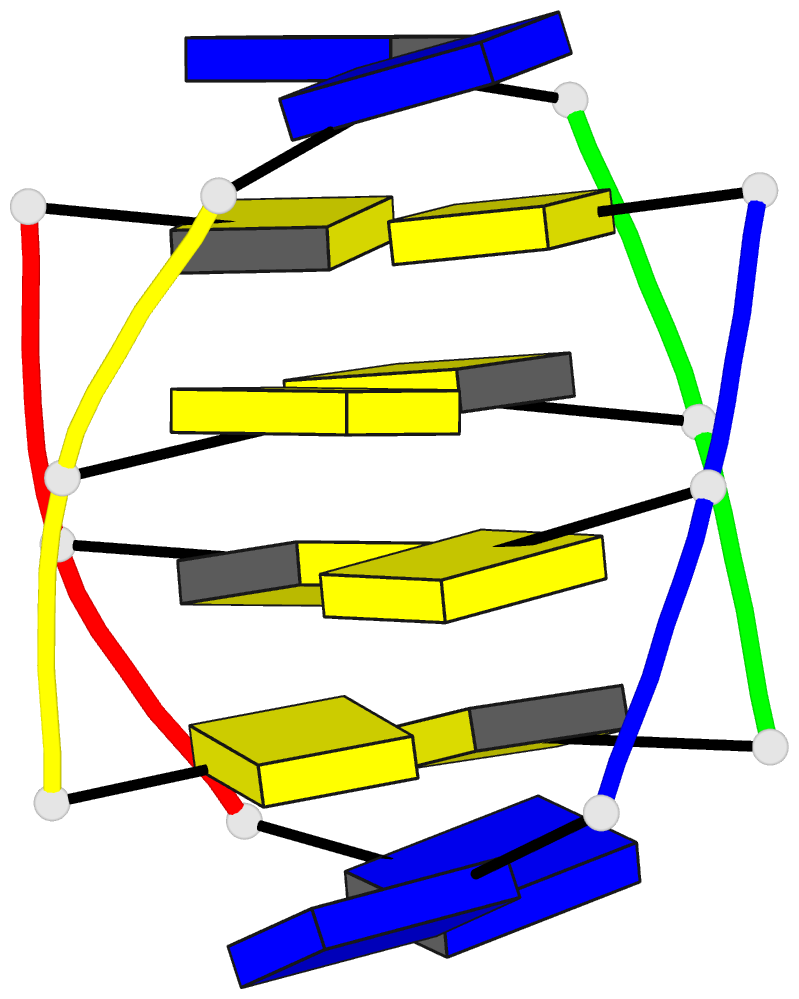
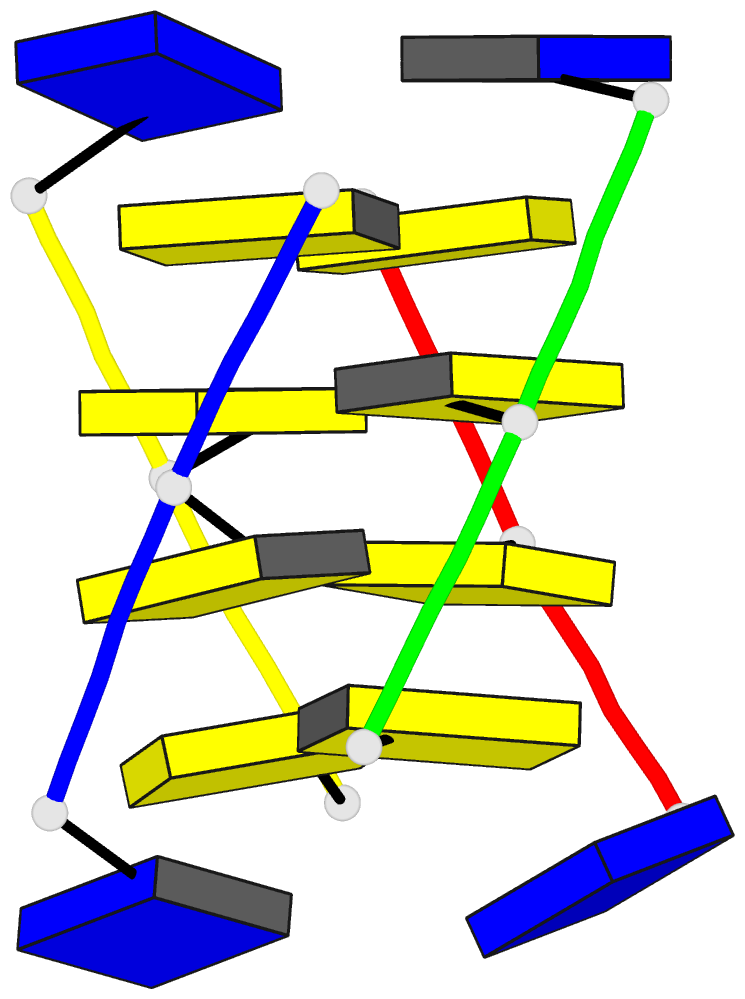
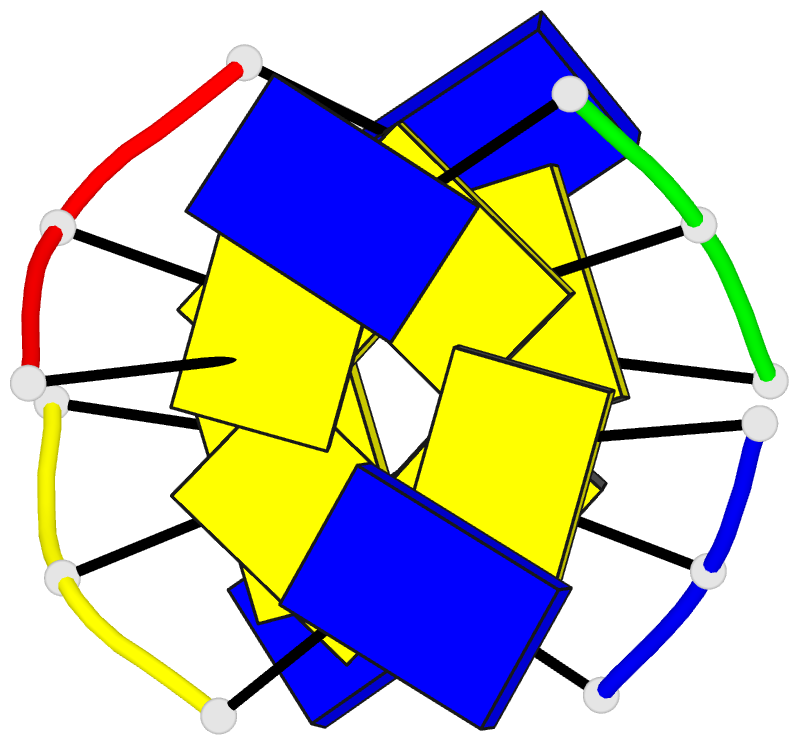
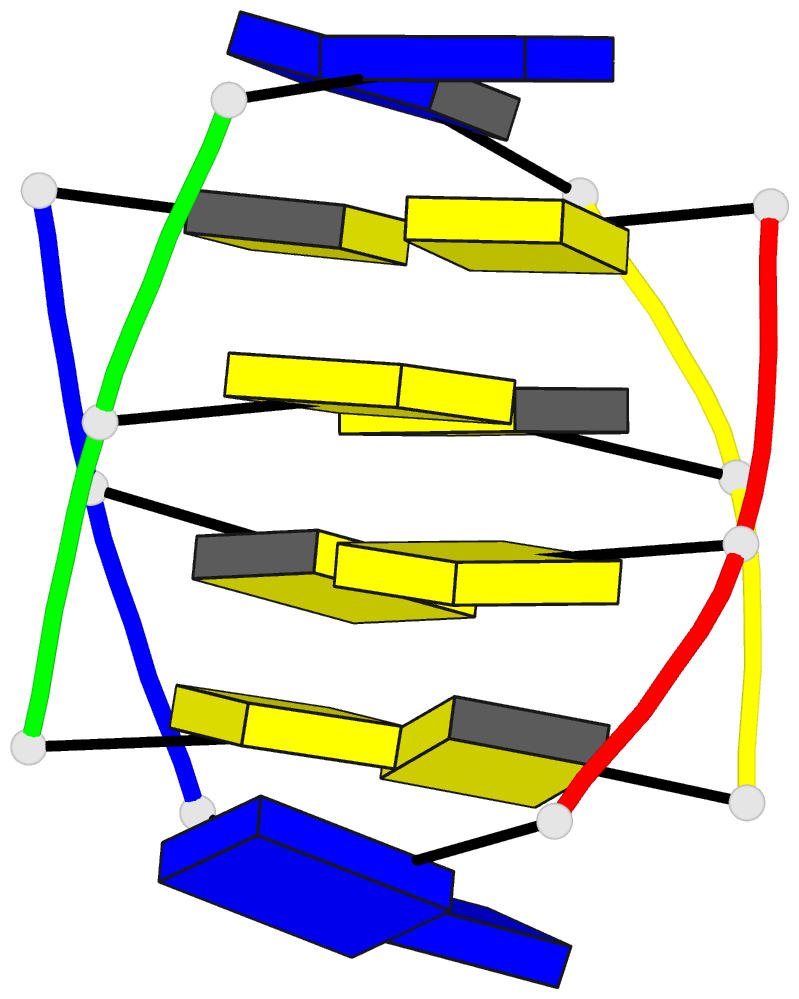
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
105d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
- Solution structures of the i-motif tetramers of d(tcc),
d(5mcct) and d(t5mcc). novel noe connections between amino
protons and sugar protons
- Reference
-
Leroy JL, Gueron M (1995): "Solution
structures of the i-motif tetramers of d(TCC),
d(5methylCCT) and d(T5methylCC): novel NOE connections
between amino protons and sugar protons."
Structure, 3, 101-120. doi:
10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00138-1.
- Abstract
- Background: At slightly acid or even neutral pH,
oligodeoxynucleotides that include a stretch of cytidines
form a tetramer structure in which two parallel-stranded
duplexes have their hemi-protonated C.C+ base pairs
face-to-face and fully intercalated, in a so-called
i-motif, first observed serendipitously in [d(TC5)]4.
Results: A high-definition structure of [d(TCC)]4 was
computed on the basis of inter-residue distances
corresponding to 21 NOESY cross-peaks measured at short
mixing times. A similarly defined structure of [d(5mCCT)]4
was also obtained. A small number of very characteristic
(amino proton)-(sugar proton) cross-peaks entails the
intercalation topology. The structure is generally similar
to that of [d(TC5)]4. The sequence d(T5mCC) forms two
tetramers in comparable proportions. The intercalation
topologies are read off the two patterns of (amino
proton)-(sugar proton) cross-peaks: one is the same as in
the d(TCC) tetramer, the other has the intercalated strands
shifted by one base, which avoids the steric hindrance
between the methyl groups of the 5mC pairs of the two
duplexes.
Conclusions: The structures obtained in this work and the
procedures introduced to characterize them and to solve the
problems linked to the symmetry of the structure provide
tools for further exploring the conditions required for
formation of the i-motif.