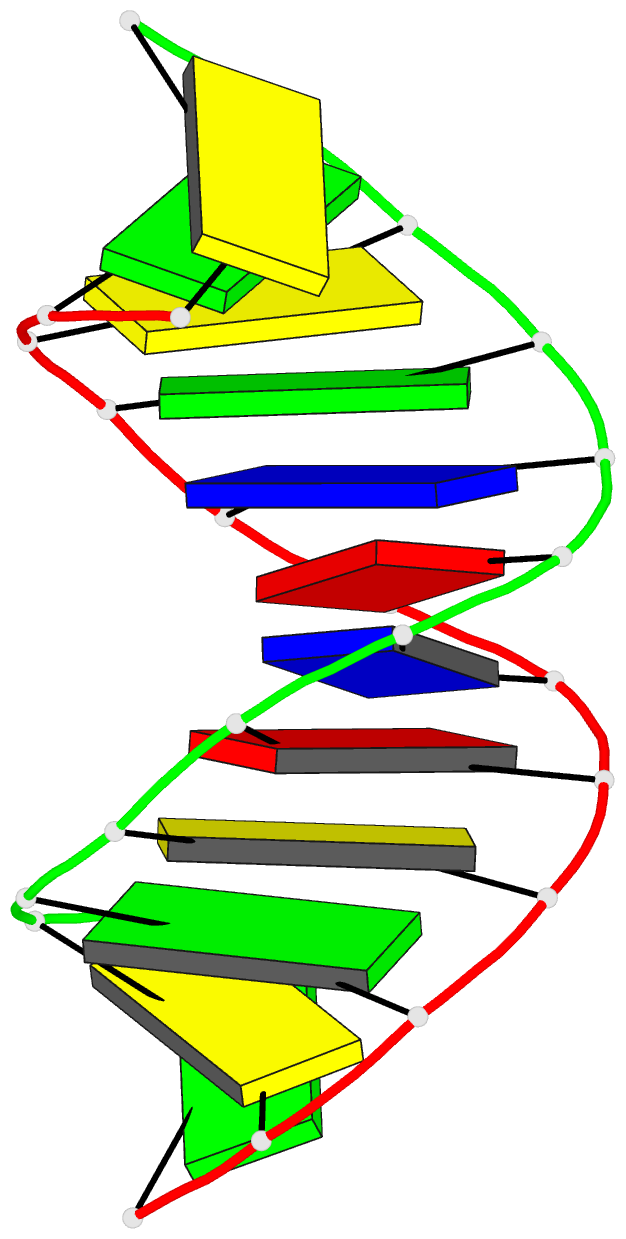
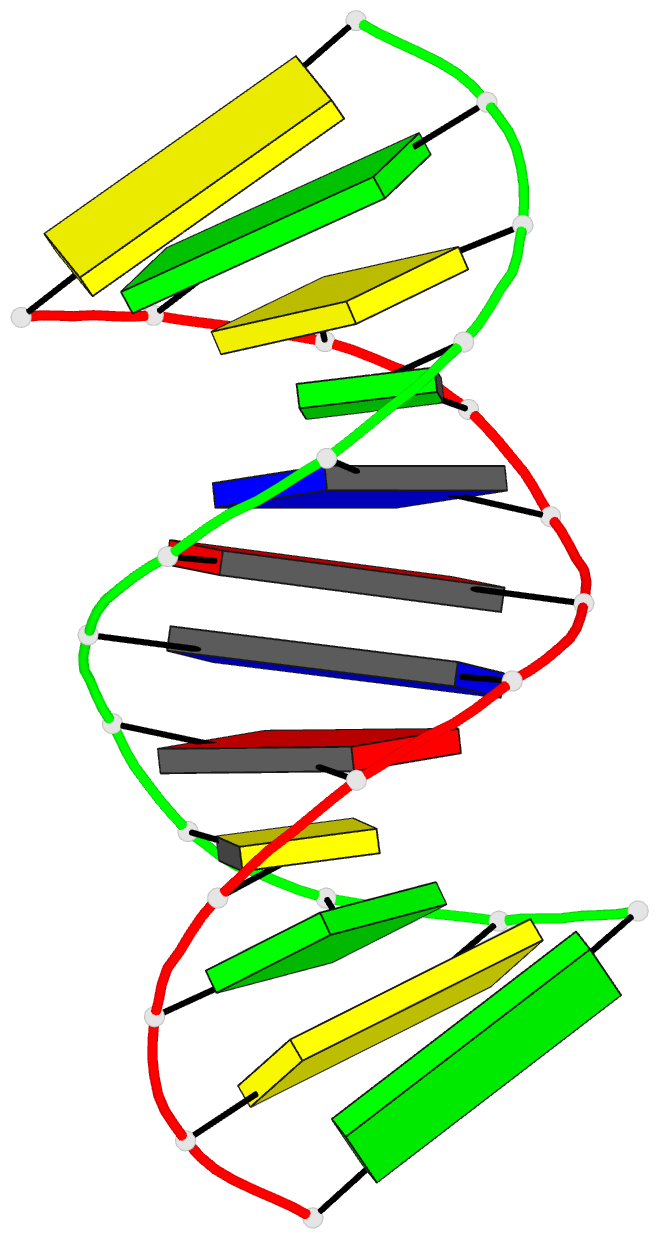
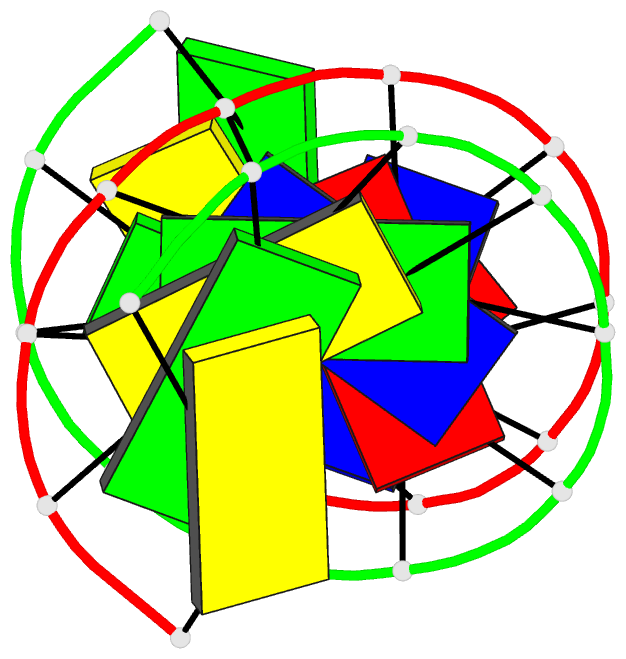
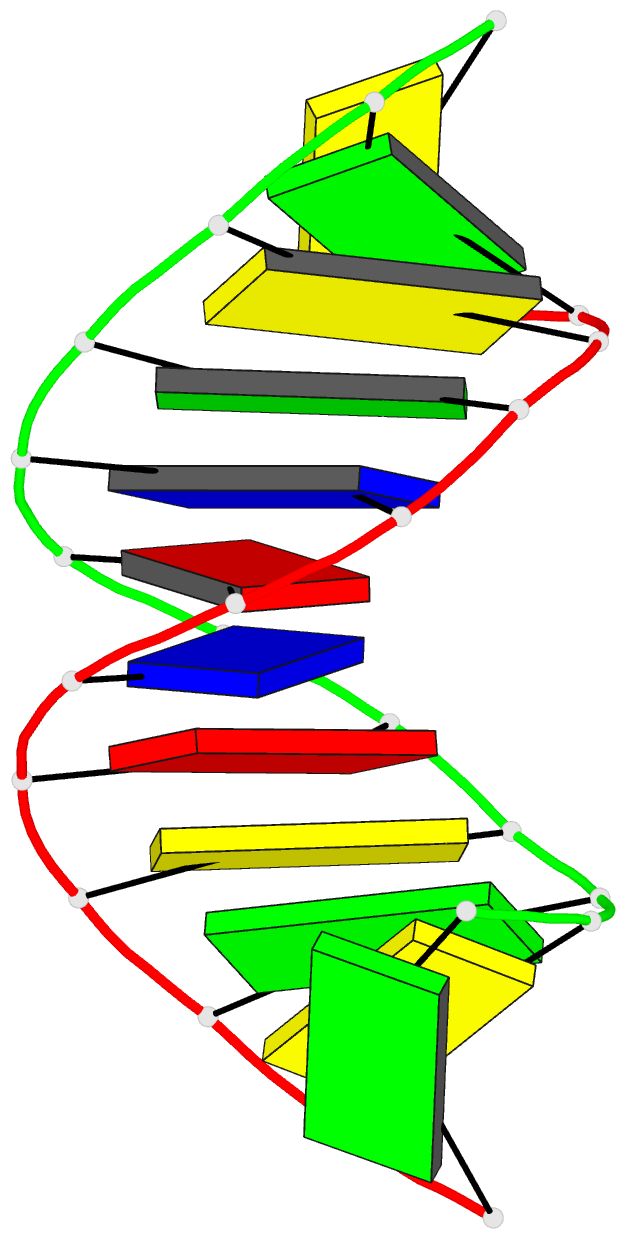
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
-
104d;
SNAP-derived features in text and
JSON formats
- Class
- DNA-RNA hybrid
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
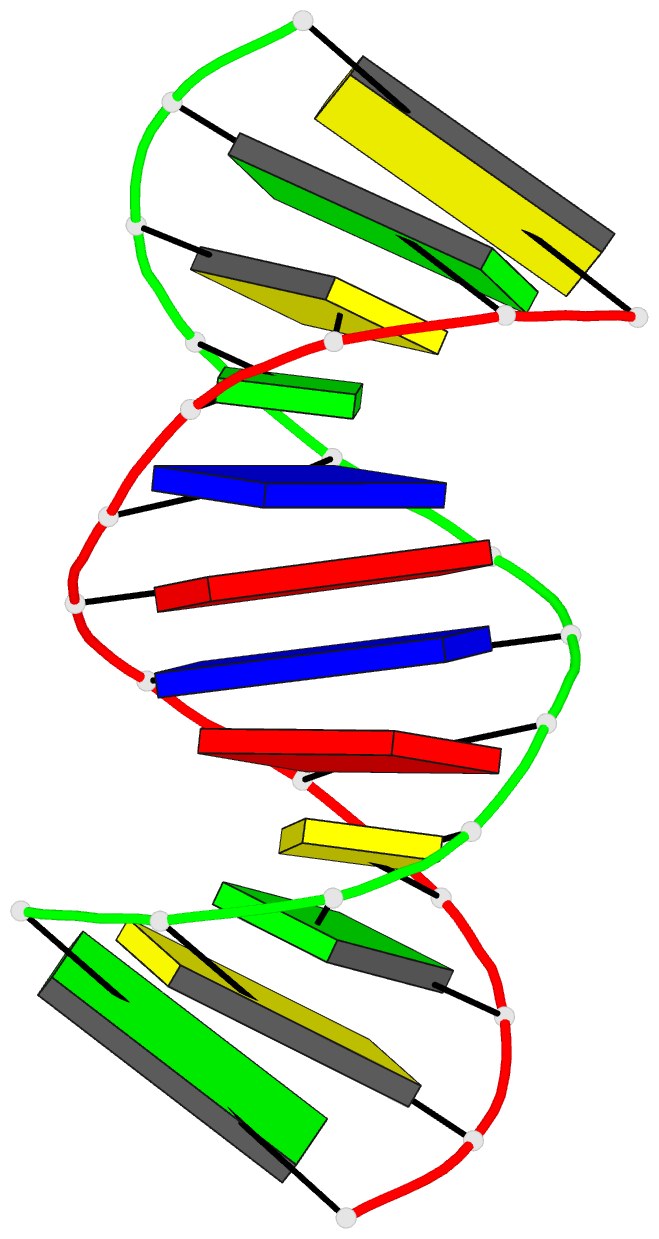
- DNA duplexes flanked by hybrid duplexes: the solution
structure of chimeric junctions in
- Reference
-
Zhu L, Salazar M, Reid BR (1995): "DNA
duplexes flanked by hybrid duplexes: the solution
structure of chimeric junctions in
[r(cgcg)d(TATACGCG)]2." Biochemistry,
34, 2372-2380. doi: 10.1021/bi00007a033.
- Abstract
- Hybrid duplexes and chimeric duplexes containing hybrid
segments linked to pure DNA (or pure RNA) segments are
involved in transcription and replication, as well as
reverse transcription. A complete understanding of the
mechanism of these processes requires detailed information
on such duplexes and the junctions between duplexes of
differing structure. Using two-dimensional NMR, restrained
molecular dynamics and mechanics, and back-calculation
refinement against the nuclear Overhauser effect spectra at
various mixing times, we have determined the solution
structure of the chimeric duplex [r(cgcg)d-(TATACGCG)]2
containing a pure DNA segment in the center of a hybrid
duplex. The solution structure differs from the previously
determined X-ray structure of the analogous duplex
[r(gcg)d(TATACGC)]2, which was found to be A-form
throughout [Wang, A.H.-J., et al. (1982) Nature 299,
601-604]. The basic features of the solution structure are
(a) the RNA residues are all A-form with C3'-endo sugar
conformations, (b) the central DNA segment is B-form, (c)
the transition from A-form RNA sugar conformations to
B-form DNA sugar conformations involves only the dT5 base
step, and (d) although the sugar conformations of the DNA
residues A6-G12 are closer to B-form, the basic helical
properties of the peripheral RNA.DNA hybrid segments are
closer to typical A-form than to B-form.