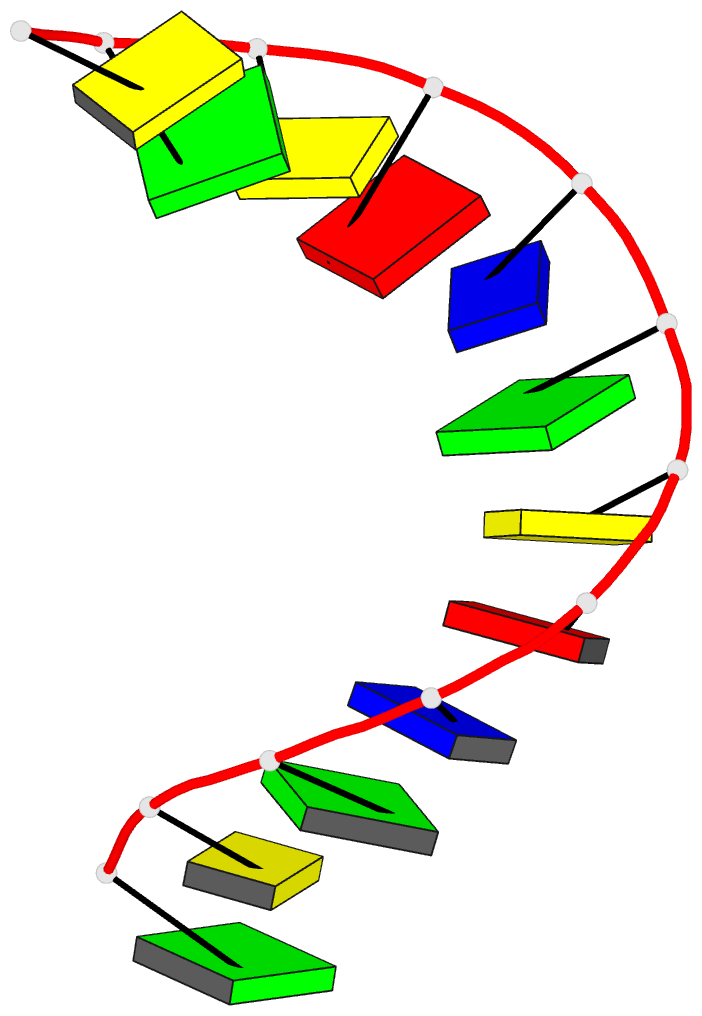
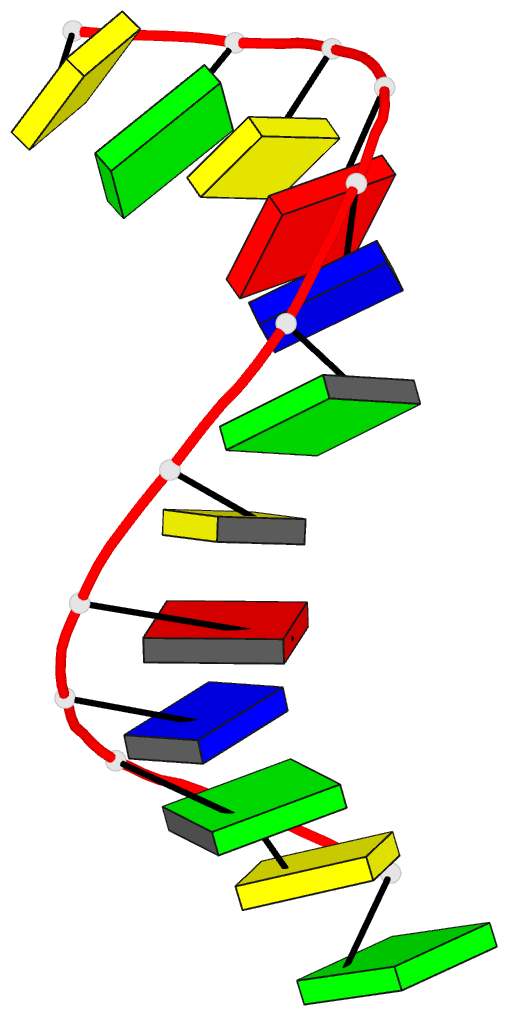
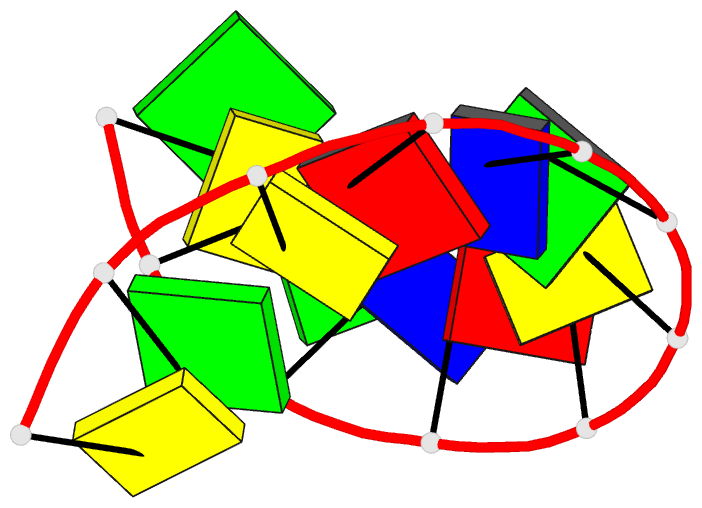
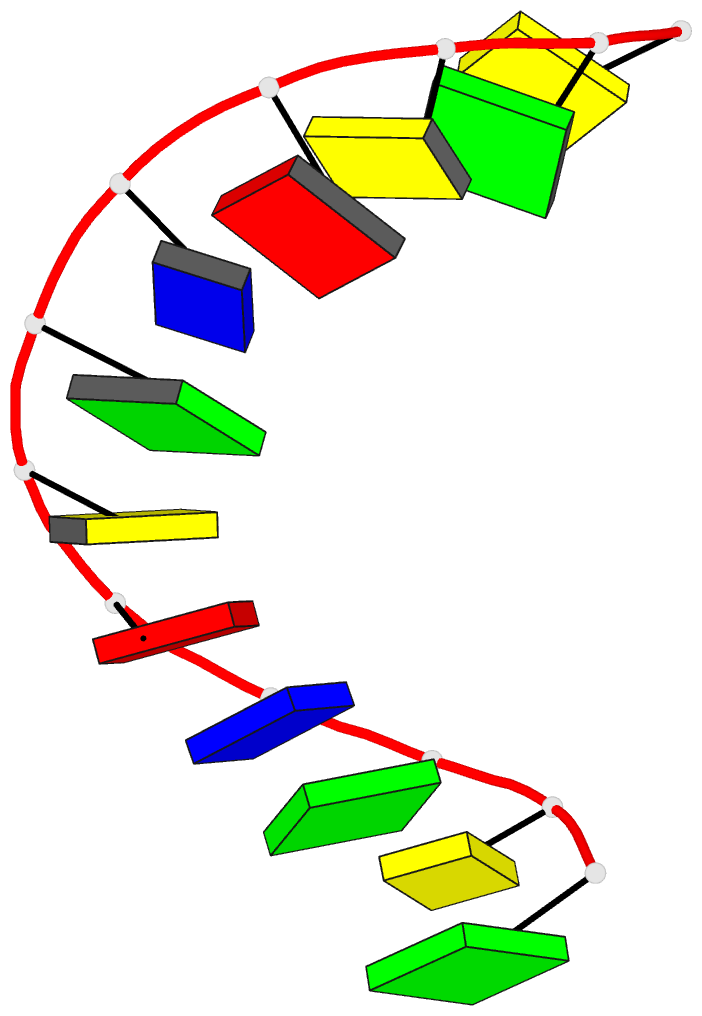
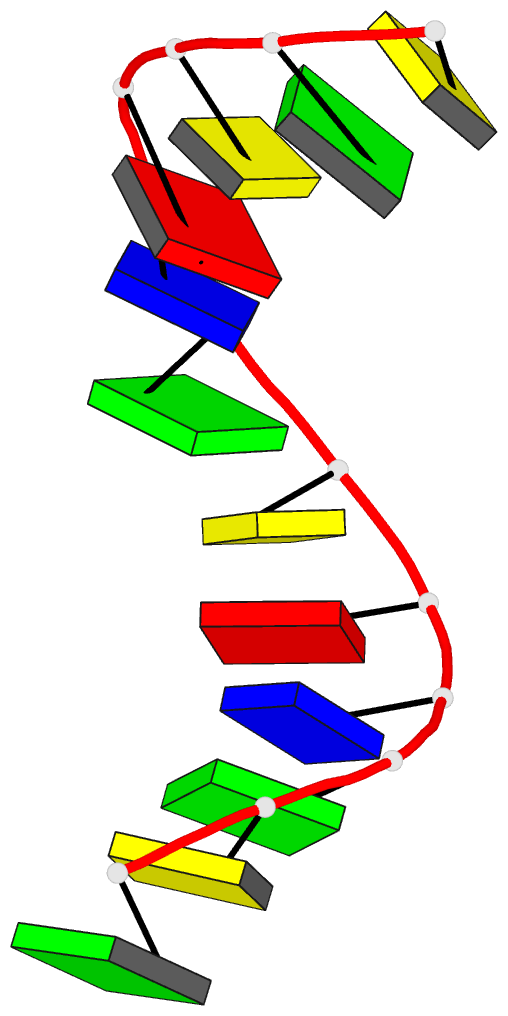
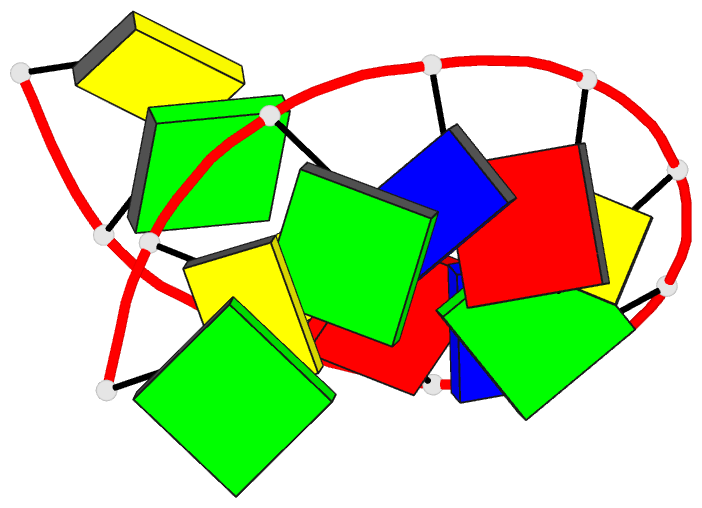
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
117d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.55 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal and molecular structure of the alternating
dodecamer d(gcgtacgtacgc) in the a-DNA form: comparison
with the isomorphous non-alternating dodecamer
d(ccgtacgtacgg)
- Reference
-
Bingman CA, Jain S, Zon G, Sundaralingam M (1992):
"Crystal and
molecular structure of the alternating dodecamer
d(GCGTACGTACGC) in the A-DNA form: comparison with the
isomorphous non-alternating dodecamer
d(CCGTACGTACGG)." Nucleic Acids Res.,
20, 6637-6647. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6637.
- Abstract
- The crystal structure of the alternating dodecamer
d(GCGTACGTACGC) (5'-GC) has been determined to a resolution
of 2.55A using oscillation film data. The crystals belong
to space group P6(1) 22, a = b = 46.2A, c = 71.5A with one
strand in the asymmetric unit, and are isomorphous with a
previously described non-alternating dodecamer,
d(CCGTACGTACGG) (5'-CC). Refinement by X-PLOR/NUCLSQ gave a
final R factor of 14.2% for 1089 observations. The molecule
adopts the A-DNA form. The interchange of the terminal base
pairs in the two dodecamers results in differences in the
intermolecular contacts and may account for the differences
in the bending. This dodecamer shows an axial deflection of
30 degrees, in the direction of the major groove compared
to 20 degrees in 5'-CC and may be a consequence of
additional contacts generated in 5'-GC by the interchange
of end base pairs. The high helical axis deflection
appreciably influences the local helical parameters. The
molecule exhibits relatively high inclination angles, and
has a narrow major groove. The helical parameters when
described relative to the dyad-related hexamer halves of
the molecule give more reasonable values. The crystal
packing, local helical parameters, torsion angles, and
hydration are described and also compared with the
non-alternating 5'-CC dodecamer.