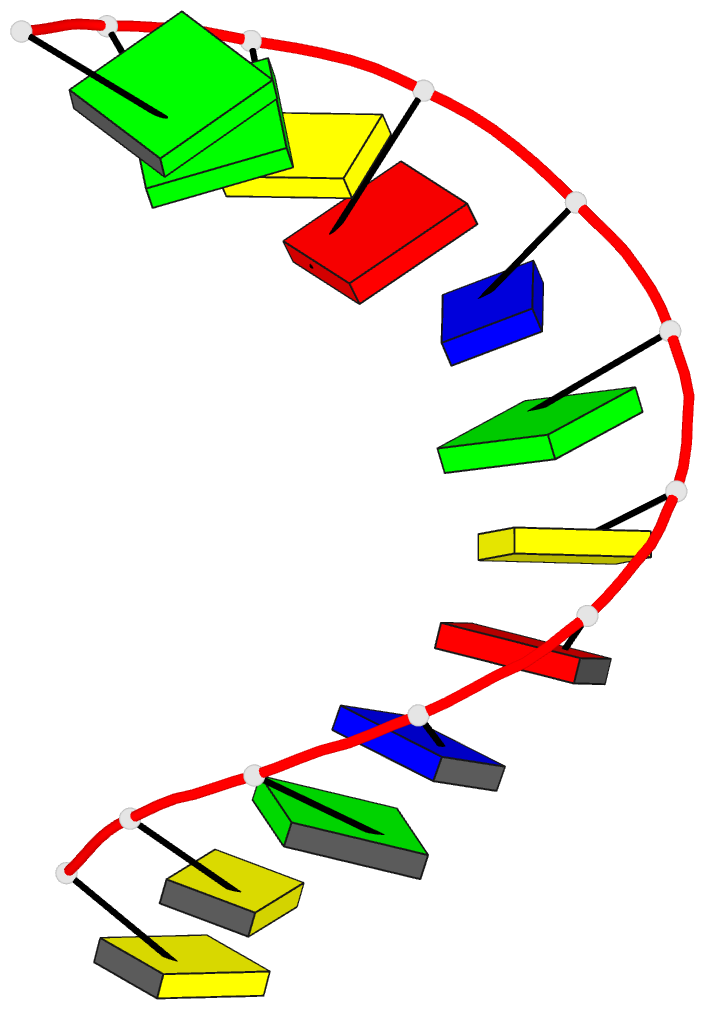
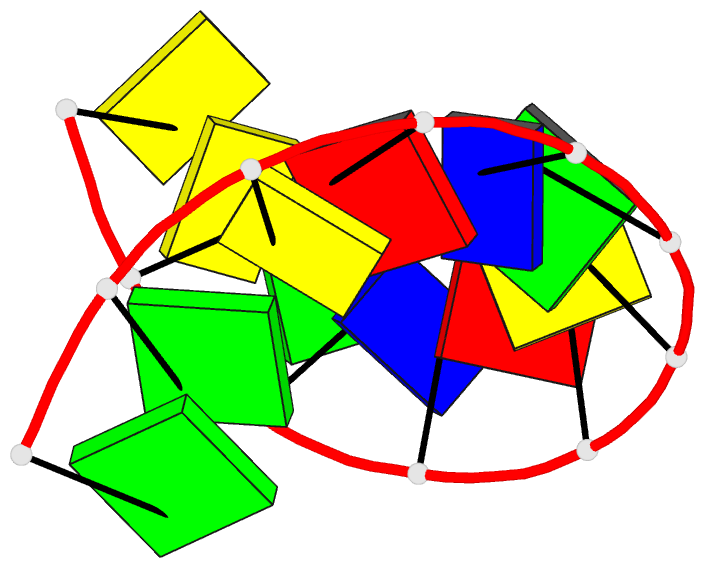
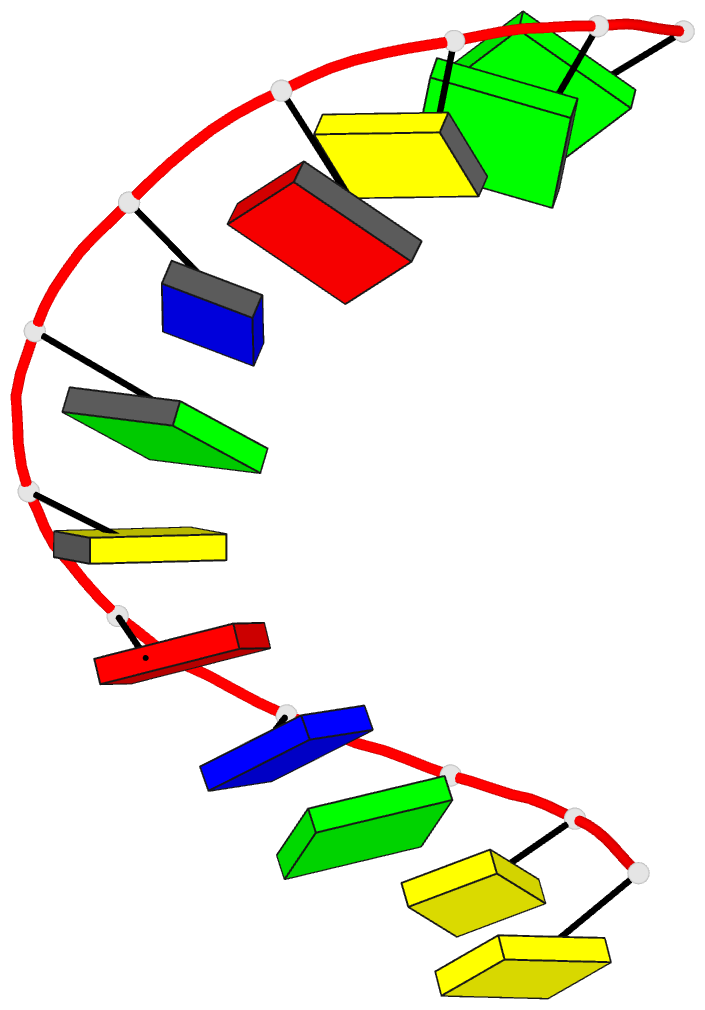
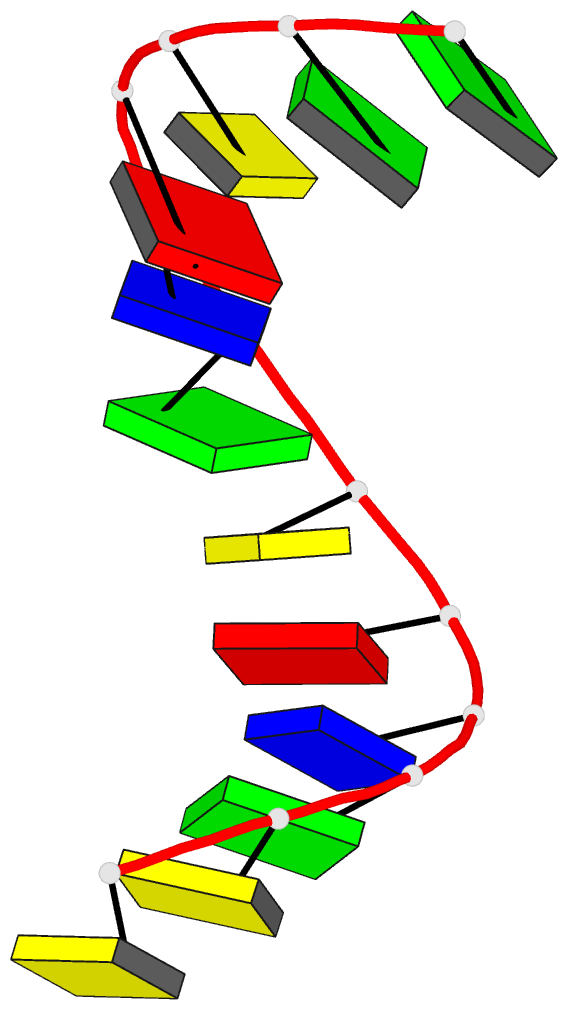
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
116d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.5 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal and molecular structure of the a-DNA dodecamer
d(ccgtacgtacgg): choice of fragment helical axis
- Reference
-
Bingman CA, Zon G, Sundaralingam M (1992): "Crystal and
molecular structure of the A-DNA dodecamer
d(CCGTACGTACGG). Choice of fragment helical axis."
J.Mol.Biol., 227, 738-756. doi:
10.1016/0022-2836(92)90221-5.
- Abstract
- The crystal structure of the dodecamer d(CCGTACGTACGG)
has been determined at 2.5 A resolution. The crystals grow
in the hexagonal space group P6(1)22, a = b = 46.2 A, c =
71.5 A with one strand as the asymmetric unit. Diffraction
data were collected by the oscillation film method yielding
1664 unique reflections with an Rmerge of 0.04. The
structure was solved by real-space rotational translational
searches with idealized helical models of A, B and Z-DNA.
The best agreement was given by an A-DNA model with its
dyad axis along the diagonal crystallographic dyad axis,
with an R-factor 0.43 and correlation coefficient of 0.59
for data between 10 and 5 A. Iterative map fitting and
restrained least-squares refinement and addition of 40
solvent molecules brought the R-factor to 0.15 and the
correlation coefficient to 0.97 for all data between 8.0
and 2.5 A. The stereochemistry of the atomic model is good,
with a root-mean-square deviation in bond distances of
0.006 A. This is the first example of an A-DNA containing a
full helical turn. The dodecamer displays a novel packing
motif. In addition to the characteristic contacts between
the terminal base-pairs and the minor grooves of
symmetry-related molecules, there are also minor groove to
minor groove interactions not previously observed. The
packing leaves an approximately 25 A diameter solvent
channel around the origin, along the c-axis. The presence
of a prominent 3.4 A meridional reflection and other
diffuse features in the diffraction pattern provided
evidence for the presence of disordered B-DNA along the
c-axis, which can be accommodated in these solvent
channels. The molecular conformation of the dodecamer also
displays novel features. The dyad-related halves of the
molecule are bent at an angle of 20 degrees, and the
helical parameters are affected by this bend. Unlike the
shorter A-DNA octamers, the dimensions of the major groove
can be directly measured. Novel correlations between local
helical parameters and global conformational features are
presented. Most of the solvent molecules are associated
with the major groove and the sugar-phosphate
backbone.