narrow
minor groove with a pronounced hydration pattern is
observed. Such features may be of importance in the
recognition of the sequence by specific enzymes. A
noteworthy feature of the hydration is the identification
of several pentagonal arrangements of hydrogen bonding
groups. Details of conformational parameters, base stacking
patterns, intermolecular interactions and hydration are
presented and comparisons with related structures are
given.