Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
118d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.64 Å)
- Summary
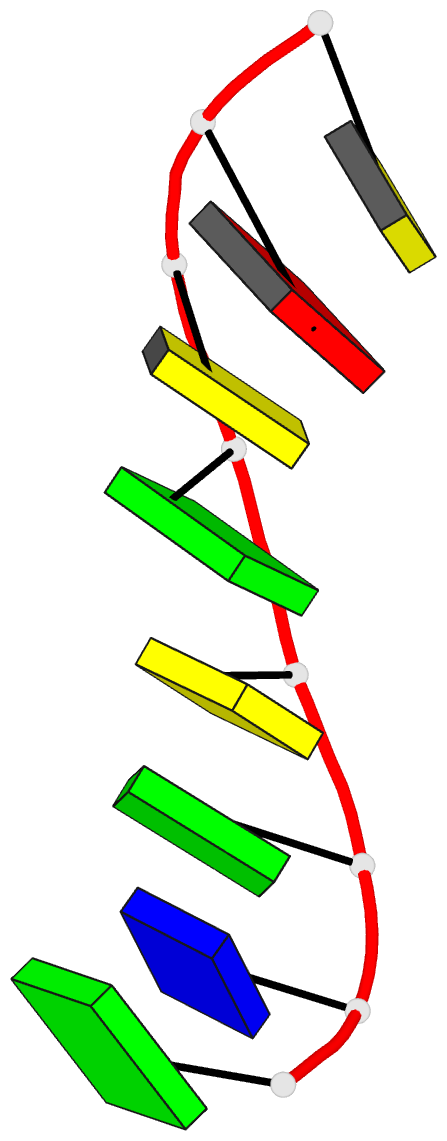
- Crystal and molecular structure of d(gtgcgcac):
investigation of the effects of base sequence on the
conformation of octamer duplexes
- Reference
-
Bingman CA, Li X, Zon G, Sundaralingam M (1992):
"Crystal
and molecular structure of d(GTGCGCAC): investigation of
the effects of base sequence on the conformation of
octamer duplexes." Biochemistry,
31, 12803-12812. doi: 10.1021/bi00166a014.
- Abstract
- The structure of the self-complementary
deoxyoctanucleotide d(GTGCGCAC), which crystallized as an
A-type helix in the space group P4(3)2(1)2, with one strand
in the crystallographic asymmetric unit has been determined
and refined to a final R-value of 0.154 using 1.64-A
diffraction data collected on an area detector. In contrast
to the closely related sequence d(GTGTACAC)tet, there was
no evidence for an ordered spermine molecule in the major
groove of this octamer. Ordered water is found associated
with almost all the exposed hydrogen bonding groups of the
octamer. A pentagonal ring of water molecules is hydrogen
bonded to O6 and N7 of G3 and the N4 and O6 of the C4.G13
base pair. A detailed comparison of the local helical
parameters of d(GTGCGCAC) and d(GTGTACAC)tet is presented.
The base sequence change at the center of the octamers
affects several of the local helical parameters, via both
intra- and interduplex interactions within the
crystal.