Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
10mh;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.55 Å)
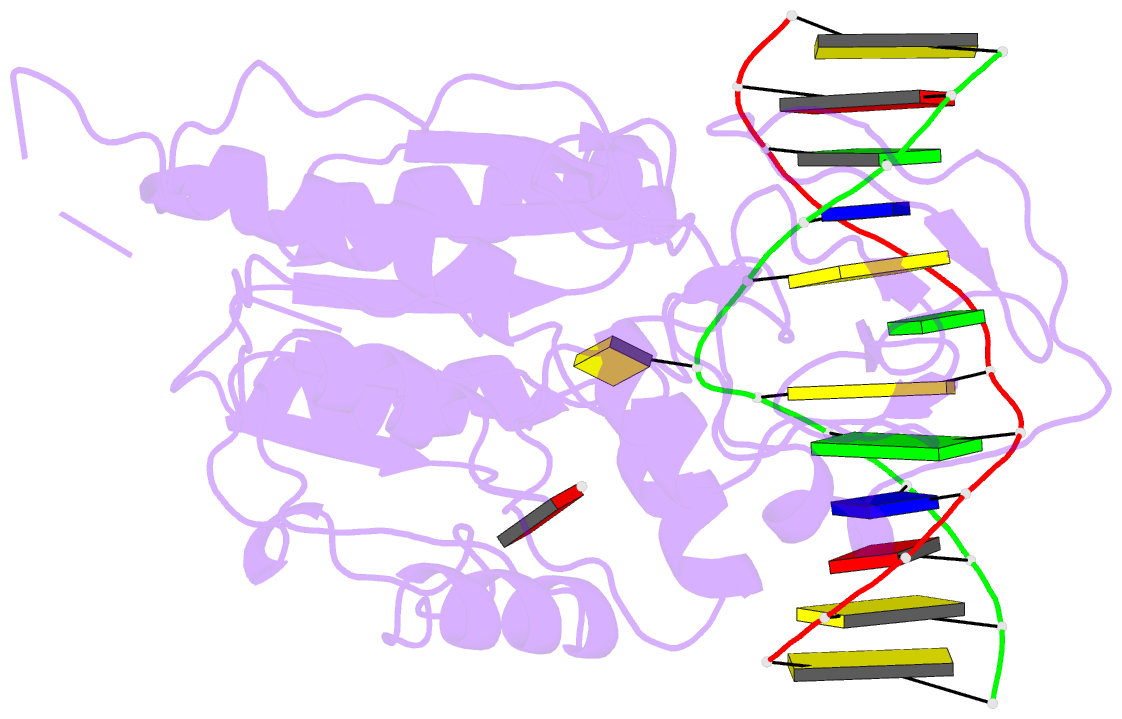
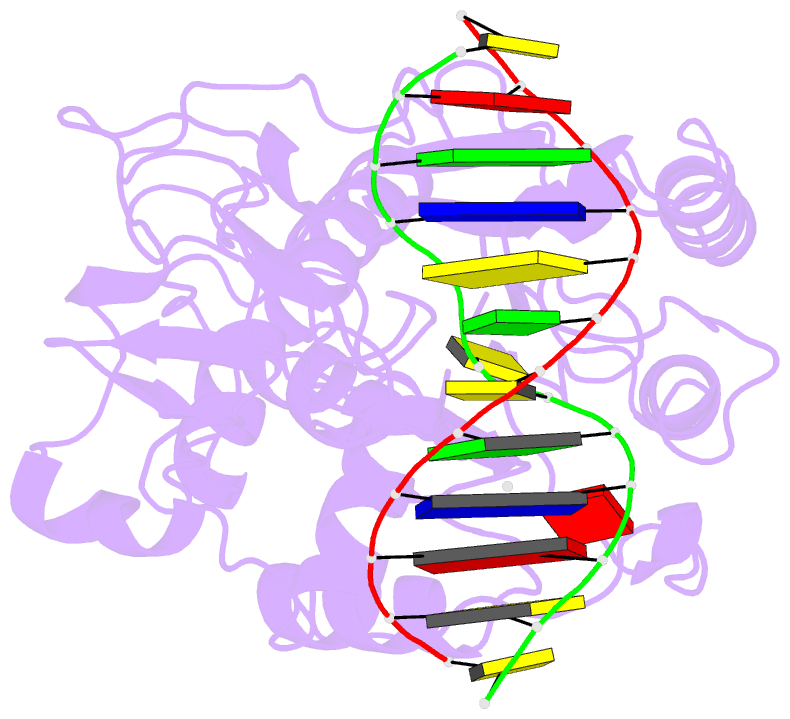
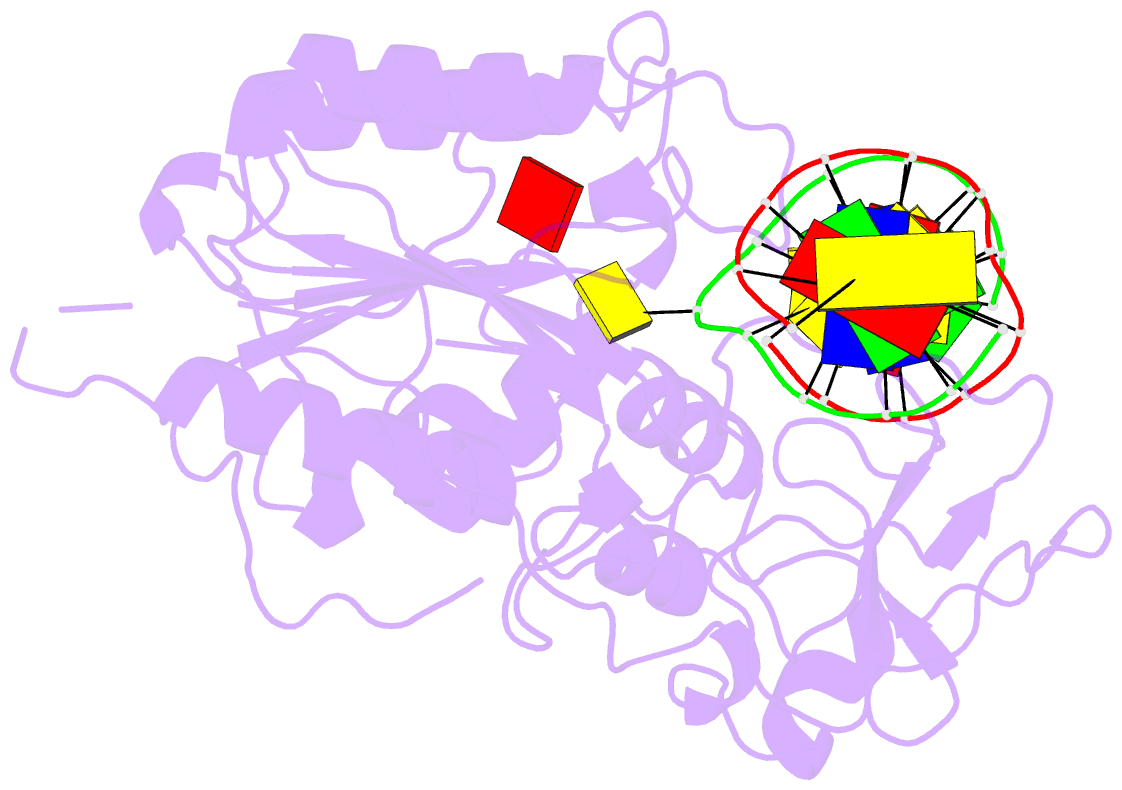
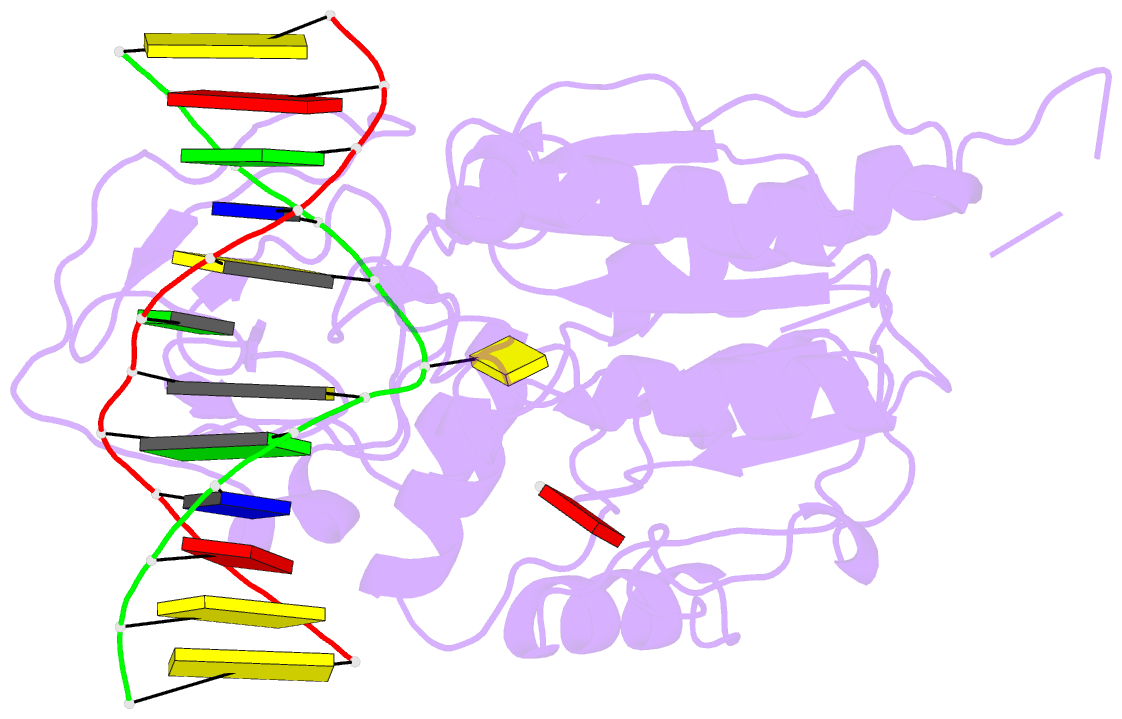
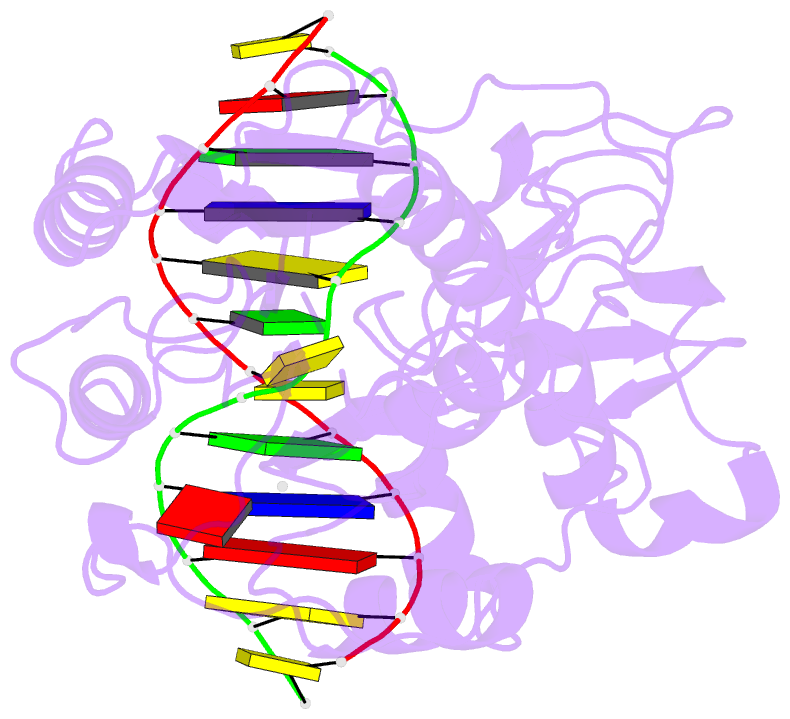
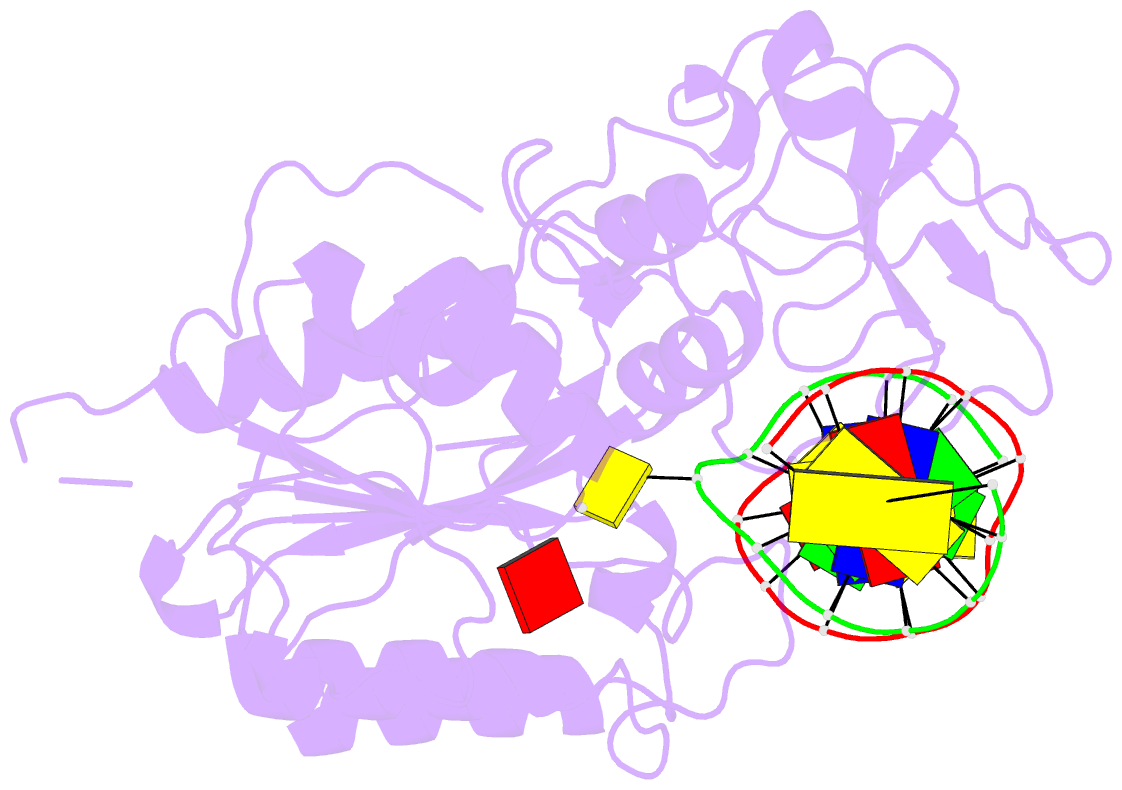
- Summary
- Ternary structure of hhai methyltransferase with adohcy
and hemimethylated DNA containing 5,6-dihydro-5-azacytosine
at the target
- Reference
-
Sheikhnejad G, Brank A, Christman JK, Goddard A, Alvarez
E, Ford Jr H, Marquez VE, Marasco CJ, Sufrin JR, O'gara
M, Cheng X (1999): "Mechanism
of inhibition of DNA (cytosine C5)-methyltransferases by
oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing
5,6-dihydro-5-azacytosine." J.Mol.Biol.,
285, 2021-2034. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2426.
- Abstract
- A key step in the predicted mechanism of enzymatic
transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosyl-l-methionine
(AdoMet) to cytosine residues in DNA is the transient
formation of a dihydrocytosine intermediate covalently
linked to cysteine in the active site of a DNA (cytosine
C5)-methyltransferase (DNA C5-MTase). Crystallographic
analysis of complexes formed by HhaI methyltransferase
(M.HhaI), AdoMet and a target oligodeoxyribonucleotide
containing 5-fluorocytosine confirmed the existence of this
dihydrocytosine intermediate. Based on the premise that
5,6-dihydro-5-azacytosine (DZCyt), a cytosine analog with
an sp3-hybridized carbon (CH2) at position 6 and an NH
group at position 5, could mimic the non-aromatic character
of the cytosine ring in this transition state, we
synthesized a series of synthetic substrates for DNA
C5-MTase containing DZCyt. Substitution of DZCyt for target
cytosines in C-G dinucleotides of single-stranded or
double-stranded oligodeoxyribonucleotide substrates led to
complete inhibition of methylation by murine DNA C5-MTase.
Substitution of DZCyt for the target cytosine in G-C-G-C
sites in double-stranded oligodeoxyribonucleotides had a
similar effect on methylation by M. HhaI.
Oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing DZCyt formed a tight
but reversible complex with M.HhaI, and were consistently
more potent as inhibitors of DNA methylation than
oligodeoxyribonucleotides identical in sequence containing
5-fluorocytosine. Crystallographic analysis of a ternary
complex involving M.HhaI, S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine and a
double-stranded 13-mer oligodeoxyribonucleotide containing
DZCyt at the target position showed that the analog is
flipped out of the DNA helix in the same manner as
cytosine, 5-methylcytosine, and 5-fluorocytosine. However,
no formation of a covalent bond was detected between the
sulfur atom of the catalytic site nucleophile, cysteine 81,
and the pyrimidine C6 carbon. These results indicate that
DZCyt can occupy the active site of M.HhaI as a transition
state mimic and, because of the high degree of affinity of
its interaction with the enzyme, it can act as a potent
inhibitor of methylation.