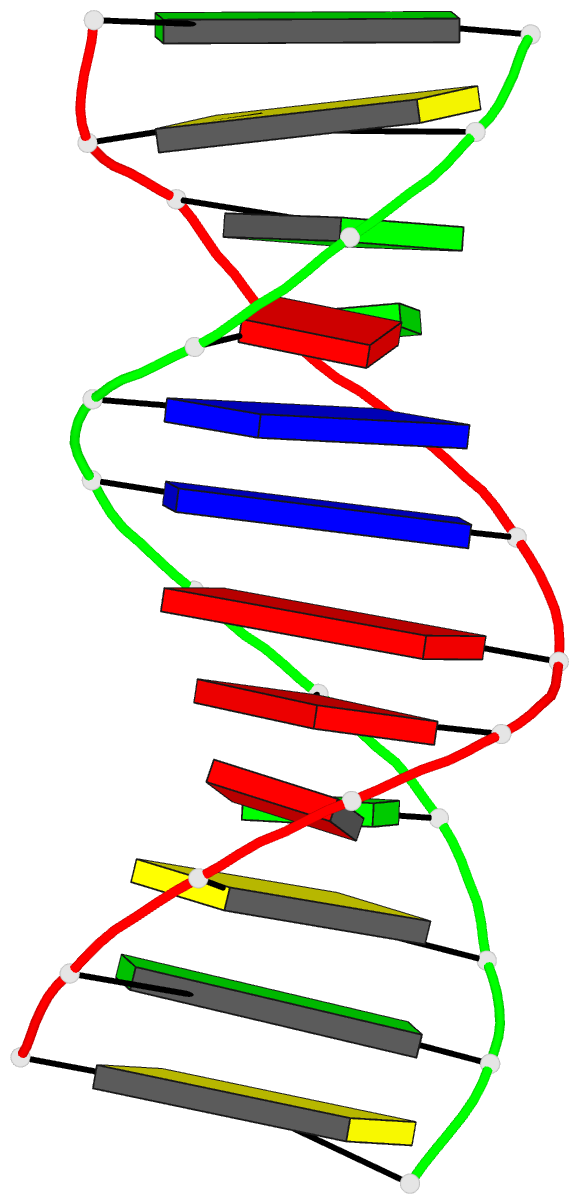
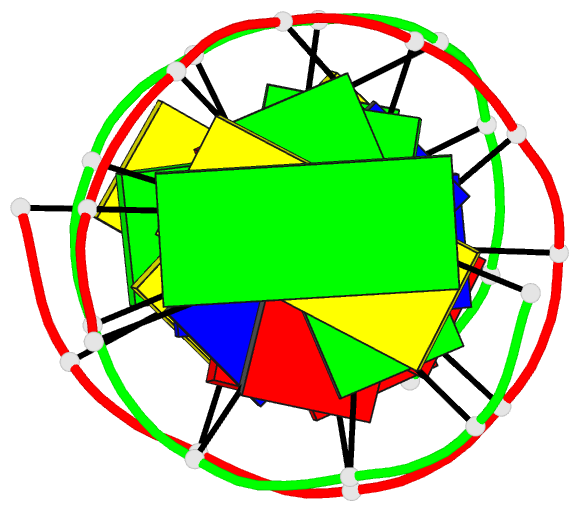
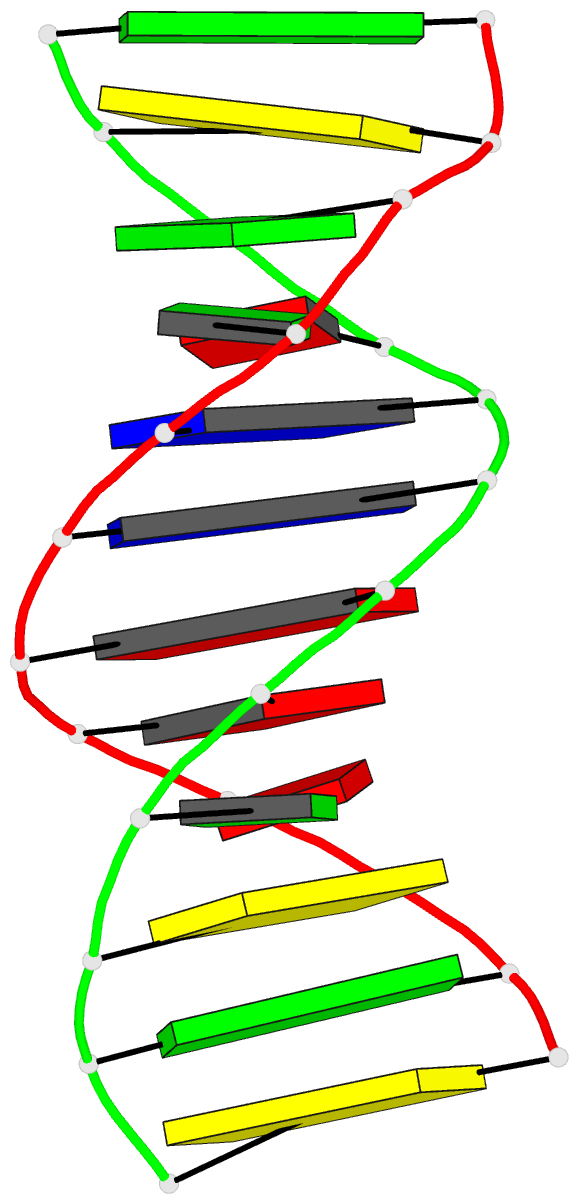
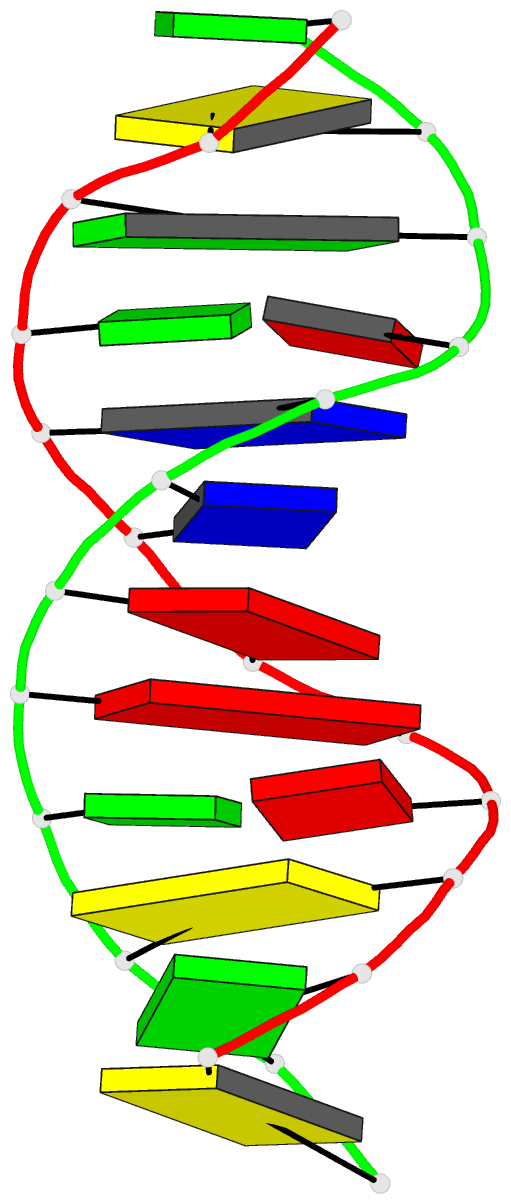
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
111d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.25 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure and stability of a DNA duplex
containing a(anti).g(syn) base-pairs
- Reference
-
Brown T, Leonard GA, Booth ED, Chambers J (1989):
"Crystal
structure and stability of a DNA duplex containing
A(anti).G(syn) base-pairs." J.Mol.Biol.,
207, 455-457. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90268-4.
- Abstract
- The synthetic dodecanucleotide d(CGCAAATTGGCG) has been
analysed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction techniques and
the structure refined to R = 0.16 and 2.25 A resolution,
with the location of 94 solvent molecules. The sequence
crystallizes as a full turn of a B-DNA helix with ten
Watson-Crick base-pairs and two adenine-guanine mispairs.
The analysis clearly shows that the mismatches are of the
form A(anti).G(syn). Thermal denaturation studies indicate
that the stability of the duplex is strongly pH dependent,
with a maximum at pH 5.0, suggesting that the base-pair is
stabilized by protonation. Three different arrangements
have been observed for base-pairs between guanine and
adenine and it is likely that A.G mismatch conformation is
strongly influenced by dipole-dipole interactions with
adjacent base-pairs.