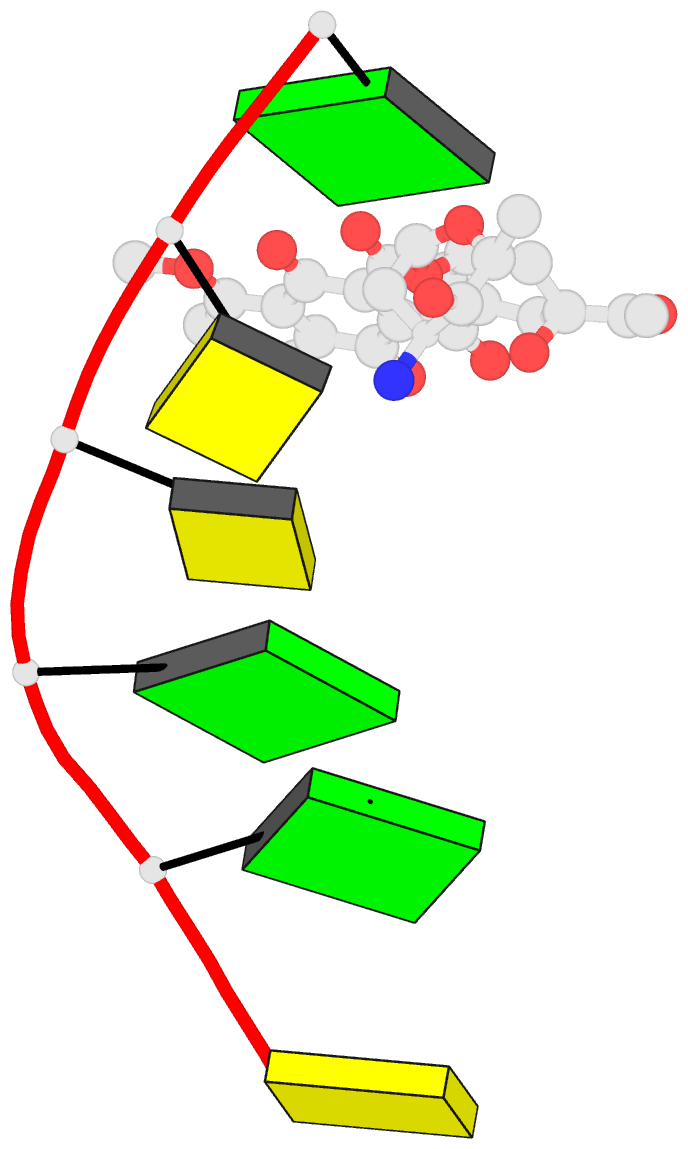
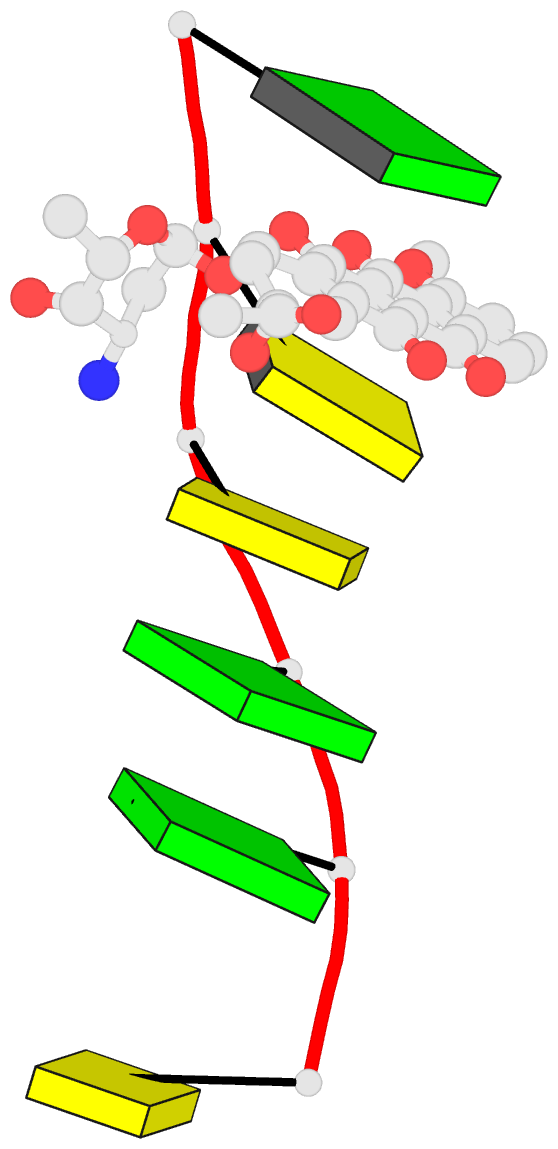
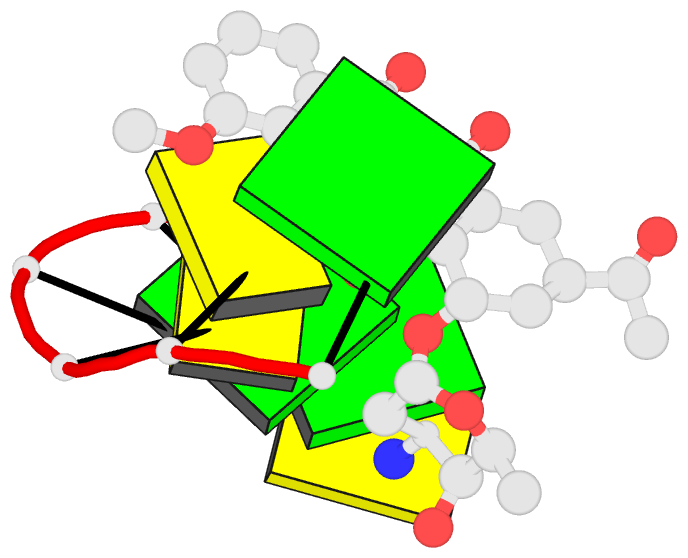
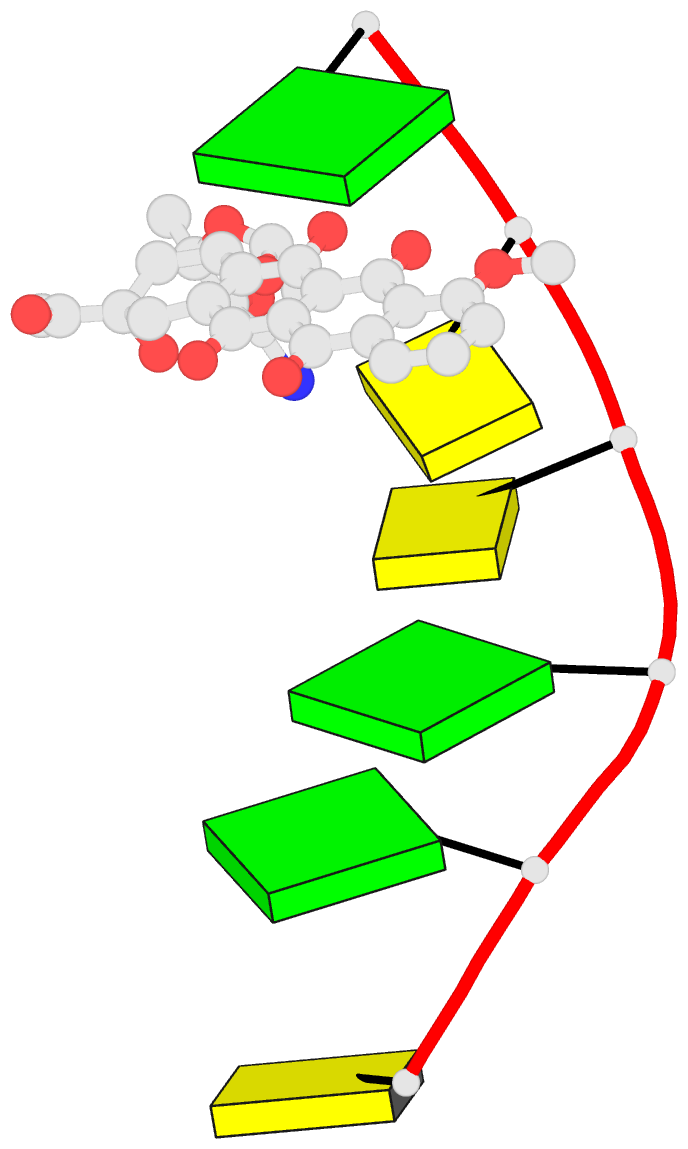
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
110d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
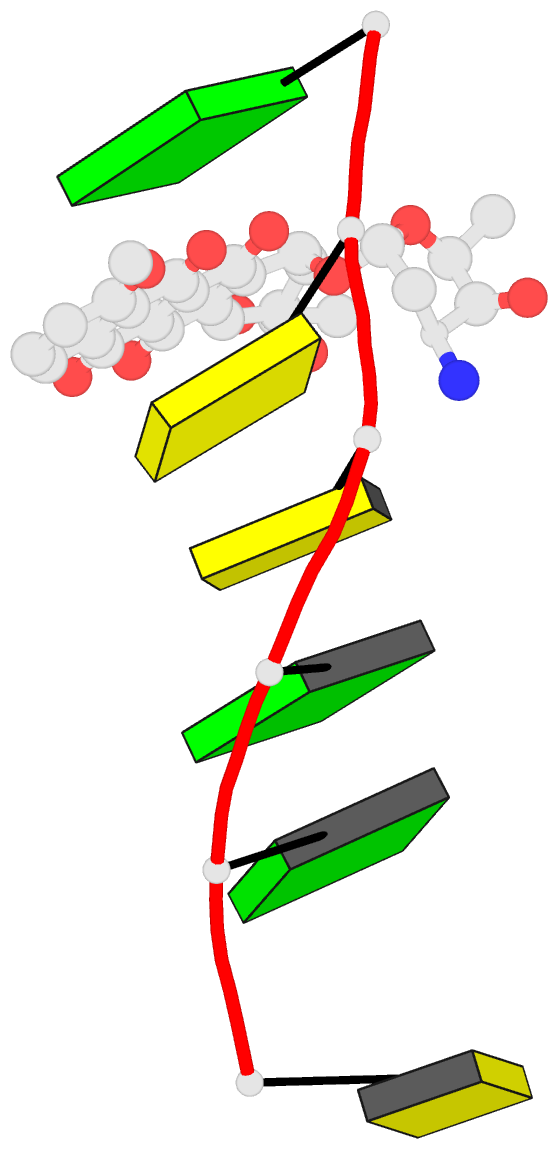
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.9 Å)
- Summary
- Anthracycline-DNA interactions at unfavourable base
base-pair triplet-binding sites: structures of
d(cggccg)-daunomycin and d(tggcca)-adriamycin compl
- Reference
-
Leonard GA, Hambley TW, McAuley-Hecht K, Brown T, Hunter
WN (1993): "Anthracycline-DNA
interactions at unfavourable base-pair triplet-binding
sites: structures of d(CGGCCG)/daunomycin and
d(TGGCCA)/adriamycin complexes." Acta
Crystallogr.,Sect.D, 49, 458-467.
doi: 10.1107/S090744499300527X.
- Abstract
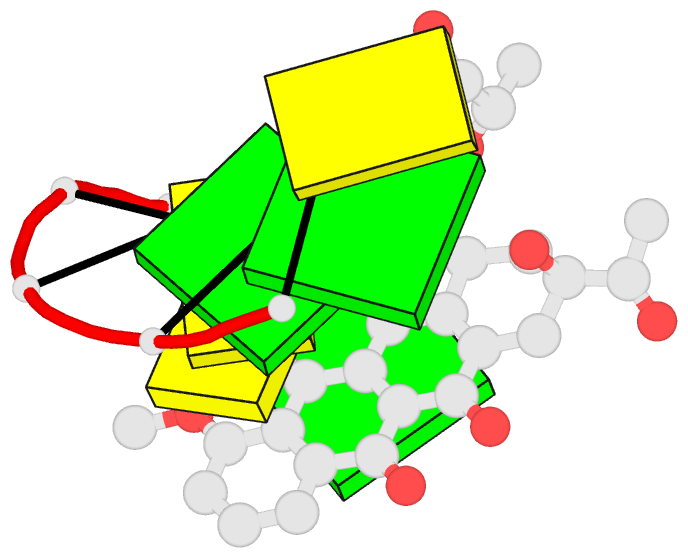
- The structures of two hexanucleotide-anthracycline
complexes d(CGGCCG)/daunomycin and d(TGGCCA)/adriamycin
have been determined using single-crystal X-ray diffraction
techniques. In both cases the anthracycline molecule is
bound to non-preferred d(YGG) base-pair triplet sites. For
both complexes the crystals are tetragonal and belong to
the space group P4(1)2(1)2. Unit-cell dimensions are a =
28.07 (2), c = 53.35 (1) and a = 28.01 (1), c = 52.99 (1)
A, respectively, and the asymmetric unit of both structures
consists of one strand of DNA, one drug molecule and
approximately 50 water molecules. For the d(CGGCCG) complex
the refinement converged with an R factor of 0.21 for 1108
reflections with F >/= 2sigma(F) in the resolution range
7.0-1.9 A. For the complex involving d(TGGCCA) the final R
value was 0.22 for 1475 reflections in the range 7.0-1.7 A
with the same criterion for observed data. Both complexes
are essentially isomorphous with related structures but
differ in terms of the number of favourable van der Waals
interactions of the amino sugars of the drug molecules with
the DNA duplexes and the formation in the minor groove of
heterodromic pentagonal arrangements of hydrogen bonds
involving water molecules which link the amino sugars to
the DNA. These differences in structure are used to
rationalize the lack of affinity of daunomycin-type
anthracyclines for d(YGG) and d(YGC) sites.